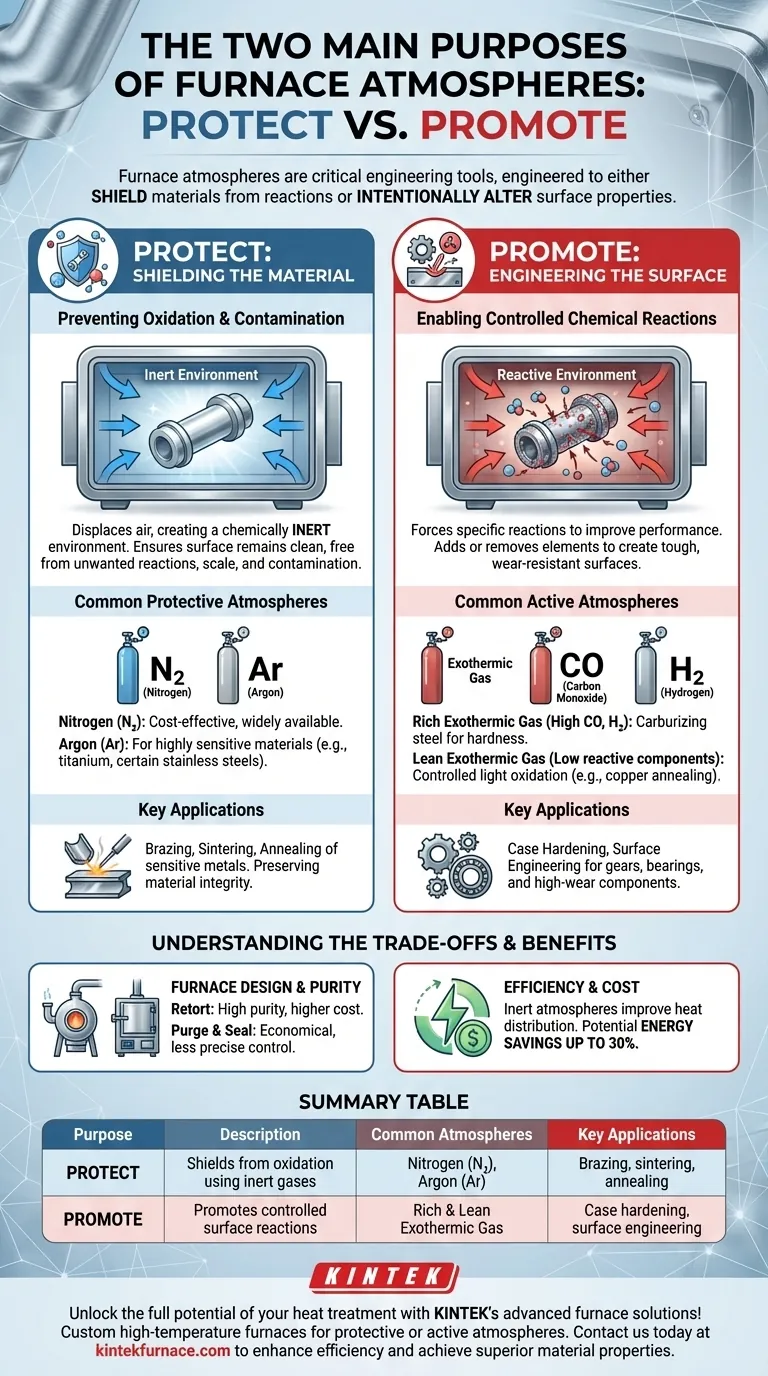
At their core, furnace atmospheres serve two distinct and opposing functions. During high-temperature processes, they are engineered either to protect a material's surface from any chemical reaction, keeping it pristine, or to intentionally promote a specific, controlled reaction to alter the surface in a desirable way. This choice between a protective or active environment is fundamental to achieving the final properties of the component.
The purpose of a furnace atmosphere is not just to fill a space; it is a critical engineering tool. The decision to use a protective (inert) or reactive (active) atmosphere directly determines whether a component will emerge from the furnace unchanged or with deliberately enhanced surface properties like hardness or corrosion resistance.

