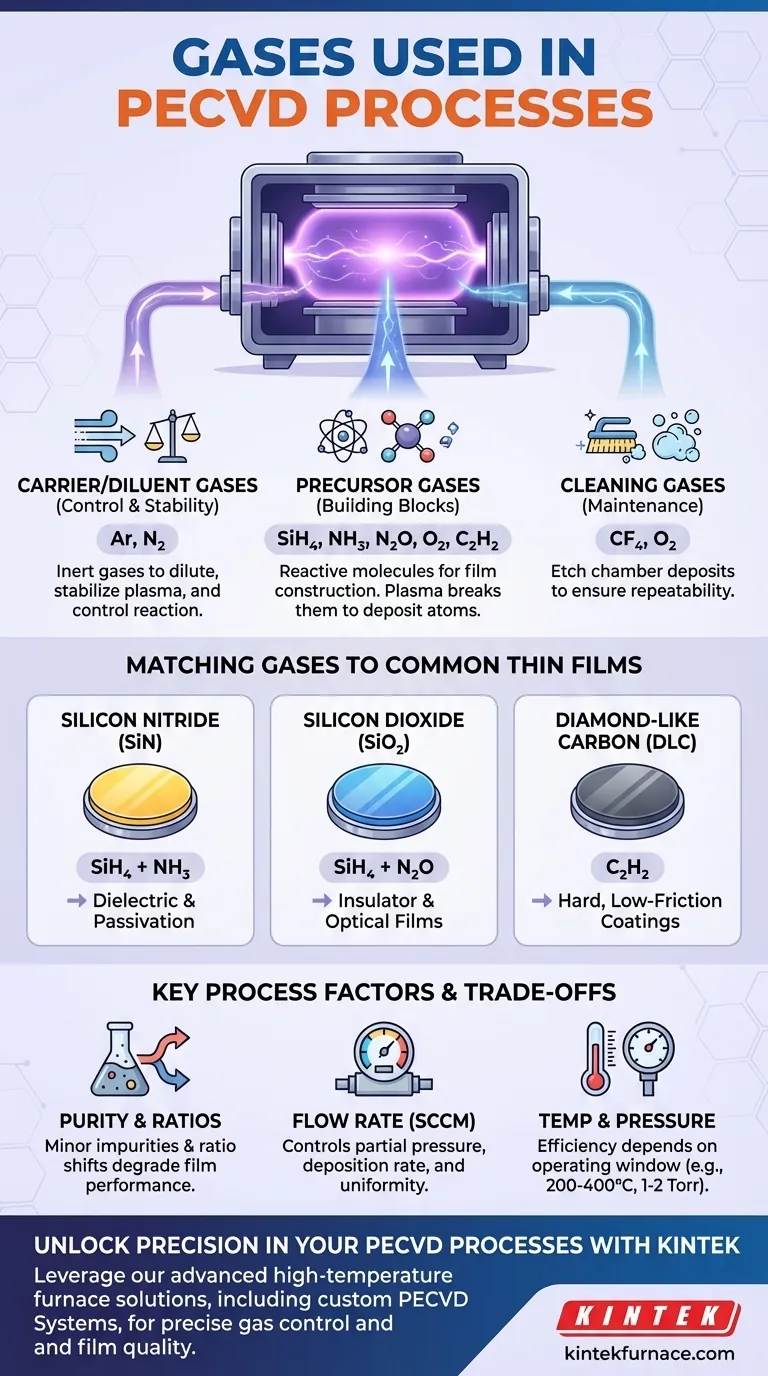
In Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), the most common gases are precursors like silane (SiH₄) and ammonia (NH₃), which provide the atomic building blocks for the film. These are almost always used with carrier gases such as nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar) to dilute the reactants and stabilize the plasma, or with cleaning gases like carbon tetrafluoride (CF₄) to maintain the chamber.
The selection of gases in a PECVD process is not arbitrary; each gas serves a distinct and critical function. Understanding these roles—as a precursor, a carrier, or a cleaning agent—is the key to controlling the properties of the final deposited material.
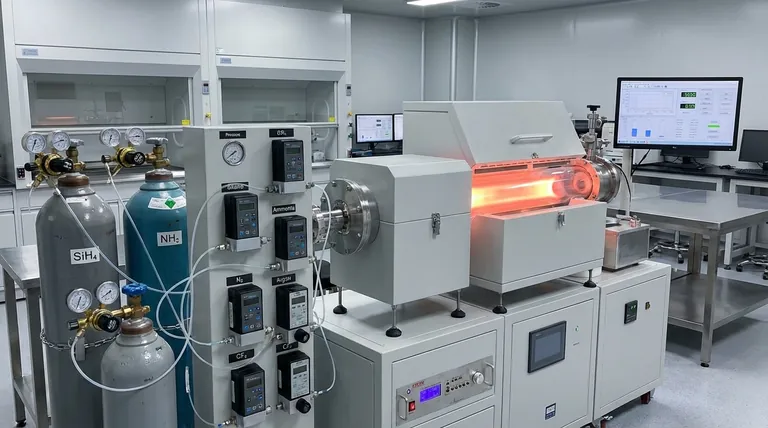

The Functional Roles of Gases in PECVD
To master a PECVD process, you must think of the gases as specialized tools, each with a specific job. They generally fall into one of three categories.
