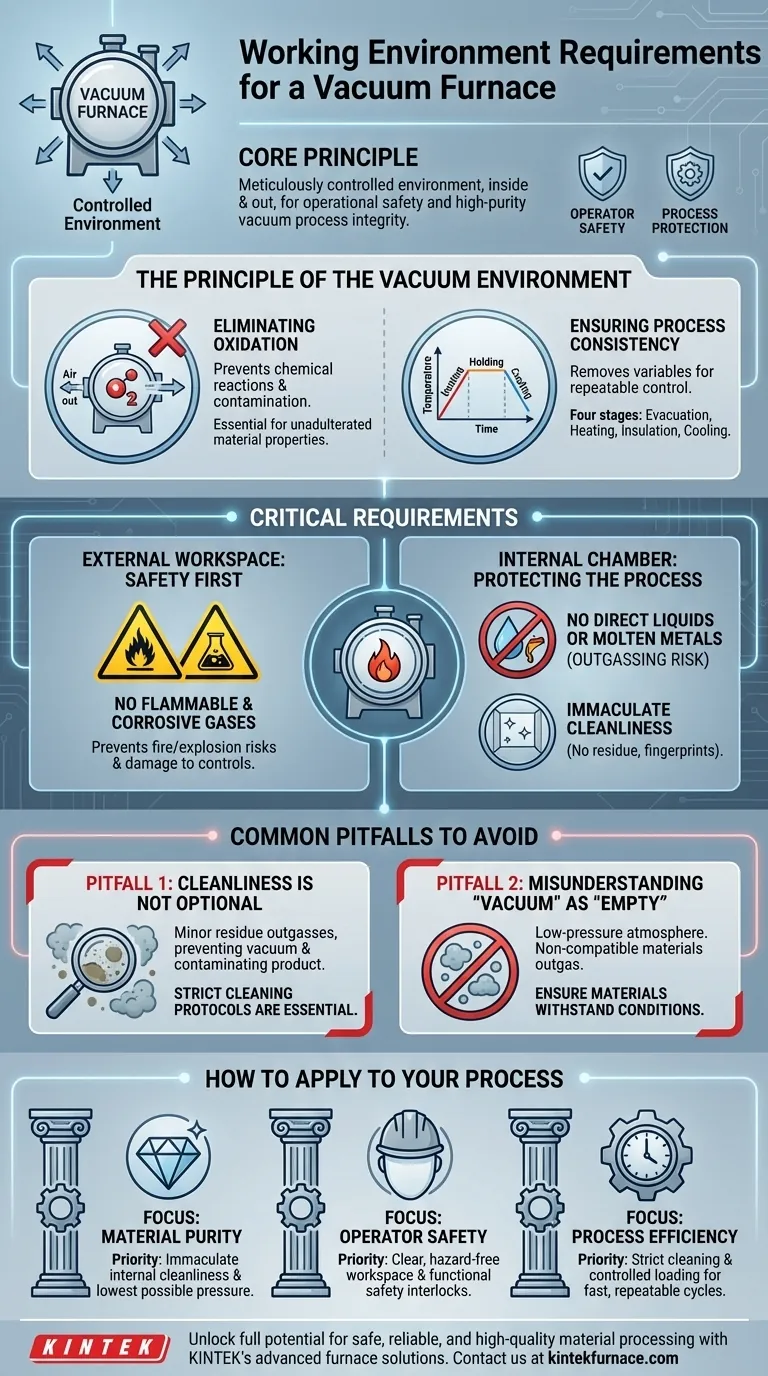
At its core, a vacuum furnace requires a working environment that is meticulously controlled both inside and outside the chamber. The external area must be free of flammable and corrosive gases, while the internal chamber must be kept immaculately clean and never have liquids or molten metals directly injected into it. These rules are not arbitrary; they are fundamental to ensuring operational safety and the integrity of the high-purity vacuum process.
The environmental requirements for a vacuum furnace are designed to accomplish two primary goals: first, to ensure the safety of the operator and the facility, and second, to protect the controlled vacuum environment inside the furnace, which is essential for preventing contamination and achieving high-quality results.

The Principle of the Vacuum Environment
To understand the external requirements, you must first appreciate the internal environment the furnace is designed to create. The entire purpose of a vacuum furnace is to heat materials in the near-total absence of air.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
The primary function of the vacuum system is to pump out air and other reactive gases from the furnace chamber. This prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions that would otherwise occur when heating materials, especially metals, at high temperatures.
This contamination-free environment is critical for producing parts with specific, unadulterated material properties.
Ensuring Process Consistency
By removing unpredictable variables like air and humidity, a vacuum allows for extremely precise and repeatable process control. The heating system can then raise, hold, and lower the temperature with high fidelity, ensuring every batch is treated under identical conditions.
The working principle follows four key stages: evacuation (creating the vacuum), heating, insulation (holding a specific temperature), and cooling.
Critical Environmental and Operational Requirements
The rules governing the furnace's environment are direct consequences of its operating principles. They are divided between the external workspace and the internal chamber.
The External Workspace: Safety First
The area surrounding the vacuum furnace must be kept free of flammable and corrosive gases. A vacuum furnace is a high-energy system using powerful electrical components to generate extreme heat.
Any flammable gas leak in the vicinity could create a risk of fire or explosion. Likewise, corrosive gases can damage the furnace's sophisticated electronic controls, wiring, and external shell over time.
The Internal Chamber: Protecting the Process
You must prohibit the direct injection of liquids or molten metal into the furnace. Such an action would cause the liquid to boil violently and instantly in the vacuum, a process called outgassing, which would compromise the vacuum level and potentially damage the system.
Furthermore, the chamber must be kept exceptionally clean. Fingerprints, grease, dust, or any other residue can vaporize under heat and vacuum, contaminating the material being processed and degrading the performance of the vacuum pumps.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Maintaining the correct environment involves more than just following the basic rules. A lack of discipline in these areas is a common source of failed processes and equipment damage.
Cleanliness Is Not Optional
A frequent mistake is underestimating the impact of minor contamination. Even small amounts of residue can outgas, preventing the system from reaching the required vacuum level and introducing impurities into the final product.
A strict cleaning protocol for both the chamber and any parts or fixtures being loaded is essential for reliable operation.
Misunderstanding "Vacuum" as "Empty"
The vacuum environment is not truly empty; it is a highly controlled, low-pressure atmosphere. Introducing materials that are not vacuum-compatible can lead to severe outgassing, which contaminates the furnace and the workpiece.
Always ensure that any materials placed in the furnace can withstand the combination of low pressure and high temperature without degrading or releasing contaminants.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your approach to the furnace environment should be dictated by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Your top priority is immaculate internal chamber cleanliness and using a high-performance vacuum system to achieve the lowest possible pressure.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Your emphasis must be on maintaining a clear, hazard-free external workspace and ensuring all safety interlocks, like automatic power-off on door opening, are fully functional.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Your goal is consistency. This means enforcing strict cleaning protocols and controlled loading procedures to ensure fast pump-down times and repeatable thermal cycles.
Ultimately, mastering the furnace's environment is the key to unlocking its full potential for safe, reliable, and high-quality material processing.
Summary Table:
| Requirement Type | Key Elements | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| External Workspace | Free of flammable and corrosive gases | Ensure operator safety and prevent equipment damage |
| Internal Chamber | Immaculate cleanliness, no liquids or molten metals | Maintain vacuum integrity and prevent contamination |
| Operational Focus | Material purity, operator safety, process efficiency | Tailor environment for specific goals like high-quality results or repeatability |
Unlock the full potential of your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your process safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability



















