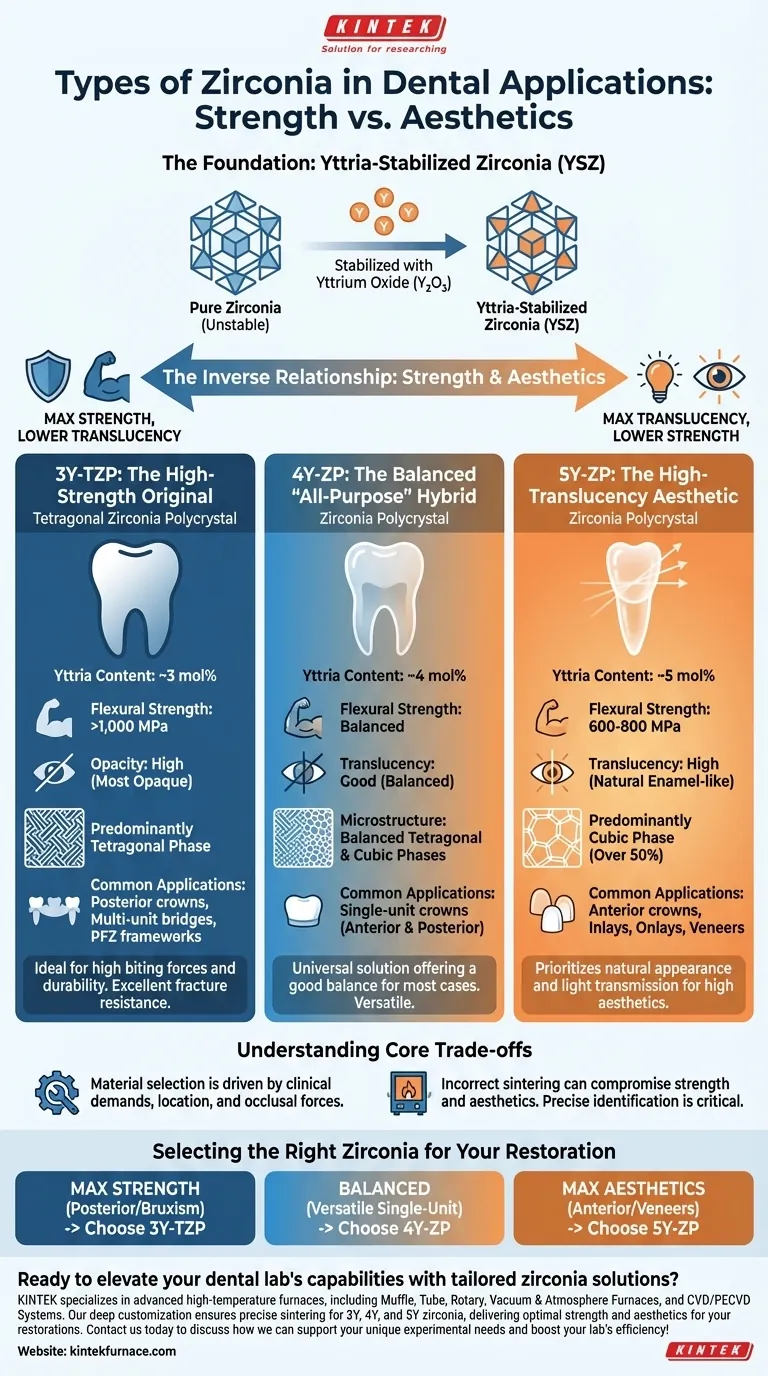
In dental applications, zirconia is not a single material but a category of ceramics classified primarily by their yttria content. The main types are 3Y, 4Y, and 5Y zirconia, where the number indicates the molar percentage of yttrium oxide added as a stabilizer. This additive fundamentally dictates the material's final balance of strength and aesthetic translucency.
The core principle to understand is the inverse relationship between strength and aesthetics in zirconia. As the yttria content increases (from 3Y to 5Y), the material becomes significantly more translucent and natural-looking, but its mechanical strength and fracture resistance decrease.

The Foundation: Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ)
What is YSZ?
All modern dental zirconia is technically yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ). Pure zirconia is unstable at room temperature, so yttrium oxide (yttria) is added to stabilize its crystalline structure, making it suitable for clinical use.
