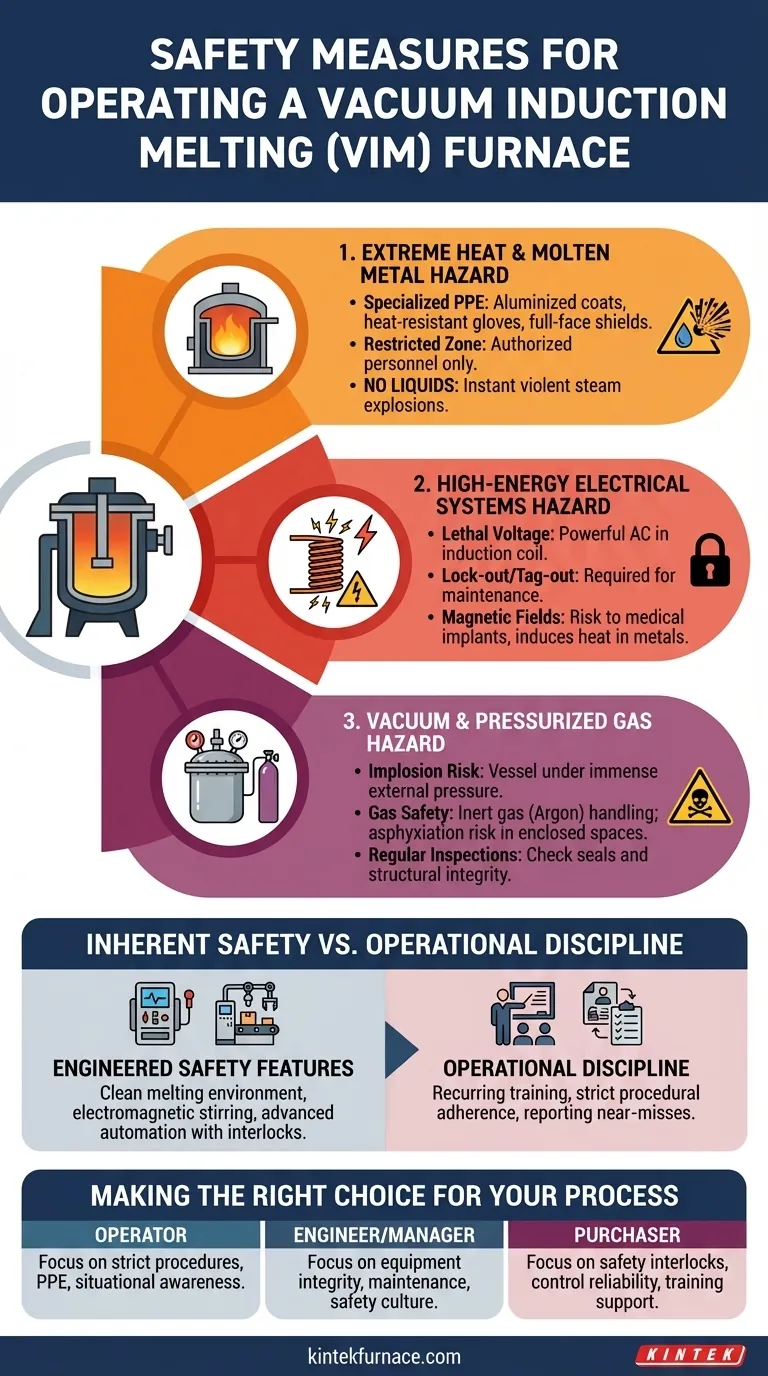
The primary safety measures for a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace are centered on managing its extreme operational conditions. This involves mandating the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), strictly controlling access to the operational area, prohibiting any liquids near the furnace to prevent steam explosions, and ensuring the correct and safe handling of all process gases.
The core principle of VIM furnace safety is not just following a checklist, but developing a deep understanding of the three primary hazards: the extreme heat of molten metal, the high-energy electrical systems, and the risks associated with both vacuum and high-pressure gas.
Understanding the Core Hazards of VIM Operation
A VIM furnace combines multiple high-risk technologies to achieve its metallurgical goals. Effective safety management requires recognizing and mitigating the dangers inherent in each of its core operational principles.
