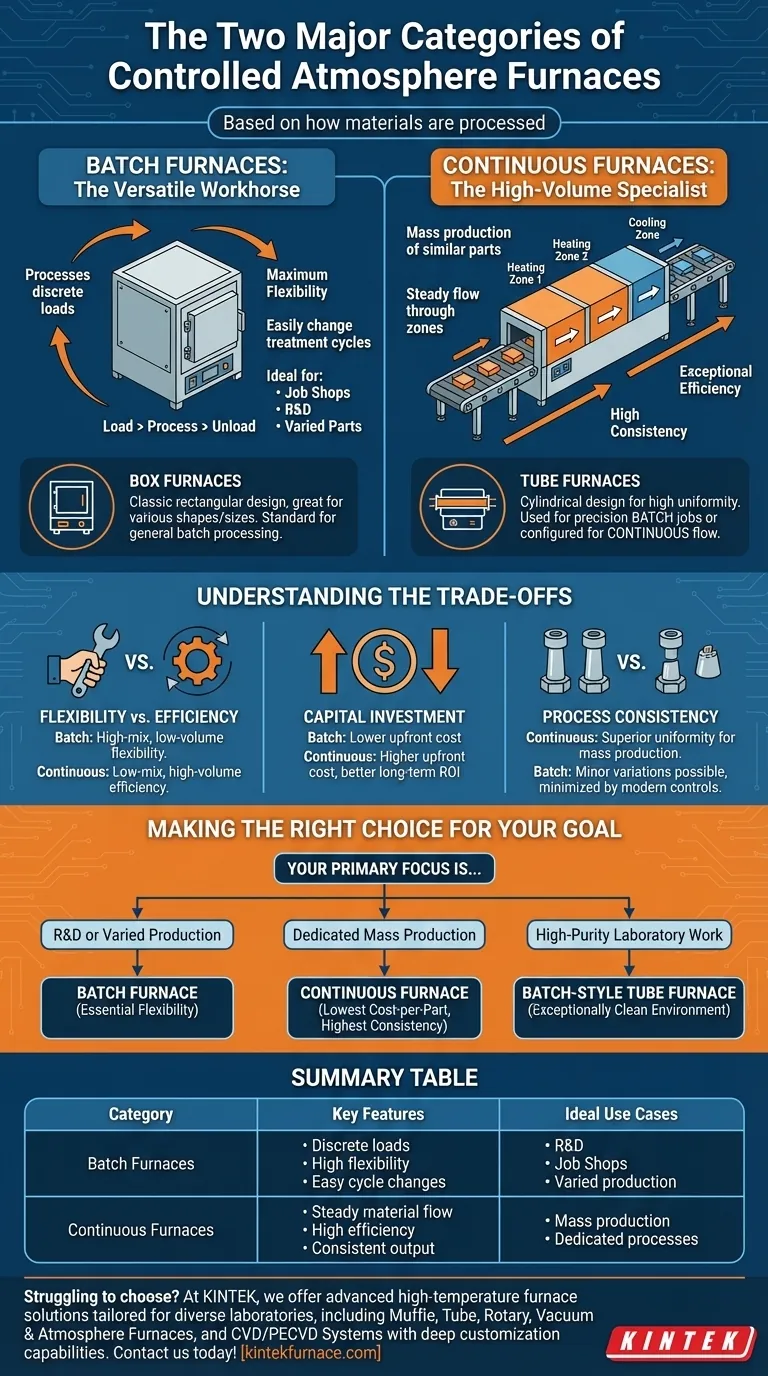
At their core, controlled atmosphere furnaces are categorized based on how materials are processed through them. The two primary categories are batch furnaces, where a set quantity of material is loaded, processed, and then unloaded, and continuous furnaces, where materials move steadily through different heating and cooling zones.
The choice between a batch or continuous furnace is not about which is "better," but which process aligns with your operational goals. The decision fundamentally balances the need for production volume and consistency against the need for process flexibility.

The Fundamental Divide: Batch vs. Continuous Processing
Understanding these two categories is the first step in selecting the right equipment for a heat-treating application. They represent two distinct philosophies of manufacturing workflow.
Batch Furnaces: The Versatile Workhorse
A batch furnace processes a single, discrete load of parts at a time. The entire chamber undergoes the full thermal cycle—heating, soaking, and cooling—along with the parts inside.
This design offers maximum flexibility. You can easily change the treatment cycle (time, temperature, atmosphere) from one batch to the next, making it ideal for job shops, research and development, or producing a wide variety of parts with different requirements.
Continuous Furnaces: The High-Volume Specialist
A continuous furnace is designed for mass production of similar parts. Materials are fed into one end, move through various temperature zones on a conveyor system, and exit the other end fully processed.
Each zone is held at a constant temperature, creating a highly stable and repeatable process. This specialization results in exceptional efficiency and part-to-part consistency, but it lacks the flexibility to easily switch between different treatment cycles.
A Second Distinction: Furnace Geometry
While batch vs. continuous describes the process, furnace geometry describes the physical construction. The two most common designs are box and tube furnaces, which often align with a specific process type.
Box Furnaces
These are classic rectangular chamber furnaces. Their large, open design makes them perfect for loading many parts of various sizes and shapes, which is why they are overwhelmingly used for batch processing. They are the standard for general-purpose heat treatment.
Tube Furnaces
As the name implies, these furnaces use a cylindrical tube to contain the parts and the atmosphere. This shape is excellent for creating a highly uniform and pure environment.
Tube furnaces can be used for small, precise batch jobs (common in laboratories) or configured for continuous flow processes where material is pushed or pulled through the tube.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace type involves weighing critical operational and financial factors. There is no universally superior option; the correct choice is context-dependent.
Flexibility vs. Efficiency
This is the central trade-off. Batch furnaces offer unparalleled flexibility for "high-mix, low-volume" production. Continuous furnaces deliver maximum efficiency and low per-part cost for "low-mix, high-volume" production.
Capital Investment
Generally, batch furnaces have a lower upfront capital cost compared to large, complex continuous systems. However, at a high enough production volume, the lower per-part operating cost of a continuous furnace can provide a better long-term return on investment.
Process Consistency
For applications requiring the highest degree of uniformity across millions of parts, the stable, zoned environment of a continuous furnace is superior. Batch furnaces can introduce minor variations from batch to batch, though modern controls minimize this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific needs should be the sole driver of your decision.
- If your primary focus is R&D or varied production: A batch furnace provides the essential flexibility to run different cycles for different parts.
- If your primary focus is dedicated mass production: A continuous furnace offers the lowest cost-per-part and the highest consistency for a single, repeatable process.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory work: A batch-style tube furnace delivers an exceptionally clean and controlled environment for small, precise samples.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace category begins with a clear understanding of your own production needs and strategic goals.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Features | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Furnaces | Processes discrete loads, high flexibility, easy cycle changes | R&D, job shops, varied production |
| Continuous Furnaces | Steady material flow, high efficiency, consistent output | Mass production, dedicated processes |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's heat treatment needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you need the flexibility of batch processing or the efficiency of continuous flow, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our expertise can enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the significance of nitrogen in atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Enhanced Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening



















