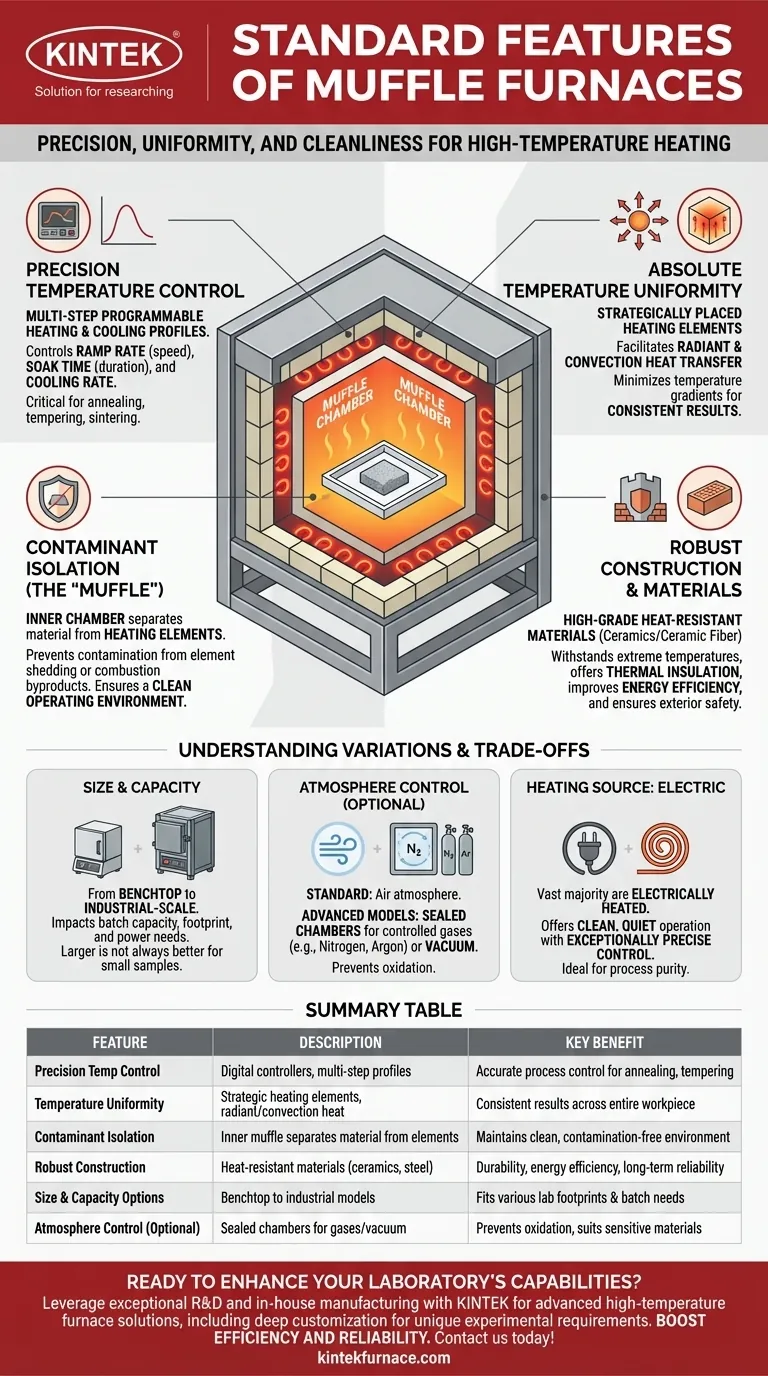
At their core, muffle furnaces are defined by a specific set of standard features designed to deliver precise, uniform, and clean high-temperature heating. These core features include advanced, programmable temperature control for managing heating and cooling rates, a chamber designed for exceptional temperature uniformity, robust construction with heat-resistant materials for durability, and a "muffle" or inner chamber that isolates the workload from contamination.
A muffle furnace is more than just a high-temperature oven; it is a precision instrument. Its standard features are engineered to achieve three critical goals: precise process control, uniform heat application, and a completely clean operating environment for the material being treated.
