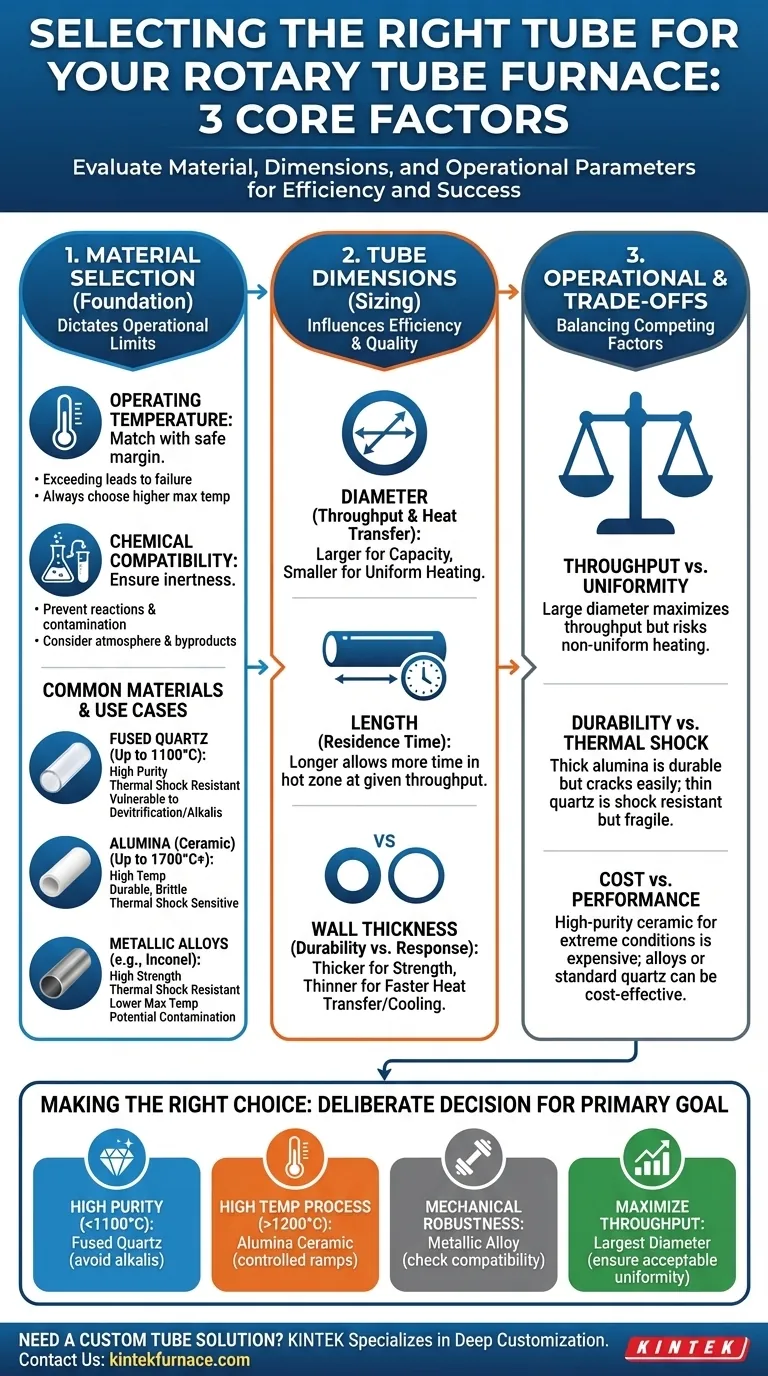
To select the right tube for a rotary furnace, you must evaluate three core areas: the material composition for temperature and chemical resistance, the physical dimensions (diameter, length, thickness) to control heat transfer and capacity, and operational parameters like rotational speed. These factors are not independent; they work together to determine the success and efficiency of your thermal process.
The optimal tube is not merely the one that fits your furnace, but the one engineered to match your specific material, process temperature, and desired outcome. Viewing the tube as an integral component of your chemical process—not just a piece of hardware—is the key to making an effective selection.

The Foundation: Material Selection
The tube's material is the single most important decision, as it dictates the operational limits of your entire process. It must withstand the thermal and chemical environment without failing or contaminating your sample.
Matching Material to Operating Temperature
Every material has a maximum service temperature. Exceeding this limit can lead to softening, deformation, or catastrophic failure of the tube.