The Protective Role: Shielding the Material
The most common purpose of a controlled atmosphere is to act as a shield. At the high temperatures used in heat treatment, most materials—especially metals—are highly reactive with the oxygen and moisture present in ambient air.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Without a controlled atmosphere, heating a steel part would result in a thick layer of oxide scale. This scale degrades the surface finish, alters the component's dimensions, and can ruin its mechanical properties.
A protective atmosphere displaces the air, creating a chemically inert environment. This ensures the part's surface remains bright and clean, free from unwanted reactions, oxidation, and contamination throughout the heating and cooling cycle.
Common Protective Atmospheres
The most widely used protective atmospheres are composed of inert gases that do not readily react with other elements.
Common choices include:
- Nitrogen (N₂): Cost-effective and widely available, it is suitable for a vast range of applications.
- Argon (Ar): More expensive than nitrogen, argon is used for highly sensitive materials that might react even with nitrogen at extreme temperatures, such as titanium or certain stainless steels.
The Active Role: Engineering the Surface
In contrast to protection, an active atmosphere is designed to intentionally cause a chemical change on the material's surface. This is a form of surface-level alchemy, where the gas composition is precisely tuned to add or remove elements.
Enabling Controlled Chemical Reactions
By introducing specific gases, engineers can force reactions that improve a material's performance. This allows for the creation of components with a tough, wear-resistant surface while maintaining a more ductile, shock-absorbent core.
This process is critical for applications like creating gears, bearings, and other high-wear components.
Examples of Active Atmospheres
Active atmospheres are mixtures formulated for a specific outcome. A well-known example is an exothermic gas, which is generated by burning fuel and can be tailored for different needs.
- Rich Exothermic Gas: A mixture high in carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H₂). It is used for processes like carburizing steel, where carbon atoms from the atmosphere diffuse into the steel's surface to increase its hardness.
- Lean Exothermic Gas: A mixture low in reactive components. It can be used for controlled, light oxidation, such as when annealing copper to achieve a specific surface finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Implementing a furnace atmosphere is not without its challenges. The choice of gas and furnace type involves a balance of cost, complexity, and the required level of purity.
Furnace Design and Atmosphere Purity
The ability to maintain a pure atmosphere depends heavily on the furnace's construction.
- Retort Furnaces: These use a sealed alloy container to hold the parts, which is then heated externally. This design provides the cleanest, highest-purity atmosphere but comes with higher equipment cost and maintenance.
- Purge and Seal Furnaces: These rely on tight seals and a continuous flow of gas to purge any air that leaks in. They are more economical but offer less precise control over atmosphere purity, particularly the dew point (a measure of moisture content).
The Hidden Benefit: Efficiency and Cost
Beyond surface treatment, controlled atmospheres offer significant operational advantages. The inert gases used in protective atmospheres can improve heat distribution and retention within the furnace.
This optimization can lead to energy savings of up to 30% compared to conventional heating methods, reducing both operational costs and environmental impact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a furnace atmosphere must be driven by the end goal for the component.
- If your primary focus is preserving material integrity: Use a protective, inert atmosphere like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation during processes like brazing, sintering, or annealing sensitive metals.
- If your primary focus is altering surface properties: Select a chemically active atmosphere, such as a carbon-rich gas for case hardening steel or a lean exothermic gas for controlled copper annealing.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Factor in the energy savings offered by inert gas atmospheres, which can offset the cost of the gas and equipment over time.
Ultimately, mastering furnace atmospheres means treating them not as a background condition, but as a precise and powerful engineering tool.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Description | Common Atmospheres | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protective | Shields materials from oxidation and contamination using inert gases | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Brazing, sintering, annealing of sensitive metals |
| Active | Promotes controlled chemical reactions to alter surface properties | Rich Exothermic Gas (e.g., for carburizing), Lean Exothermic Gas (e.g., for copper annealing) | Case hardening, surface engineering for gears and bearings |
Unlock the full potential of your heat treatment processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for protective or active atmospheres. Contact us today to enhance efficiency, achieve superior material properties, and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment
- What are the two main types of atmosphere furnaces and their characteristics? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab



