The Hazard of Extreme Heat and Molten Metal
The most obvious risk is the immense heat generated to melt metal. A failure to manage this can result in severe burns or catastrophic equipment failure.
Operators must wear specialized PPE, including aluminized coats, heat-resistant gloves, and full-face shields, especially during charging, sampling, and tapping operations.
The area around the furnace must be designated a restricted zone, accessible only to trained and authorized personnel. This prevents accidental exposure and interference.
Crucially, all liquids must be kept far away from the furnace. Any contact between a liquid like water and the molten metal bath can cause an instantaneous and violent steam explosion, ejecting molten metal over a wide area.
The Hazard of High-Energy Electrical Systems
The furnace operates using electromagnetic induction, which requires a powerful alternating current running through its main coil. This presents a significant and often invisible electrical hazard.
The induction coil carries lethal levels of voltage and current. All maintenance and inspection of these systems must be performed by qualified electricians after a complete lock-out/tag-out procedure.
The strong magnetic field itself can pose a risk to individuals with medical implants like pacemakers and can induce heat in nearby metallic objects, including tools or personal items.
The Hazard of Vacuum and Pressurized Gas Systems
The "vacuum" in VIM is essential for purity but introduces unique physical risks. The furnace vessel is under immense external pressure when under vacuum, creating a risk of implosion if its structural integrity is compromised.
Regular inspection of all seals, viewports, and the vessel itself is critical to ensure it can withstand atmospheric pressure.
The process often uses inert gases like argon from high-pressure cylinders. Improper handling of these cylinders or a failure in the gas delivery system can lead to an uncontrolled release of pressure or create an asphyxiation hazard in an enclosed space.
Inherent Safety vs. Operational Discipline
While VIM furnaces present significant hazards, their design also includes inherent safety advantages. True safety is achieved when these engineered features are paired with unwavering operational discipline.
Engineered Safety Features
VIM furnaces offer a clean, controlled melting environment. This prevents the formation of non-metallic oxide inclusions and removes harmful volatile elements, which are safety and quality benefits.
The electromagnetic stirring action ensures the molten metal is homogenous, preventing the segregation of elements that could lead to unpredictable material properties.
Modern furnaces are equipped with advanced control and automation systems that monitor temperature, pressure, and power, with interlocks designed to prevent operation outside of safe parameters.
The Critical Role of Human Factors
The engineered benefits are nullified by complacency or procedural error. The most robust furnace cannot protect against an operator bypassing a safety interlock or neglecting to wear proper PPE.
Comprehensive and recurring training is the cornerstone of VIM safety. Operators must not only know the procedures but also understand the reasons behind them.
A strong culture of safety, where reporting near-misses is encouraged and procedural adherence is non-negotiable, is the ultimate defense against accidents.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your safety strategy should be tailored to your specific role and responsibilities within the VIM operation.
- If you are a furnace operator: Your primary focus is strict procedural adherence, correct use of all PPE, and maintaining constant situational awareness around the equipment.
- If you are an engineer or facility manager: Your focus is on ensuring equipment integrity through rigorous maintenance schedules, providing comprehensive training, and fostering a culture where safety overrides production pressure.
- If you are evaluating a VIM furnace for purchase: Your focus should be on its built-in safety interlocks, the reliability of its control systems, and the quality of the manufacturer's operational training and support.
Ultimately, safety in a VIM environment is the foundation upon which all goals of quality, purity, and productivity are built.

Summary Table:
| Safety Measure | Key Focus | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Operator Protection | Use aluminized coats, heat-resistant gloves, and full-face shields to prevent burns from extreme heat and molten metal. |
| Electrical System Safety | Hazard Mitigation | Implement lock-out/tag-out procedures for high-energy induction coils; avoid risks from magnetic fields and electrical currents. |
| Vacuum and Gas Handling | System Integrity | Regularly inspect seals and vessels for implosion risks; safely manage inert gases like argon to prevent asphyxiation or pressure releases. |
| Operational Discipline | Human Factors | Enforce strict access control, keep liquids away to avoid steam explosions, and provide recurring training for procedural adherence. |
Ensure the highest safety standards in your lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your operational safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















