The proper procedure after completing an experiment with a muffle furnace is to first turn off the power, then allow the furnace to cool with the door closed to a safe handling temperature. Once cooled, you can carefully open the door and use tongs to remove your sample, immediately transferring it to a desiccator to prevent moisture absorption.
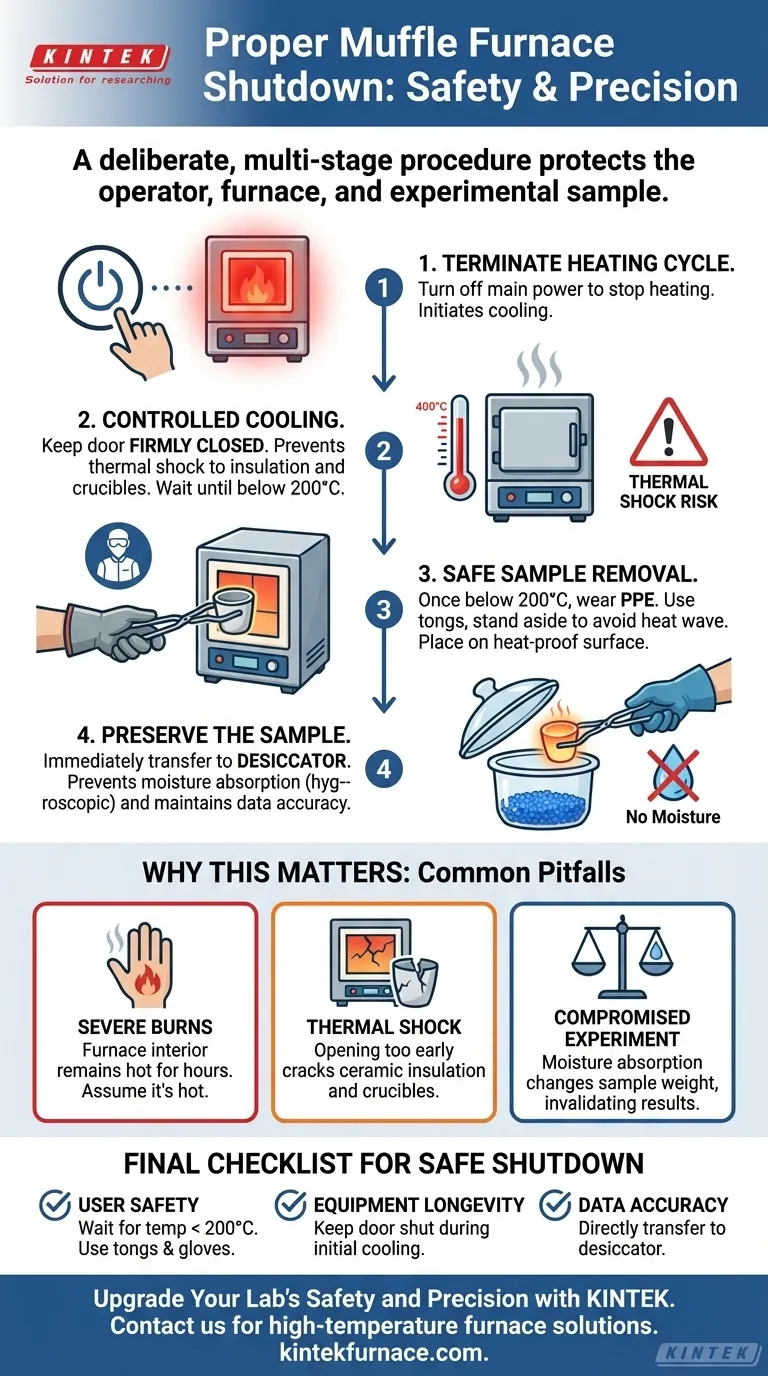
The shutdown process for a muffle furnace is not simply about turning it off. It is a deliberate, multi-stage procedure designed to protect three critical things: the operator from severe burns, the furnace from damage via thermal shock, and the experimental sample from contamination.
The Shutdown Protocol: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Following a precise sequence is essential for ensuring safety and the integrity of your results. Each step serves a specific purpose.
Step 1: Terminate the Heating Cycle
The first and most immediate action is to turn off the main power to the furnace. This can be done via the control panel or a dedicated external power switch.
This step stops any further energy from being supplied to the heating elements, initiating the cooling process.
Step 2: Controlled Cooling (The Critical Phase)
Keep the furnace door firmly closed after the power is off. The furnace must be allowed to cool down naturally.
Opening the door while the interior is at a very high temperature (e.g., above 300°C) will cause a sudden inrush of cool room air. This creates thermal shock, which can crack the furnace's internal ceramic insulation and potentially shatter your crucible.
Allow the temperature to drop to a safe level, typically below 200°C, before proceeding. Some protocols may involve slightly opening the door a crack to vent once the temperature is lower, but it should never be thrown open abruptly.
Step 3: Safe Sample Removal
Once the furnace has reached a manageable temperature, you may open the door fully. Always stand to the side, not directly in front, to avoid the wave of residual heat.
Using long-handled tongs and wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses, carefully reach in and clamp the crucible. Remove it slowly and place it on a heat-proof surface.
Step 4: Preserve the Sample
Immediately transfer the hot crucible containing your sample into a desiccator.
A desiccator is a sealed container with a desiccant (a drying agent) that provides a dry, moisture-free environment. Many materials, especially after ashing, are hygroscopic, meaning they will absorb moisture from the air as they cool. This absorption will alter the sample's final weight and compromise the accuracy of your results.
Common Pitfalls and Why They Matter
Understanding the risks associated with improper shutdown is key to appreciating the correct procedure. Ignoring these steps can have costly consequences.
The Risk of Severe Burns
A muffle furnace looks inert from the outside, but the interior can remain dangerously hot for hours after being turned off. Always assume it is hot until a temperature reading confirms otherwise. Contact burns from the furnace body or the crucible are a serious and common lab injury.
The Danger of Thermal Shock
The refractory ceramic that lines a muffle furnace is an excellent insulator but is brittle. Rapid temperature change is its primary enemy. Subjecting it to thermal shock by opening the door too early will lead to cracks, reducing the furnace's efficiency and lifespan.
Compromising Your Experiment
The entire purpose of a controlled experiment can be undone in the final moments. Allowing a cooled sample to sit on a lab bench exposes it to atmospheric humidity, which can fundamentally alter its mass and invalidate your data. Using a desiccator is non-negotiable for accurate quantitative analysis.
Final Checklist for Safe Shutdown
To ensure you cover all bases, follow this simple checklist based on your primary concern.
- If your primary focus is user safety: Always wait for the furnace display to show a temperature below 200°C and use long tongs and heat-resistant gloves for removal.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Keep the furnace door shut during the initial, high-temperature cooling phase to prevent cracking the insulation.
- If your primary focus is data accuracy: Transfer your crucible directly from the furnace to a desiccator to prevent moisture from corrupting your final sample weight.
Following a disciplined shutdown procedure ensures your safety, protects your equipment, and guarantees the integrity of your hard-earned results.

Summary Table:
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Turn off power | Stop heating and initiate cooling |
| 2 | Cool with door closed | Prevent thermal shock to furnace |
| 3 | Remove sample with tongs | Ensure operator safety |
| 4 | Transfer to desiccator | Avoid moisture absorption for accuracy |
Upgrade Your Lab's Safety and Precision with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Ensure your experiments are safe and accurate—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















