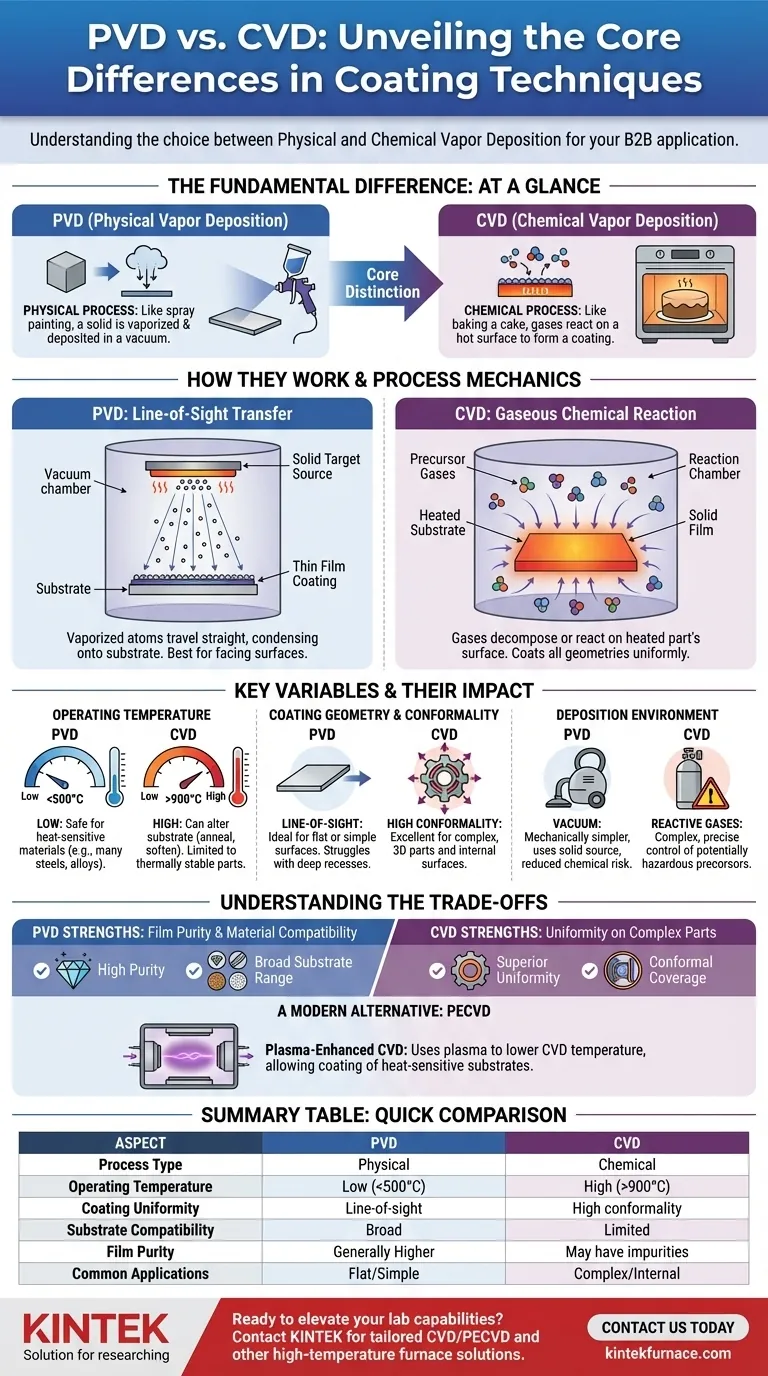
At its core, the difference between Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is how the coating material arrives on a surface. PVD is a physical process, where a solid material is vaporized and deposited in a vacuum, much like spray painting. CVD is a chemical process, where gases react on a hot surface to form the coating, similar to how a cake bakes and forms a crust.
The choice between PVD and CVD hinges on a critical trade-off: PVD provides precision and is safe for heat-sensitive materials due to its lower operating temperatures. In contrast, CVD excels at uniformly coating complex geometries but requires high temperatures that can alter the underlying part.

The Fundamental Difference: Physical vs. Chemical Process
The names themselves reveal the primary distinction. One process is purely physical, involving a change of state, while the other relies on a chemical reaction to create an entirely new material on the substrate surface.
How PVD Works: A Line-of-Sight Transfer
Physical Vapor Deposition is a mechanical transfer process. It typically occurs in a high-vacuum chamber at relatively low temperatures.
