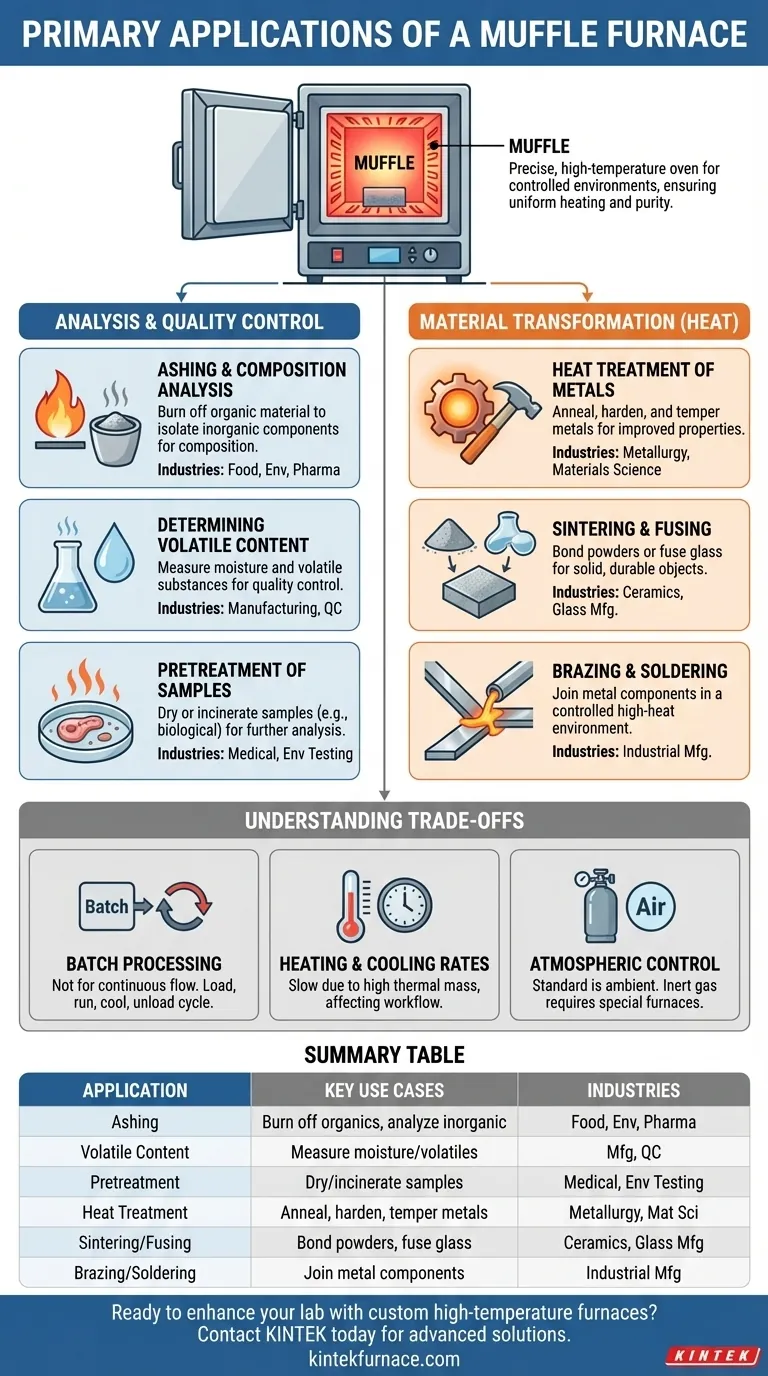
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for a wide range of industrial and laboratory applications. Its primary uses revolve around subjecting materials to precise, extreme heat in a controlled environment, most commonly for chemical analysis (ashing), heat treatment of metals, and testing the properties of materials like ceramics and glass.
A muffle furnace's unique value comes from its "muffle"—an insulated inner chamber that separates the sample from the direct heat source. This design ensures uniform heating and prevents contamination from combustion byproducts, making it essential for processes requiring high purity and temperature accuracy.

