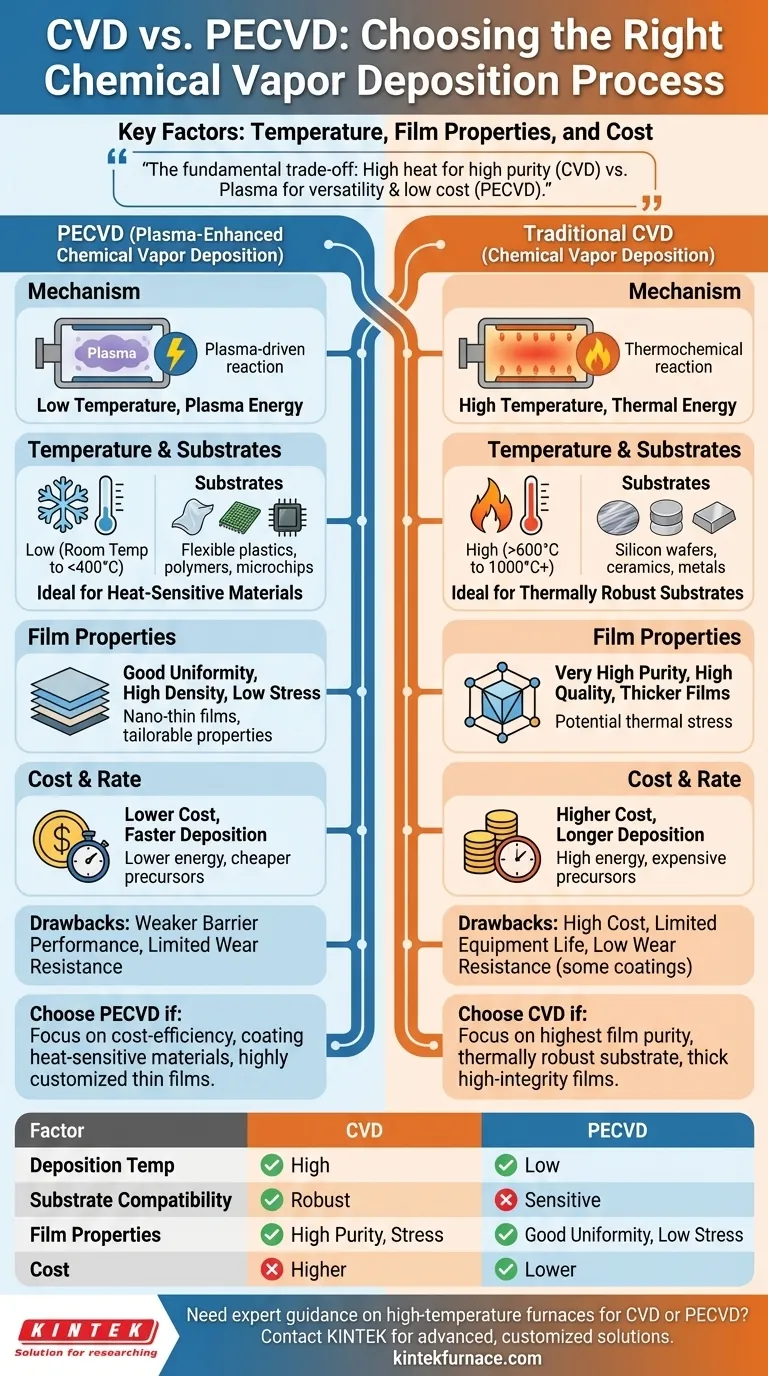
The choice between CVD and PECVD is a critical engineering decision that hinges on three primary factors: the required deposition temperature, the desired final film properties, and the total production cost. While both are methods of chemical vapor deposition, PECVD uses plasma to enable reactions at much lower temperatures, making it suitable for heat-sensitive substrates and often more cost-effective. Traditional CVD relies on high thermal energy, which is ideal for creating highly pure films on robust materials but comes at a higher cost.
The fundamental trade-off is this: Traditional CVD uses high heat to achieve high purity, while PECVD uses plasma to achieve high versatility and low cost at low temperatures. Your substrate's heat tolerance and your project's budget will be the most significant determining factors.

Understanding the Core Mechanisms: Heat vs. Plasma
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the fundamental difference in how each process drives the chemical reaction needed for film deposition.
How Traditional CVD Works
Traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a thermochemical process. It uses high temperatures, often ranging from several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius, to provide the energy needed to break down precursor gases.