The Role of Crystal Phases
The amount of yttria determines the ratio of two critical crystal phases within the material: the tetragonal phase and the cubic phase. Understanding this ratio is the key to understanding the different types of zirconia. The tetragonal phase provides immense strength, while the cubic phase allows light to pass through, creating translucency.
The Primary Classes of Dental Zirconia
3Y-TZP: The High-Strength Original
3Y-TZP (Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystal) contains approximately 3 mol% yttria. This composition results in a predominantly tetragonal crystal structure.
This is the strongest class of dental zirconia, with flexural strengths often exceeding 1,000 MPa. Its high strength makes it exceptionally resistant to fracture, but its dense tetragonal structure also makes it the most opaque.
Due to its opacity and maximum strength, 3Y zirconia is the ideal choice for posterior crowns, multi-unit bridges, and frameworks for porcelain-fused-to-zirconia (PFZ) restorations.
5Y-ZP: The High-Translucency Aesthetic
5Y-ZP (Zirconia Polycrystal) contains approximately 5 mol% yttria. This higher yttria content stabilizes a much larger volume of the cubic phase (often over 50%).
The high concentration of cubic crystals makes 5Y zirconia the most translucent, rivaling the aesthetics of lithium disilicate or even natural enamel. However, this comes at the cost of strength, with flexural strengths typically in the 600-800 MPa range.
Its primary application is for monolithic anterior restorations—such as crowns, inlays, onlays, and veneers—where aesthetics are the highest priority and biting forces are lower.
4Y-ZP: The Balanced "All-Purpose" Hybrid
4Y-ZP is a more recent formulation containing approximately 4 mol% yttria. It was developed to bridge the gap between the strength of 3Y and the aesthetics of 5Y.
This material offers a balanced blend of tetragonal and cubic phases, providing good translucency suitable for most cases while retaining higher strength than 5Y zirconia.
It is often marketed as a "universal" or "all-purpose" zirconia, versatile enough for single-unit crowns in both the anterior and posterior regions.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
Strength vs. Translucency
The central trade-off is clear: you are choosing a point on a spectrum between maximum strength and maximum aesthetics. There is no single zirconia that is both the strongest and the most translucent.
Material selection must be driven by the clinical demands of the specific case, particularly the location in the mouth and the occlusal forces involved.
Implications for Preparation and Sintering
The different compositions also have practical implications for the dental laboratory. Each class of zirconia requires specific milling and sintering parameters to achieve its intended properties.
Using the incorrect sintering cycle for a specific zirconia type can severely compromise its strength, aesthetics, and long-term stability. This is why precise material identification is critical.
Selecting the Right Zirconia for Your Restoration
Choosing the correct zirconia is about matching the material's properties to the clinical requirements of the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a posterior bridge or a patient with bruxism: Choose a 3Y-TZP zirconia for its superior fracture resistance.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible aesthetic outcome for an anterior crown: Choose a 5Y-ZP zirconia for its exceptional translucency and natural appearance.
- If your primary focus is a versatile, single-unit crown with a solid balance of strength and aesthetics: Choose a 4Y-ZP zirconia as a reliable all-around solution.
Understanding this classification empowers you to make informed material decisions that lead to predictable, durable, and aesthetic clinical outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Type | Yttria Content | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Y-TZP | ~3 mol% | High strength (>1000 MPa), opaque | Posterior crowns, bridges, PFZ frameworks |
| 4Y-ZP | ~4 mol% | Balanced strength and translucency | All-purpose single-unit crowns |
| 5Y-ZP | ~5 mol% | High translucency, lower strength (600-800 MPa) | Anterior crowns, veneers, inlays/onlays |
Ready to elevate your dental lab's capabilities with tailored zirconia solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise sintering for 3Y, 4Y, and 5Y zirconia, delivering optimal strength and aesthetics for your restorations. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your unique experimental needs and boost your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- Why is using a universal setting for all materials in a dental furnace a mistake? Master Precision Sintering for Perfect Restorations
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations
- Why is temperature range important when selecting a dental furnace? Unlock Material Compatibility and Precision



















