Choosing the right controlled atmosphere furnace is a critical decision that hinges on three primary factors. You must first define your specific process requirements, then identify the furnace type that accommodates that process, and finally, verify the build quality and safety systems to ensure reliable, long-term performance and consistent results.
Choosing a controlled atmosphere furnace goes beyond comparing technical specifications. The core task is to match the furnace's design, atmosphere management, and safety features directly to the unique requirements of your material process to ensure consistent, high-quality results.

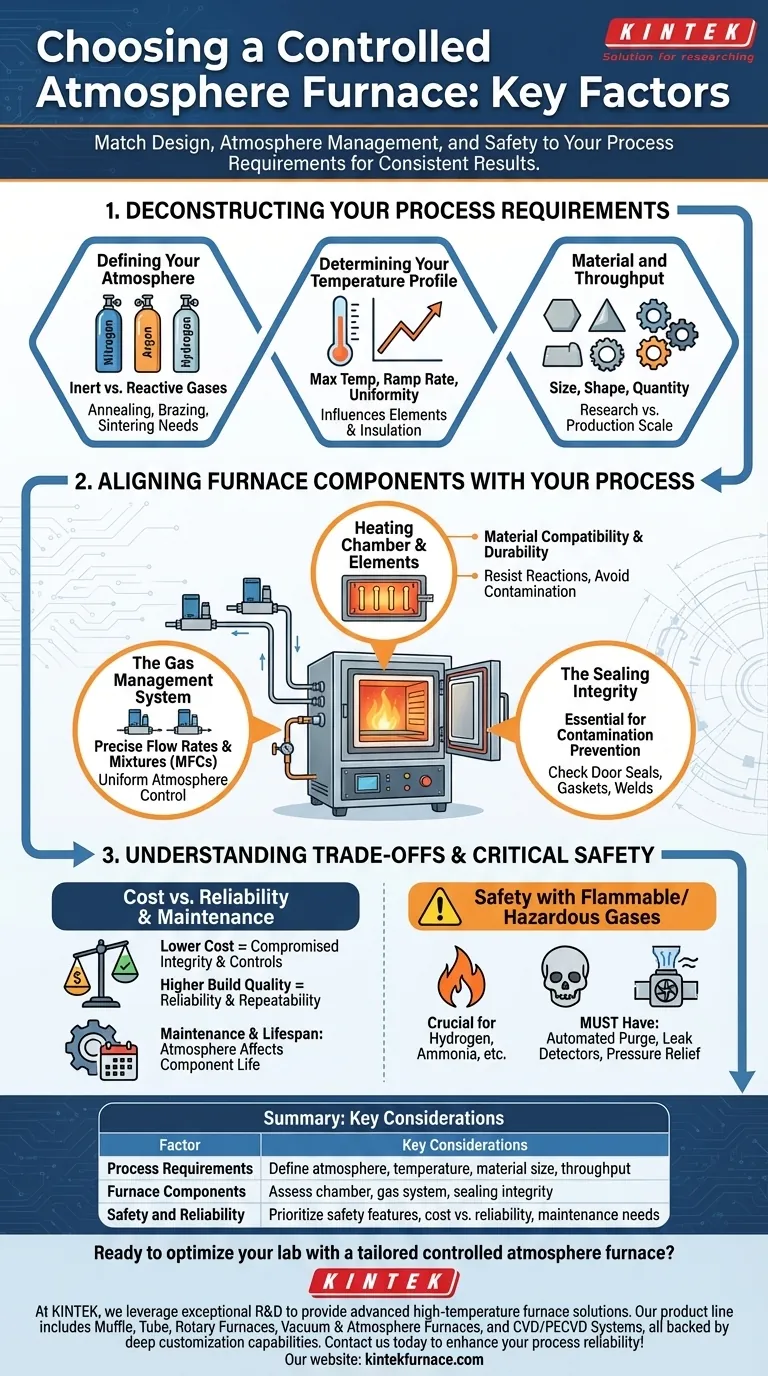
Deconstructing Your Process Requirements
Before evaluating any hardware, you must have a complete understanding of your application. The furnace is a tool to serve the process, not the other way around.