The most common methods are sputtering or evaporation. A solid source material (the "target") is bombarded with ions or heated until it vaporizes. These vaporized atoms then travel in a straight line and condense onto the substrate, forming a thin, hard film.
Because the material travels in a straight line, PVD is a line-of-sight process. Surfaces directly facing the source material receive the most coating.
How CVD Works: A Gaseous Chemical Reaction
Chemical Vapor Deposition relies on thermochemical reactions. The process involves introducing volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing the heated substrate.
At high temperatures, typically ranging from several hundred to over a thousand degrees Celsius, these gases decompose or react with each other on the part's surface.
This chemical reaction forms a solid film of the desired coating material. Because the gas surrounds the part, CVD can coat all surfaces, including complex internal geometries, with high conformality.
Key Process Variables and Their Impact
The differences in mechanism lead to significant variations in process requirements, which in turn dictate which method is suitable for a given application.
Operating Temperature
This is the most critical differentiator. PVD processes are "cold", operating at temperatures low enough (typically <500°C) that they do not affect the properties of most steel substrates or other sensitive materials.
CVD processes are "hot", often requiring temperatures above 900°C. This high heat can anneal, soften, or warp the substrate material, limiting its use to components that can withstand such thermal stress without degrading.
Coating Geometry and Conformality
PVD's line-of-sight nature makes it ideal for coating flat or simple surfaces. It struggles to provide a uniform coating inside deep recesses, sharp corners, or on parts with highly complex shapes.
CVD's use of precursor gases allows it to excel in this area. The gas flows around and into the part, ensuring a consistent and uniform coating thickness even in confined areas like the bore of a needle.
Deposition Environment and Precursors
PVD is a mechanically simpler process that uses a solid source material within a vacuum. This reduces the risk of chemical contamination or hazardous byproducts.
CVD is more complex, requiring precise control over precursor gases, which can be toxic, corrosive, or flammable. This introduces more variables and potential chemical hazards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior; they are tools designed for different outcomes. Your choice depends entirely on your project's specific constraints and performance goals.
Film Purity vs. Uniformity
PVD generally produces films of higher purity with fewer defects, as it involves the direct transfer of the source material.
CVD offers superior uniformity (conformality) on complex parts. However, incomplete chemical reactions can sometimes introduce impurities into the coating. The part's surface condition and material can also affect the CVD reaction rate, leading to variations in thickness.
Substrate Material Limitations
The low temperature of PVD makes it compatible with a wide range of materials, including hardened steels, alloys, and some plastics, without altering their fundamental properties.
The high heat of CVD restricts its use to materials that are thermally stable, such as carbides, ceramics, or certain refractory metals. It is generally not suitable for materials that have been heat-treated to achieve specific hardness.
A Modern Alternative: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
To bridge the temperature gap, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) was developed. This process uses plasma to excite the precursor gases, allowing the chemical reaction to occur at much lower temperatures (room temperature to a few hundred degrees Celsius).
PECVD combines the chemical reaction benefits of CVD with a low-temperature process window, making it a powerful alternative for coating heat-sensitive substrates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must first define your most important outcome.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials or achieving the highest film purity: PVD is typically the superior choice due to its low-temperature, physical deposition mechanism.
- If your primary focus is achieving a perfectly uniform coating on complex, three-dimensional parts: CVD offers unmatched conformality, provided the substrate can withstand the high processing temperatures.
- If your primary focus is balancing CVD's uniform coverage with a need for lower temperatures: You should investigate Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) as a viable and effective alternative.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between the process, the material, and the desired geometry is the key to mastering thin-film coating technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (vaporization and deposition) | Chemical (gas reaction on surface) |
| Operating Temperature | Low (<500°C), safe for heat-sensitive materials | High (>900°C), can alter substrate |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight, less uniform on complex shapes | High conformality, uniform on all surfaces |
| Substrate Compatibility | Broad (e.g., steels, alloys, some plastics) | Limited to thermally stable materials (e.g., carbides, ceramics) |
| Film Purity | Generally higher purity with fewer defects | May have impurities from incomplete reactions |
| Common Applications | Flat or simple surfaces, precision coatings | Complex geometries, internal surfaces |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's capabilities with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse labs with tailored furnace systems. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're working with PVD, CVD, or other coating techniques, we can help optimize your processes for better performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific applications and drive innovation in your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications



















