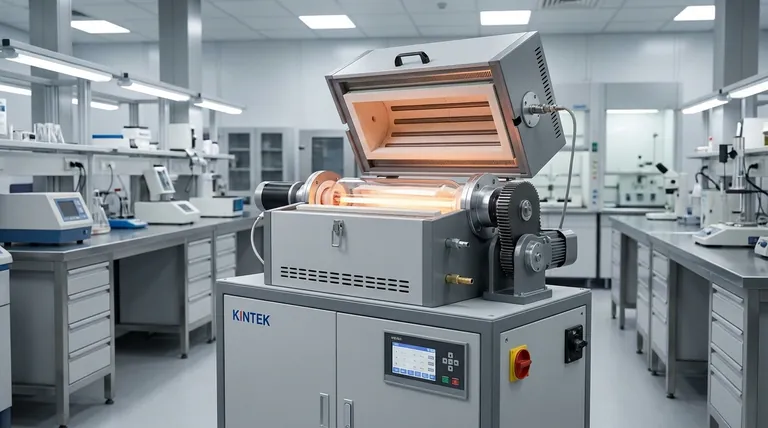
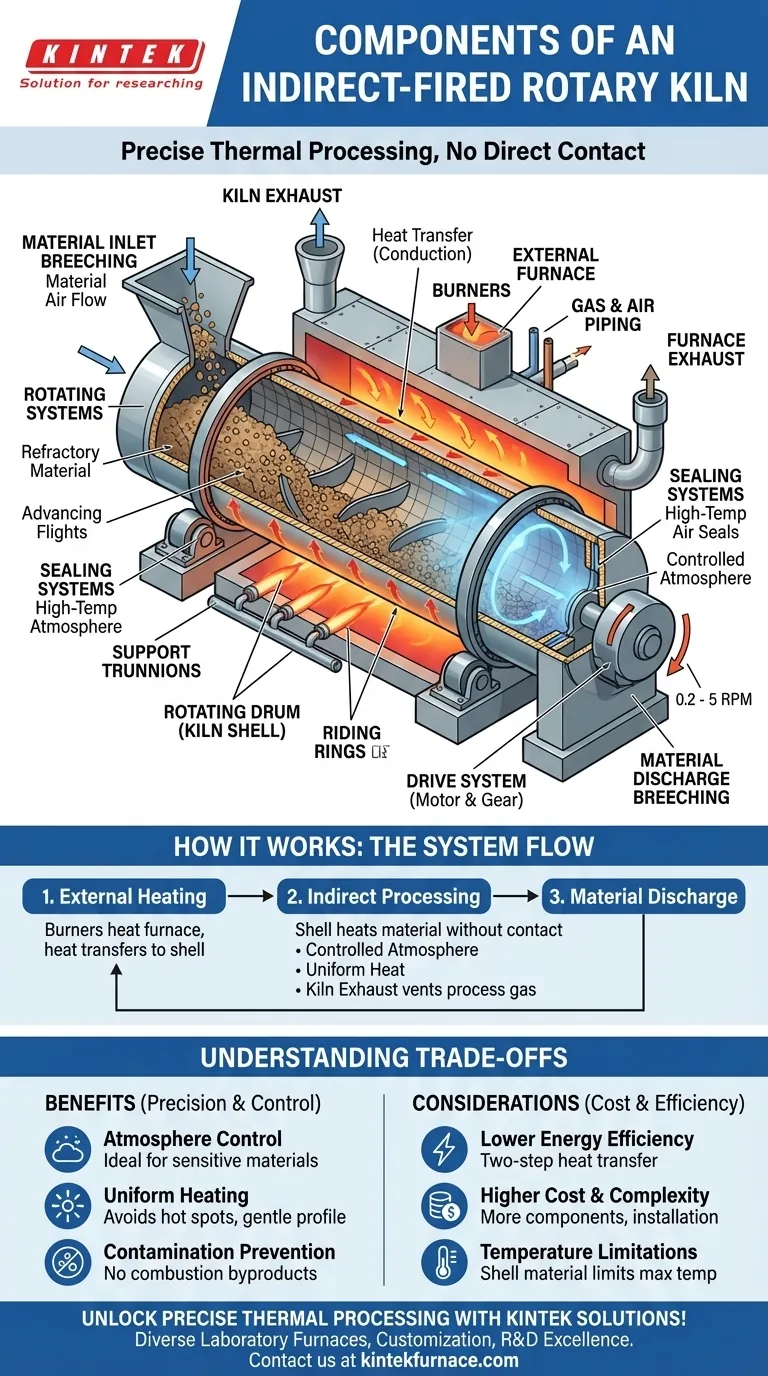
At its core, an indirect-fired rotary kiln is a system designed for precise thermal processing without direct contact between the material and the heat source. The main components include the rotating kiln drum, an external furnace that encloses it, a drive system, seals to control the internal atmosphere, and systems for material feed and discharge. This design is fundamentally different from direct-fired kilns, where combustion gases flow directly over the material.