Always select a material with a maximum operating temperature that provides a safe margin above your intended process temperature.
Ensuring Chemical Compatibility
Your process material and any atmospheric gases will interact with the tube wall at high temperatures. The tube material must be chemically inert to your specific process to prevent unwanted reactions and sample contamination.
Consider the reactivity of your powders, the process atmosphere (e.g., inert, oxidizing, reducing), and any byproducts that may be generated.
Common Tube Materials and Their Use Cases
-
Fused Quartz: An excellent choice for high-purity applications up to approximately 1000-1100°C. It offers superior resistance to thermal shock but is susceptible to devitrification (crystallization) and attack by alkaline compounds.
-
Alumina (Ceramic): Ideal for higher temperatures (up to 1700°C or more, depending on purity). It is durable and chemically stable but is more brittle than quartz and more susceptible to failure from rapid temperature changes (thermal shock).
-
Metallic Alloys (e.g., Inconel): These alloys provide excellent mechanical strength and are highly resistant to thermal shock. They are often used in industrial settings but may have lower maximum temperatures than ceramics and can be a source of metallic contamination.
Sizing for Performance: Tube Dimensions
The geometry of the tube directly influences process efficiency, material throughput, and the quality of the final product.
Diameter's Role in Heat Transfer and Throughput
The inner diameter dictates the furnace's batch capacity and how heat penetrates the material bed. A larger diameter allows for greater throughput.
However, heat must travel from the tube wall to the center of the material. A very large diameter can result in non-uniform heating, with material at the surface being over-processed while the core remains under-processed.
Length's Impact on Residence Time
The heated length of the tube, combined with rotational speed and tilt angle, determines the residence time—how long the material spends in the hot zone.
A longer tube allows for a longer residence time at a given throughput, which can be critical for reactions or processes that require more time to complete.
Wall Thickness: The Durability vs. Thermal Response Dilemma
A thicker wall provides greater mechanical strength and longevity. It is more robust and resistant to physical wear from abrasive materials.
Conversely, a thinner wall allows for faster heat transfer, enabling quicker heating and cooling cycles. However, it is more fragile and less durable over the long term.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a tube is an exercise in balancing competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for avoiding common pitfalls.
Throughput vs. Heating Uniformity
Choosing a large-diameter tube to maximize throughput can compromise heating uniformity. If your process is sensitive to precise temperature control, a smaller diameter may be necessary to ensure every particle experiences the same thermal profile.
Durability vs. Thermal Shock Resistance
A thick-walled alumina tube is extremely durable but can easily crack if heated or cooled too quickly. A thin-walled quartz tube is far more resistant to thermal shock but is mechanically fragile. Your process's heating/cooling rates must match your material choice.
Cost vs. Purity and Temperature
High-purity ceramic tubes for extreme temperatures are significantly more expensive than metallic alloy tubes. If your process does not require ultra-high purity or temperatures above 1100°C, a metallic alloy or standard quartz tube may be a more cost-effective solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your final selection should be a deliberate decision based on the primary goal of your thermal application.
- If your primary focus is high purity at moderate temperatures (<1100°C): Choose a fused quartz tube, ensuring your process chemicals are not alkaline.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (>1200°C): An alumina ceramic tube is the standard choice, but you must implement controlled heating and cooling ramps.
- If your primary focus is mechanical robustness and thermal cycling: A metallic alloy tube offers the best resistance to thermal and mechanical shock, provided it is chemically compatible with your process.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material throughput: Select the largest diameter tube that still allows for acceptable heating uniformity for your specific material and process sensitivity.
By systematically evaluating your process needs against these material and dimensional factors, you can equip your furnace with a tube that ensures reliable, efficient, and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Material | Temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, purity (e.g., quartz, alumina, alloys) |
| Dimensions | Diameter (affects throughput and heat transfer), length (determines residence time), wall thickness (durability vs. thermal response) |
| Operational Parameters | Rotational speed, process atmosphere, heating/cooling rates |
| Trade-offs | Throughput vs. uniformity, durability vs. thermal shock resistance, cost vs. performance |
Need a Custom Tube Solution for Your Rotary Furnace?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer advanced products like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can design tubes that precisely match your material, process temperature, and operational requirements—enhancing efficiency, reliability, and purity in your laboratory.
Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes and deliver superior results! Get in touch now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