Core Applications in Analysis and Quality Control
The most common use for a muffle furnace is in analytical chemistry, where precision and purity are paramount. It serves as a powerful tool for preparing and analyzing samples across numerous industries.
Ashing and Composition Analysis
Ashing is the process of burning off all organic material in a sample to isolate the non-combustible, inorganic components (the ash). This is critical for determining the mineral or filler content in materials.
This technique is fundamental in the food industry for nutritional analysis, in environmental science for analyzing pollutants in soil or water, and in the pharmaceutical industry for quality control.
Determining Volatile Content
By heating a sample to a controlled temperature, a muffle furnace can be used to determine the amount of moisture and other volatile substances.
This is crucial for quality control in manufacturing, ensuring materials meet specific composition requirements before they are used in production.
Pretreatment of Samples
In many fields, including medical and environmental testing, samples must be prepared before they can be analyzed by more sensitive equipment.
A muffle furnace can be used for the pretreatment of samples, such as drying or incinerating biological material, to ready them for subsequent elemental or chemical analysis.
Transforming Materials with Heat
Beyond analysis, muffle furnaces are workhorses in materials science and manufacturing, used to fundamentally change the properties of materials.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Metallurgists use muffle furnaces for various heat treatment processes. These include annealing (to soften metal and improve ductility), hardening (to increase strength), and tempering (to reduce brittleness).
The furnace's precise temperature control is essential for achieving the desired metallurgical properties in steel and other alloys.
Sintering and Fusing
In ceramics, powder metallurgy, and glass manufacturing, sintering is a key process. The furnace heats compacted powders to just below their melting point, causing the particles to bond together into a solid, durable object.
It is also used for glass fusing, where pieces of glass are melted together to create artistic or functional items.
Brazing and Soldering
Muffle furnaces provide the high-heat, controlled environment necessary for brazing and soldering. These processes join metal components together using a filler metal, which is melted in the furnace to create a strong bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a muffle furnace is a specific tool with inherent limitations that are important to understand.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
A muffle furnace is fundamentally a batch-processing tool. You load samples, run a heating cycle, wait for it to cool, and then unload.
This design is not suitable for high-volume, continuous manufacturing lines where materials flow constantly through a process.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The heavy insulation required to reach and maintain high temperatures means that muffle furnaces have significant thermal mass.
Consequently, they can take a long time to heat up and, more importantly, to cool down. This can impact laboratory workflow and overall process efficiency.
Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in an ambient air atmosphere. While the muffle prevents contamination from heating elements or fuel, it does not control the gasses surrounding the sample.
Preventing oxidation or creating a specific chemical reaction requires a more complex and expensive furnace with atmospheric controls that can introduce inert gases like argon or nitrogen.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific goal determines which application of the furnace is most relevant to you.
- If your primary focus is analytical chemistry: You will use it for ashing samples to determine their inorganic content for quality control or regulatory compliance in food, pharma, or environmental labs.
- If your primary focus is materials science: Your main use will be heat-treating metals or sintering ceramics to test and develop materials with new or improved physical properties.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing: You will employ it for specific production steps like brazing components, hardening tools, or fusing glass elements together.
Understanding these core functions allows you to leverage the muffle furnace as a precise tool for material transformation and analysis.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use Cases | Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing and Composition Analysis | Burn off organic material to analyze inorganic content | Food, Environmental, Pharmaceutical |
| Determining Volatile Content | Measure moisture and volatile substances for quality control | Manufacturing, Quality Assurance |
| Pretreatment of Samples | Dry or incinerate samples for further analysis | Medical, Environmental Testing |
| Heat Treatment of Metals | Annealing, hardening, tempering for improved properties | Metallurgy, Materials Science |
| Sintering and Fusing | Bond powders or fuse glass for solid objects | Ceramics, Glass Manufacturing |
| Brazing and Soldering | Join metal components with filler metals in controlled heat | Industrial Manufacturing |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your processes in analysis, heat treatment, and material transformation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















