At its core, the feasibility of electrifying rotary kilns is limited by fundamental challenges in achieving very high temperatures at a massive industrial scale. While technically possible for smaller or lower-temperature applications, current electric heating technology struggles to replicate the raw power density and economic efficiency of fossil fuel combustion used in processes like cement manufacturing.
The decision to electrify a rotary kiln is not a simple switch from one energy source to another. It represents a fundamental trade-off between the high-volume, high-temperature capabilities of combustion and the precision and cleanliness of electricity, with significant engineering and economic consequences.

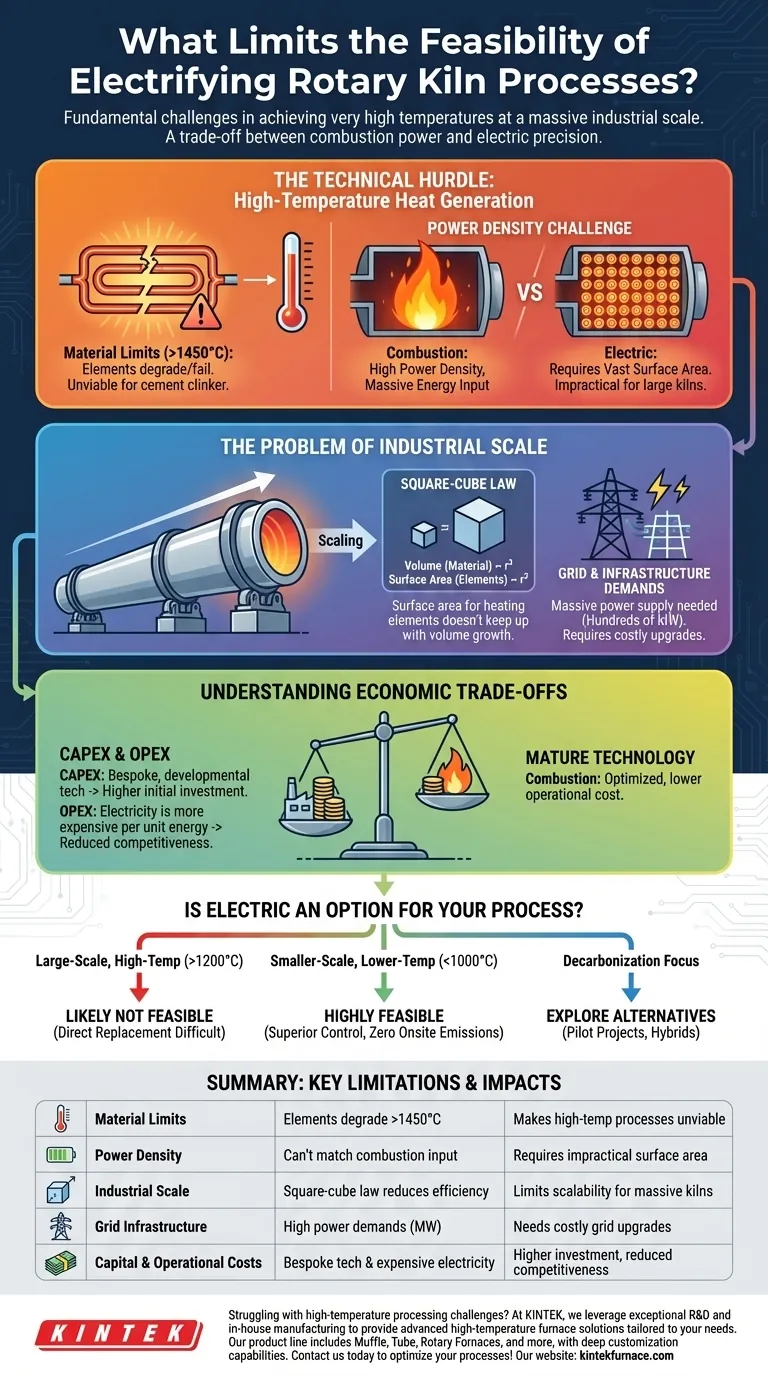
The Technical Hurdle: High-Temperature Heat Generation
The most significant barrier is rooted in the physics of heat generation and transfer. Combustion-based systems are exceptionally good at producing and delivering vast amounts of high-temperature energy.
