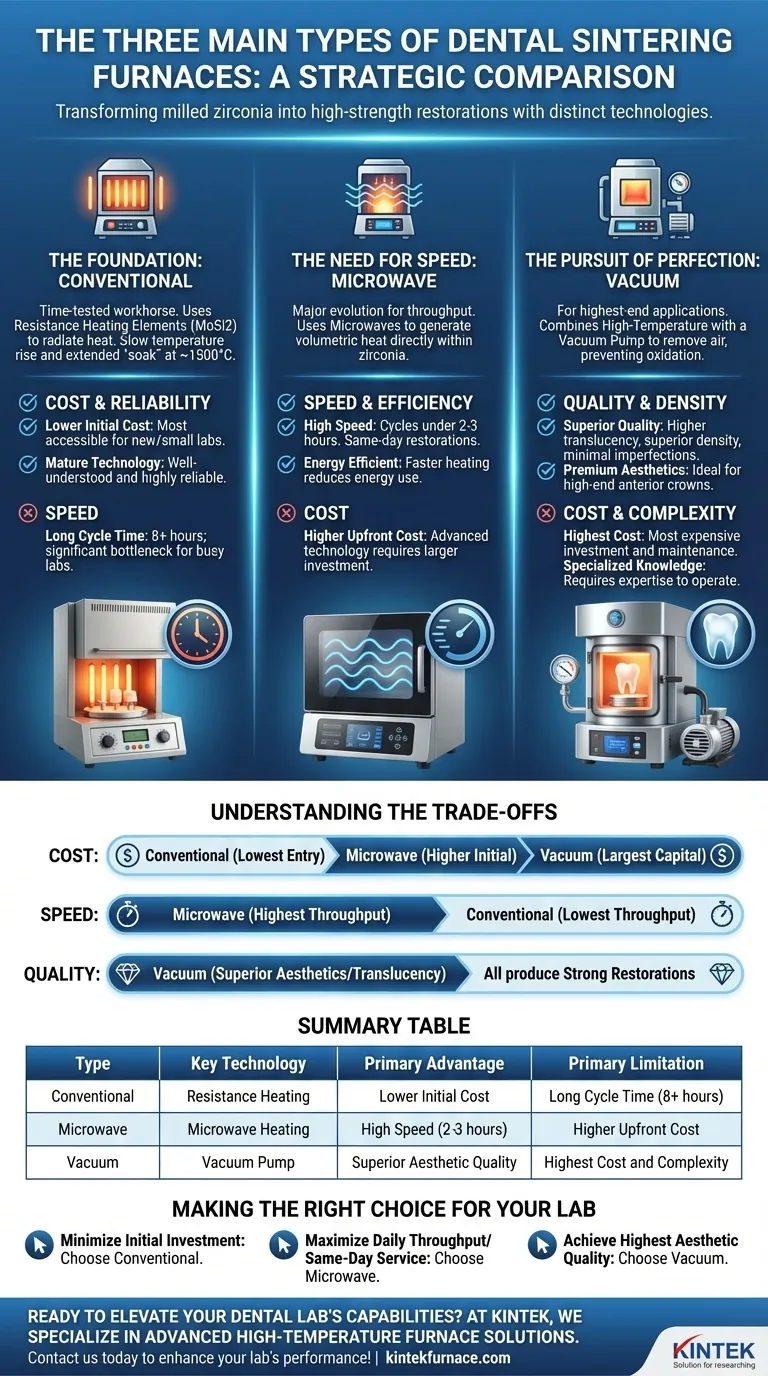
The three main types of dental sintering furnaces are conventional (resistance heating), microwave, and vacuum furnaces. Each uses a distinct technology to transform milled zirconia into a final, high-strength restoration. While all achieve the same fundamental goal, they differ significantly in speed, cost, and the final quality of the restoration.
The choice between a conventional, microwave, or vacuum sintering furnace is a strategic decision for any dental lab. It represents a fundamental trade-off between initial cost, operational speed, and the ultimate aesthetic quality of the final dental restoration.

The Foundation: Conventional Sintering Furnaces
A conventional sintering furnace is the traditional workhorse of the dental lab, relying on time-tested technology.
