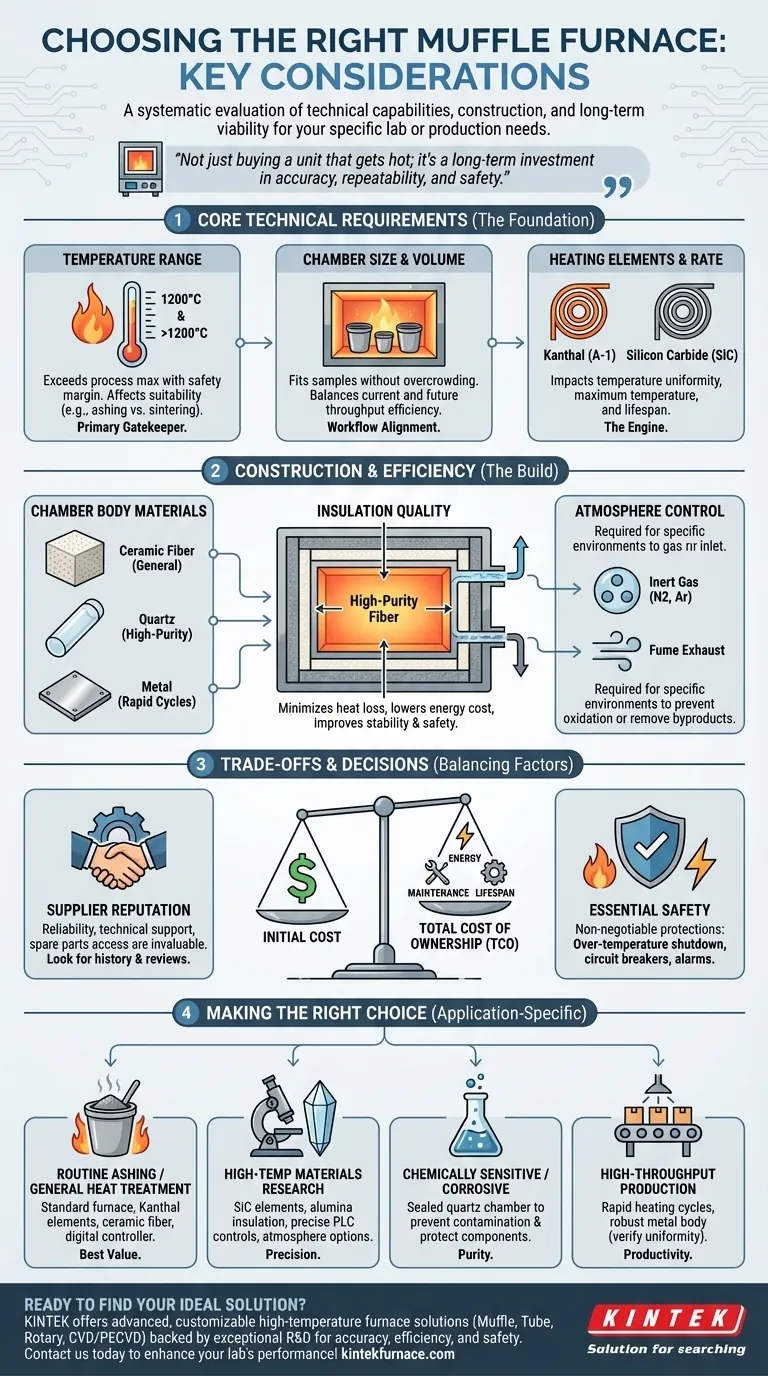
Choosing the right muffle furnace requires a systematic evaluation of its technical capabilities, construction, and long-term viability for your specific needs. The most critical factors to consider are the required temperature range, the chamber size and material, the precision of the temperature controls, and the presence of essential safety features. These elements directly determine the furnace's suitability for your applications, from simple ashing to complex materials research.
A muffle furnace is a long-term investment in your lab or production process. The goal is not simply to buy a unit that gets hot, but to select a system whose performance, materials, and safety features are precisely aligned with your specific applications to ensure accuracy, repeatability, and operational safety.

Defining Your Core Technical Requirements
Before comparing models, you must first define the non-negotiable parameters of your work. These core requirements will immediately narrow your search and prevent you from over-investing in unnecessary features or under-investing in critical ones.
Temperature Range: The Primary Gatekeeper
Your first consideration is the temperature range. The furnace must be able to safely and consistently reach the maximum temperature your process demands, while also maintaining stability at lower setpoints if needed.
Different applications, such as ashing, heat treating, alloying, or ceramic sintering, have vastly different thermal requirements. Ensure the furnace's specified maximum operating temperature provides a safe margin above your highest process temperature.
Chamber Size and Volume: Aligning with Your Workflow
The internal chamber must be large enough to accommodate your samples or crucibles without them touching the walls or heating elements. Overcrowding a chamber can lead to poor temperature uniformity and inaccurate results.