Precursor Gases: The Building Blocks
Precursor gases are the reactive molecules that contain the primary atoms needed to construct the thin film. The plasma provides the energy to break these molecules apart, allowing the desired atoms to deposit on the substrate.
The choice of precursor directly determines the material you create.
- For Silicon (Si): Silane (SiH₄) is the universal source.
- For Nitrogen (N): Ammonia (NH₃) or Nitrogen (N₂) are used.
- For Oxygen (O): Nitrous Oxide (N₂O) or Oxygen (O₂) are common choices.
- For Carbon (C): Hydrocarbon gases like acetylene (C₂H₂) are used for films like Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC).
Carrier and Diluent Gases: Controlling the Reaction
These are chemically inert gases that do not become part of the final film but are critical for process control.
Their primary functions are to dilute the highly reactive precursor gases, enabling safer handling and more precise control over concentration. They also help sustain a stable and uniform plasma across the chamber.
Common carrier gases include Argon (Ar) and **Nitrogen (N₂) **, often pre-mixed with the precursor, such as "5% SiH₄ in N₂".
Cleaning Gases: Maintaining the System
Over time, deposition occurs on all surfaces inside the chamber, not just the wafer. This buildup can flake off and create defects in subsequent runs.
To prevent this, a plasma-cleaning step is performed using etchant gases. A mixture of Carbon Tetrafluoride (CF₄) and Oxygen (O₂) is frequently used to etch away unwanted silicon-based deposits from the chamber walls, ensuring process repeatability.
Matching Gases to Common Thin Films
The combination of precursor and reactive gases dictates the film's chemical composition (stoichiometry).
For Silicon Nitride (SiN)
A film of silicon nitride is created by combining a silicon source with a nitrogen source. The most common gas recipe is Silane (SiH₄) + Ammonia (NH₃). Using pure Nitrogen (N₂) is also possible but often requires higher plasma power.
For Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂)
To deposit silicon dioxide, a silicon source is combined with an oxygen source. A typical combination is Silane (SiH₄) + Nitrous Oxide (N₂O). N₂O is often preferred over pure O₂ as it can lead to a more stable process and better film quality.
For Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC)
For these hard, low-friction carbon-based coatings, a hydrocarbon precursor is required. Acetylene (C₂H₂) is a common choice, which decomposes in the plasma to provide the carbon atoms for the film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Gas selection is only the first step. The precise control of these gases, in conjunction with other process parameters, determines the final outcome.
Gas Purity and Ratios
Even minor impurities in a gas source can become incorporated into your film, degrading its performance. Likewise, small shifts in the flow ratio between two precursor gases (e.g., SiH₄ to NH₃) can dramatically alter the film's stoichiometry, stress, and optical properties.
The Role of Flow Rate (SCCM)
Gas flow is controlled in Standard Cubic Centimeters per Minute (SCCM). The flow rate directly impacts the partial pressure of the reactants in the chamber, which in turn influences the deposition rate and the uniformity of the film across the wafer.
Interaction with Temperature and Pressure
PECVD is valued for its low-temperature processing (typically 200-400°C). The behavior of the chosen gases and the efficiency of their chemical reactions are highly dependent on operating within the correct temperature and pressure (1-2 Torr) window for which the process was designed.
How to Select the Right Gas Combination
Your choice of gases should be driven entirely by the material you intend to create and the process stability you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is depositing silicon-based dielectrics: You will use a silane precursor combined with an oxygen source (N₂O, O₂) for SiO₂ or a nitrogen source (NH₃) for SiN.
- If your primary focus is creating hard, low-friction coatings: You will need a hydrocarbon precursor gas, such as acetylene, to deposit DLC films.
- If your primary focus is process stability and repeatability: You must precisely control the flow rates of both your precursor and your inert carrier gases (Ar, N₂), and implement a robust chamber cleaning process with etchant gases (CF₄/O₂).
Ultimately, mastering the interplay between these different gas functions is fundamental to achieving control over your PECVD results.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Common Examples | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor | Silane (SiH₄), Ammonia (NH₃), Acetylene (C₂H₂) | Provide atoms for film deposition (e.g., Si, N, C) |
| Carrier/Diluent | Argon (Ar), Nitrogen (N₂) | Dilute reactants, stabilize plasma, control reaction |
| Cleaning | Carbon Tetrafluoride (CF₄), Oxygen (O₂) | Etch chamber deposits to prevent defects and ensure repeatability |
Unlock Precision in Your PECVD Processes with KINTEK
Struggling with gas selection or film quality in your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, whether you're depositing silicon nitride, silicon dioxide, or diamond-like carbon films.
Contact us today to discuss how our tailored PECVD systems can enhance your process stability and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- How is silicon dioxide deposited from tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) in PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality SiO2 Films



