How They Work
These furnaces use resistance heating elements, typically made of molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), to radiate heat and slowly raise the temperature inside the chamber. The zirconia restoration "soaks" at a high temperature (around 1500°C) for an extended period to achieve full density and strength.
Key Advantages: Cost and Reliability
The primary advantage is their lower initial cost, making them the most accessible option for new labs or those with smaller budgets. Their technology is mature, well-understood, and highly reliable.
Primary Limitation: Speed
The biggest drawback is the long cycle time. A conventional sintering cycle can take 8 hours or more, which can become a significant bottleneck for a busy lab, limiting daily production capacity.
The Need for Speed: Microwave Sintering Furnaces
Microwave furnaces represent a major evolution, designed to drastically reduce processing time and increase lab throughput.
How They Work
Instead of external heating elements, these furnaces use microwaves to generate heat directly within the zirconia material itself. This "volumetric" heating is fundamentally faster and more energy-efficient.
Key Advantages: Speed and Efficiency
A microwave furnace can complete a sintering cycle in a fraction of the time of a conventional unit, often in under 2-3 hours. This allows for same-day restorations and significantly boosts a lab's daily output and energy efficiency.
Primary Limitation: Cost
This advanced technology comes at a higher upfront cost. While operational savings can offset this over time, the initial investment is a key consideration.
The Pursuit of Perfection: Vacuum Sintering Furnaces
Vacuum furnaces are designed for the highest-end applications where final aesthetic quality and material purity are paramount.
How They Work
These units combine high-temperature heating with a vacuum pump that removes ambient air from the firing chamber. Sintering in this oxygen-free environment prevents oxidation and reduces microscopic air bubbles or porosity within the material.
Key Advantages: Quality and Density
The vacuum environment produces restorations with superior density, higher translucency, and minimal imperfections. This is critical for high-end anterior crowns where aesthetics are the top priority.
Primary Limitation: Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are the most expensive type in terms of both initial investment and maintenance. They also require more specialized knowledge to operate and maintain correctly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is not about finding the "best" one, but the one that best aligns with your lab's specific operational goals.
Cost: Initial vs. Operational
Conventional furnaces have the lowest entry cost. Microwave furnaces have a higher initial cost but can offer long-term savings on energy bills. Vacuum furnaces represent the largest capital investment.
Speed: Throughput vs. Cycle Time
Microwave furnaces provide the highest throughput, making them ideal for high-volume production labs. Conventional furnaces have the lowest throughput, which may be sufficient for smaller labs or as a backup unit.
Quality: Aesthetics vs. Strength
All three types can produce clinically acceptable, strong restorations. However, vacuum furnaces excel at producing the highest level of aesthetic quality and translucency by minimizing porosity, which is a key factor for premium cosmetic work.
Making the Right Choice for Your Lab
Your decision should be guided by your lab's business model and primary focus.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment: A conventional sintering furnace is the most logical and cost-effective starting point.
- If your primary focus is maximizing daily throughput and offering same-day service: A microwave sintering furnace is the clear choice for its unmatched speed.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible aesthetic quality for premium cases: A vacuum sintering furnace will provide the best material density and translucency.
Ultimately, the right furnace empowers your lab to deliver on its specific promises of cost, speed, or quality.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Technology | Primary Advantage | Primary Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | Resistance Heating | Lower Initial Cost | Long Cycle Time (8+ hours) |
| Microwave | Microwave Heating | High Speed (2-3 hours) | Higher Upfront Cost |
| Vacuum | Vacuum Pump | Superior Aesthetic Quality | Highest Cost and Complexity |
Ready to elevate your dental lab's capabilities? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to precisely match your experimental requirements. Whether you prioritize cost-efficiency, speed, or top-tier quality, our expertise ensures you get the right sintering furnace for superior restorations. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of a dental furnace? Mastering Precision Sintering & Firing for Crowns
- What are the recommended maintenance practices for dental furnaces? Ensure Precision and Longevity for Your Lab
- What are the primary functions of ceramic dental furnaces? Achieve Precision and Durability in Dental Restorations
- Why is accurate temperature control important in dental furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations Every Time
- What role does temperature range and accuracy play in dental furnace performance? Ensure Precision for Superior Dental Restorations



