Defining Your Atmosphere
The type of gas you use is the most fundamental requirement. Atmospheres can be inert (Nitrogen, Argon) to prevent oxidation, or reactive (Hydrogen, forming gas) to actively participate in the process.
Processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering each have unique atmospheric needs that dictate the furnace's gas handling capabilities and material compatibility.
Determining Your Temperature Profile
You must define your maximum required temperature, the rate at which you need to heat and cool (ramp rate), and the allowable temperature variation within the chamber (uniformity).
These factors directly influence the choice of heating elements, insulation materials, and the sophistication of the temperature control system.
Material and Throughput
Consider the size, shape, and quantity of the parts you will be processing. This determines the necessary dimensions of the heating chamber and influences the overall furnace design, such as choosing between a smaller tube furnace for research and a larger box furnace for production.
Aligning Furnace Components with Your Process
Once you know your process needs, you can assess how a furnace's specific components are designed to meet them.
The Heating Chamber and Elements
The chamber must be constructed from materials that can withstand your maximum temperature and resist chemical reactions with your process atmosphere.
The heating elements must also be compatible. Certain elements degrade quickly in specific atmospheres, leading to contamination and high replacement costs.
The Gas Management System
A reliable system for introducing and exhausting gases is critical. This includes the gas inlets, outlets, and the atmosphere control system itself.
For precise work, look for mass flow controllers (MFCs) that allow you to accurately manage gas flow rates and mixtures, ensuring a uniform and consistent atmosphere throughout the chamber.
The Sealing Integrity
This is a non-negotiable feature. A tightly sealed environment is essential to prevent contamination from external air and to maintain the precise gas composition your process demands.
Pay close attention to the quality of door seals, gaskets, and weld points, as even a small leak can compromise sensitive experiments and ruin production batches.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Safety
A furnace is a long-term investment where upfront cost-cutting can lead to significant downstream problems.
Cost vs. Process Reliability
Lower-cost furnaces may compromise on sealing integrity or the precision of their temperature and atmosphere controls. This can result in inconsistent product quality, failed batches, and ultimately, higher operational costs.
Investing in a furnace with superior build quality and process control provides a higher return through reliability and repeatability.
Safety with Flammable or Hazardous Gases
If your process involves hydrogen, ammonia, or other hazardous gases, safety is your primary concern. The furnace must be equipped with appropriate safety mechanisms.
Look for features like automated purge cycles, gas leak detectors, pressure relief valves, and emergency shut-off systems. These are not optional features; they are essential for protecting personnel and facilities.
Maintenance and Lifespan
The interaction between your process atmosphere and the furnace's internal components, particularly heating elements and insulation, will dictate the maintenance schedule.
Understand how your specific atmosphere will affect component lifespan to accurately forecast operational costs and minimize unplanned downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be a direct reflection of your primary operational goal. Use your specific process requirements as a filter to evaluate your options.
- If your primary focus is high-purity research or sensitive materials (e.g., semiconductor annealing): Prioritize superior sealing integrity and a high-precision atmosphere control system above all else.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production (e.g., sintering or brazing): Focus on furnace durability, energy efficiency, and automation features to maximize throughput and reduce operating costs.
- If you are working with hazardous or flammable gases (e.g., hydrogen-based processes): Your non-negotiable first priority must be certified safety systems, including leak detection and emergency purge capabilities.
Ultimately, a successful investment is one where the furnace becomes a transparent and reliable enabler of your core process.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Process Requirements | Define atmosphere type, temperature profile, material size, and throughput |
| Furnace Components | Assess heating chamber, gas management system, and sealing integrity |
| Safety and Reliability | Prioritize safety features, cost vs. reliability, and maintenance needs |
Ready to optimize your lab with a tailored controlled atmosphere furnace?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your process reliability and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the relationship between temperature and the furnace atmosphere in material processing? Master the Critical Heat-Environment Balance
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