Consider both your current and future throughput. A slightly larger chamber may offer more flexibility, but an excessively large chamber is inefficient, consuming more energy and taking longer to heat up for small batches.
Heating Elements and Rate: The Engine of the Furnace
The heating elements dictate the furnace's maximum temperature, lifespan, and heating speed. Common materials include Kanthal (A-1) wire, which is excellent for temperatures up to around 1200°C, and silicon carbide (SiC), which is used for higher-temperature applications.
The quality and placement of these elements directly impact temperature uniformity—the consistency of temperature throughout the entire chamber. Poor uniformity can ruin sensitive experiments where precise thermal conditions are paramount.
Understanding Construction and Efficiency
The physical build of the furnace affects its performance, energy consumption, and suitability for specialized processes. Pay close attention to the materials used in its construction.
The Chamber Body: Quartz, Ceramic, or Metal?
The material of the furnace body itself is a critical choice based on your application.
- Ceramic Fiber: The most common material, offering excellent insulation and thermal stability. It's ideal for general-purpose heat treatment and material testing.
- Quartz: Offers high-purity, high-temperature, and corrosion-resistant properties, making it essential for experiments where sample contamination is a major concern.
- Metal: Provides excellent thermal conductivity for rapid heating and cooling cycles, often favored in high-throughput or industrial production environments.
Insulation Quality: The Key to Efficiency and Stability
High-quality insulation, typically made of high-purity ceramic or alumina fiber, is crucial. Good insulation minimizes heat loss, which directly translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs.
More importantly, effective insulation ensures better temperature stability and protects the outer casing from becoming dangerously hot, improving lab safety.
Atmosphere Control: Do You Need a Special Environment?
Standard muffle furnaces operate in an air atmosphere. If your process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, you must select a furnace equipped with a gas inlet port and a proper vent.
A well-designed ventilation or exhaust system is also critical for safely removing fumes or byproducts generated during processes like ashing or chemical decomposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace always involves balancing cost, features, and long-term reliability. A low initial price can sometimes mask higher lifetime costs.
Balancing Initial Cost vs. Total Cost of Ownership
A less expensive furnace might use lower-grade insulation or less durable heating elements. This can lead to higher energy bills and more frequent, costly replacements of elements or thermocouples.
Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes the purchase price, energy consumption, and anticipated maintenance costs over the furnace's lifespan.
The Importance of Supplier Reputation and Support
Purchase from a reputable manufacturer with a history of reliability and good customer support. Access to technical assistance, spare parts, and service is invaluable if you encounter issues.
Reading reviews from professionals in your industry can provide real-world insights into a model's performance and the manufacturer's dependability.
Essential Safety Features: Non-Negotiable Protections
Safety should never be a trade-off. Ensure any furnace you consider has fundamental safety features built-in.
These must include over-temperature protection to shut the furnace down if it exceeds a set limit, circuit breakers to prevent electrical damage, and ideally, an alarm system to alert operators to faults.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your specific process needs to guide your final decision.
- If your primary focus is routine ashing or general heat treatment: A standard furnace with durable Kanthal elements, good ceramic fiber insulation, and a reliable digital controller offers the best value.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials research: Prioritize a furnace with silicon carbide elements, high-purity alumina insulation, and precise PLC controls, with options for gas atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is processing chemically sensitive or corrosive samples: A furnace with a sealed quartz chamber is essential to prevent sample contamination and protect the furnace components.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: A furnace designed for rapid heating cycles, possibly with a robust metal body, will maximize productivity, but verify its temperature uniformity meets your quality standards.
Ultimately, a methodical evaluation of these factors will lead you to a furnace that serves as a reliable and precise tool in your work for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Must exceed process max with a safety margin; affects application suitability (e.g., ashing vs. sintering). |
| Chamber Size | Should fit samples without overcrowding; balance current and future throughput needs for efficiency. |
| Heating Elements | Type (e.g., Kanthal for ≤1200°C, SiC for higher temps) impacts temperature uniformity and lifespan. |
| Chamber Material | Ceramic fiber (general use), quartz (high-purity), or metal (rapid cycles); chosen based on contamination risks. |
| Insulation Quality | High-quality insulation reduces energy costs and improves temperature stability and safety. |
| Atmosphere Control | Required for inert gases; includes gas inlets and ventilation for processes like oxidation prevention. |
| Safety Features | Essential protections like over-temperature shutdowns and alarms to ensure operational safety. |
| Cost Considerations | Evaluate total cost of ownership, including purchase price, energy use, and maintenance over time. |
Ready to find the ideal muffle furnace for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials research, production, or handling sensitive samples, we ensure accuracy, efficiency, and safety. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