Material Limits of Heating Elements
Electric kilns rely on resistive heating elements, which convert electricity into heat. These elements, often made of specialized alloys or materials like silicon carbide, have maximum operating temperatures.
For processes requiring temperatures above 1450°C (2640°F), such as cement clinker production, many conventional heating elements begin to degrade, soften, or fail. This makes direct electric replacement in the hottest applications technically unviable with current off-the-shelf technology.
The Challenge of Power Density
A fossil fuel flame injects an enormous amount of energy (high power density) directly into the kiln's volume. Replicating this thermal input with electricity is a major engineering problem.
To deliver the same energy, an electric kiln would require a vast surface area of heating elements. In a very large kiln, there simply isn't enough space on the kiln shell to mount the number of elements needed to match the power of a large industrial burner.
The Problem of Industrial Scale
The challenges of heat generation are magnified as the size of the rotary kiln increases. The principles that make combustion kilns efficient at large scales do not translate directly to electric designs.
Scaling and the Square-Cube Law
As a kiln's diameter increases, its internal volume (the amount of material to be processed) grows by a power of three (the cube). However, the surface area of its shell, where heating elements would be mounted, only grows by a power of two (the square).
This means that for very large kilns, the available surface area for electric heating becomes insufficient to heat the rapidly increasing volume of material inside. This is a fundamental geometric limitation.
Grid and Infrastructure Demands
Large-scale industrial processes require an immense and constant power supply. A single large cement kiln could require hundreds of megawatts of power, equivalent to the demand of a small city.
Electrifying such a facility would necessitate massive upgrades to the local electrical grid and the construction of dedicated substations, representing a formidable logistical and financial barrier.
Understanding the Economic Trade-offs
Even when technically possible, electrification must make economic sense. The comparison between the capital and operational costs of electric versus combustion kilns is a deciding factor.
High Capital Expenditure (CAPEX)
Combustion-fired rotary kilns are a mature, optimized technology. In contrast, a large-scale, high-temperature electric kiln is essentially a bespoke piece of developmental equipment.
The research, engineering, and manufacturing costs for such a system are substantially higher than for a conventional kiln, leading to a much larger initial investment.
The Reality of Operational Expenditure (OPEX)
In most energy markets worldwide, electricity is significantly more expensive per unit of energy (e.g., dollar per kilowatt-hour) than natural gas (dollar per therm/MMBtu).
This price difference means that even if an electric kiln operates with higher thermal efficiency, the total daily cost of energy can make the final product uncompetitive in the marketplace. The economic viability is often entirely dependent on regional energy pricing and the presence of significant carbon taxes that penalize fossil fuel use.
Is Electric an Option for Your Process?
The decision to electrify is not a universal "yes" or "no." It depends entirely on the specific requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is a large-scale, high-temperature process (>1200°C): Current electric kiln technology is likely not a feasible direct replacement for your existing combustion system.
- If your primary focus is a smaller-scale, lower-temperature process (<1000°C): Electrification is highly feasible and can offer superior temperature control, product quality, and zero onsite emissions.
- If your primary focus is decarbonization at any cost: You should investigate pilot projects, hybrid systems (using electricity for pre-heating), or alternative technologies to the rotary kiln itself.
Ultimately, the feasibility of electrifying a rotary kiln hinges on a clear-eyed assessment of your specific temperature, scale, and economic realities.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Material Limits | Heating elements degrade above 1450°C | Makes high-temperature processes like cement production unviable |
| Power Density | Electric elements can't match combustion's energy input | Requires impractical surface area in large kilns |
| Industrial Scale | Square-cube law reduces heating efficiency | Limits scalability for massive kilns |
| Grid Infrastructure | High power demands (e.g., hundreds of MW) | Needs costly grid upgrades |
| Capital Costs | Electric kilns are bespoke and developmental | Higher initial investment vs. combustion kilns |
| Operational Costs | Electricity is more expensive per energy unit | Increases product costs, reducing competitiveness |
Struggling with high-temperature processing challenges? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in research or industrial production, we can help optimize your processes for efficiency and precision. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating



