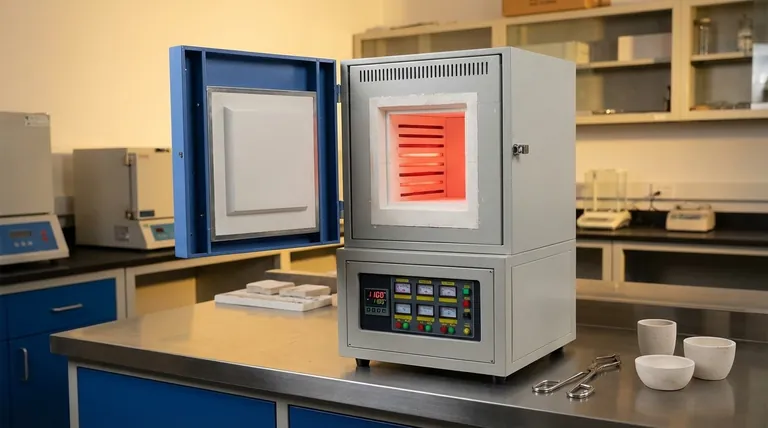

The Core Principles of Muffle Furnace Design
Every standard feature of a muffle furnace serves a fundamental purpose in the heat-treating process. Understanding these principles is key to appreciating the value and function of the equipment.
Precision Temperature Control and Programmability
Modern muffle furnaces are equipped with sophisticated digital controllers. These are not simple thermostats.
A key standard feature is the ability to program multi-step heating and cooling profiles. This allows you to control the ramp rate (how quickly it heats up), the soak time (how long it holds a temperature), and the cooling rate, which is critical for processes like annealing, tempering, and sintering.
Absolute Temperature Uniformity
For any heat treatment to be successful, the entire workpiece must experience the exact same temperature. Muffle furnaces are engineered to provide this.
Heating elements are strategically placed around the chamber, and the interior is designed to facilitate both radiant and convection heat transfer. This combination ensures that temperature gradients within the chamber are minimized, leading to consistent and repeatable results.
Contaminant Isolation (The "Muffle")
The defining feature of this furnace is the muffle itself—an inner chamber that separates the material being processed from the heating elements.
This design is crucial for preventing contamination. In electrically heated furnaces, it protects the sample from any potential shedding from the heating elements. In fuel-fired models, it provides an essential barrier against the byproducts of combustion, ensuring a clean process environment.
Robust Construction and Material Science
Muffle furnaces are built for extreme conditions and long-term reliability. The outer body is typically a sturdy steel construction.
The inner chamber and insulation are made from high-grade, heat-resistant materials like dense ceramics or ceramic fiber. These materials not only withstand the high temperatures but also possess excellent thermal insulation properties, improving energy efficiency and ensuring the exterior remains safe to the touch.
Understanding the Variations and Trade-offs
While the core principles are consistent, muffle furnaces come in different configurations, and it's important to understand the practical differences.
Size and Capacity
Furnaces are available in a wide range of sizes, from small benchtop units suitable for labs to large, industrial-scale production models.
The choice of size directly impacts your batch capacity, laboratory footprint, and power requirements. A larger chamber is not always better if your typical sample size is small, as it will consume more energy to heat.
Standard vs. Advanced Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace provides isolation from the heating elements, operating with the air inside the chamber.
However, many applications require more. Advanced models offer sealed chambers with ports for introducing controlled atmospheres (like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation) or for drawing a vacuum. These are technically customizations but are common options.
Heating Source: The Rise of Electric
The vast majority of modern laboratory muffle furnaces are electrically heated. This method is inherently clean, quiet, and offers exceptionally precise control.
While larger industrial furnaces may still use gas or other fuels for economic reasons, the electric furnace is the standard for applications demanding cleanliness and process purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific application and priorities.
- If your primary focus is repeatable lab research: Prioritize a model with a multi-segment programmable controller and certified temperature uniformity specifications.
- If your primary focus is industrial production: Evaluate the robust construction, chamber volume, energy efficiency, and expected lifespan of consumable parts like heating elements.
- If your primary focus is working with highly sensitive materials: Confirm the muffle design provides complete isolation and investigate models that offer optional atmosphere or vacuum control.
By understanding these core features and their purpose, you can confidently select an instrument that meets your exact technical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Temperature Control | Digital controllers with multi-step heating/cooling profiles | Ensures accurate process control for annealing, tempering, etc. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Strategically placed heating elements for radiant and convection heat | Provides consistent results across the entire workpiece |
| Contaminant Isolation | Inner muffle chamber separates material from heating elements | Maintains a clean environment, free from contamination |
| Robust Construction | Made with heat-resistant materials like ceramics and steel | Offers durability, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability |
| Size and Capacity Options | Available from benchtop to industrial models | Fits various lab footprints and batch capacity needs |
| Atmosphere Control (Optional) | Sealed chambers for controlled gases or vacuum | Prevents oxidation and suits sensitive material processing |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's capabilities with a high-performance muffle furnace? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need precise temperature control, uniform heating, or contaminant isolation for sensitive materials, we can deliver tailored solutions that boost efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK can support your research or production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