These reactive gas molecules then deposit onto the heated substrate, forming a solid thin film. The process typically occurs under a slight vacuum or at normal pressure.
How PECVD Works
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) uses a different energy source: plasma. An electrical field is used to excite the precursor gases, creating a mixture of high-energy electrons, ions, and free radicals.
This energized plasma drives the chemical reactions, allowing them to occur at much lower temperatures—from room temperature up to a few hundred degrees Celsius. This single difference is the source of most of PECVD's distinct advantages.
Key Factors in Your Decision
Your choice will ultimately be guided by the specific constraints and goals of your application. Let's break down the most important factors.
Factor 1: Deposition Temperature and Substrate Compatibility
This is often the first and most critical filter. The temperature of the process dictates what materials you can coat.
PECVD's low-temperature process makes it ideal for coating heat-sensitive substrates like plastics, polymers, and other materials that would be damaged or degraded by the high heat of traditional CVD.
CVD's high-temperature requirement restricts its use to thermally robust substrates, such as silicon wafers, ceramics, and certain metals that can withstand the intense heat without deforming or melting.
Factor 2: Film Properties and Quality
The final properties of the deposited film—such as its purity, density, thickness, and internal stress—are directly impacted by the deposition method.
PECVD typically produces films with good uniformity, high density, and fewer pinholes. The lower temperature reduces thermal stress and lattice mismatch between the film and the substrate. It excels at creating nano-thin barrier films (50nm and up) with highly tailorable properties like hydrophobicity.
CVD is capable of producing very high-quality, high-purity films. However, the high temperatures can introduce significant thermal stress, potentially causing defects or poor adhesion if the thermal expansion coefficient of the film and substrate are not well-matched. The process also tends to create thicker films, with a minimum of around 10 micrometers often needed for high integrity.
Factor 3: Deposition Rate and Cost
For any production environment, time and money are paramount.
PECVD is generally the more cost-effective option. Its lower operating temperatures translate directly to lower energy consumption. Furthermore, it often allows for faster deposition times and the use of cheaper precursor materials, further reducing production costs.
CVD is typically a more expensive process. The high heat requires significant energy input, and the process can have long deposition times. The specialized precursors required for high-purity films can also be costly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is perfect. An objective assessment requires acknowledging the drawbacks of each method.
PECVD Drawbacks
The primary trade-offs for PECVD involve film robustness. While versatile, the films can have weaker barrier performance compared to specialized methods like Parylene deposition.
Additionally, PECVD films are often softer and can have limited wear resistance. Finally, the use of certain precursor gases, particularly halogenated ones, can raise health or environmental concerns that must be managed.
CVD Drawbacks
The main drawback for CVD is cost, driven by high energy consumption and long process times. The intense heat also leads to limited operating life for the equipment itself, as components suffer from aging due to thermal stress and oxidation.
Like PECVD films, some CVD coatings can also exhibit low wear resistance, making them unsuitable for certain exterior or high-contact applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct process, anchor your decision in your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency and coating heat-sensitive materials: PECVD is the clear choice due to its low-temperature process, lower energy use, and faster deposition rates.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity on a thermally robust substrate: Traditional CVD is often the superior method, provided you can tolerate the higher costs and potential for thermal stress.
- If your primary focus is creating thin, low-stress, and highly customized functional films: PECVD offers unmatched flexibility for engineering specific properties like hydrophobicity or UV protection at the nanoscale.
Ultimately, your decision rests on whether your application's material constraints and budget align with the high-heat, high-purity regime of CVD or the versatile, low-temperature, and cost-effective nature of PECVD.
Summary Table:
| Factor | CVD | PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition Temperature | High (hundreds to over 1000°C) | Low (room temp to a few hundred °C) |
| Substrate Compatibility | Thermally robust (e.g., silicon, ceramics) | Heat-sensitive (e.g., plastics, polymers) |
| Film Properties | High purity, potential thermal stress | Good uniformity, high density, low stress |
| Cost | Higher (energy, time, precursors) | Lower (energy, faster deposition, cheaper precursors) |
| Ideal For | High-purity films on robust substrates | Cost-effective, versatile coatings on sensitive materials |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right high-temperature furnace for your CVD or PECVD processes? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your lab's productivity and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- How is silicon dioxide (SiO2) used in PECVD applications? Key Roles in Microfabrication
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