The defining feature of an indirect-fired rotary kiln is not just its parts, but its design philosophy: isolating the material within a rotating shell while heating it externally. This allows for unparalleled control over the processing atmosphere, a capability essential for sensitive materials.

How the System Works: A Functional Breakdown
To understand an indirect-fired kiln, you must see its components as an integrated system working to achieve a specific thermal and chemical goal.
The Rotating Drum (Kiln Shell)
The kiln shell is the cylindrical heart of the system where the material is processed. It is mounted at a slight angle, typically between 1% and 4%, to facilitate the steady movement of material from the inlet to the discharge end as it rotates.
Inside, the shell is often lined with a refractory material to protect the metal structure from extreme temperatures. It can also be fitted with advancing flights or lifters to tumble the material, ensuring it is heated evenly as it makes contact with the hot inner wall of the shell.
The External Furnace and Burner System
This is the key differentiator. The entire rotating drum is enclosed within a stationary external furnace.
Burners and associated gas and air piping are mounted on this outer furnace. They heat the outside of the rotating kiln shell. Heat is then transferred by conduction through the shell wall to the material inside. This indirect method prevents any contamination from combustion byproducts.
The Drive and Support System
The massive kiln drum is mounted on two or more riding rings, which rest on support trunnions or wheels.
A drive system, typically consisting of an electric motor and a large gear or chain sprocket, rotates the drum at a slow, controlled speed, usually between 0.2 and 5 revolutions per minute (rpm). This rotation speed is a critical process parameter that dictates the material's retention time inside the kiln.
The Sealing System
Because controlling the internal atmosphere is often the primary reason for choosing an indirect kiln, the sealing system is critical.
High-temperature air seals, often of a spring or leaf design, are installed at both the material inlet and discharge ends. These seals prevent uncontrolled air from entering the kiln and allow for the maintenance of an inert or specialized gas environment within the processing drum.
Material Handling and Exhaust
Material enters the kiln through the inlet breeching and exits via the discharge breeching.
The kiln exhaust vents the gases and moisture released from the material itself during processing. This is separate from the furnace exhaust, which vents the combustion gases from the external heating system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an indirect-fired kiln involves accepting a specific set of engineering trade-offs. Its benefits are significant, but they come at a cost.
Atmosphere Control vs. Energy Efficiency
The primary benefit of an indirect kiln is absolute control over the processing atmosphere, making it ideal for products that are sensitive to oxygen or combustion byproducts.
However, this design is typically less energy-efficient than a direct-fired kiln. Heat must first transfer to the kiln shell and then conduct through it to the material, a two-step process that introduces thermal losses.
Precision vs. Cost and Complexity
The external furnace and robust sealing systems make indirect-fired kilns more mechanically complex and expensive to build, install, and maintain.
The trade-off is superior temperature control. External heating provides a more uniform and gentle heat profile, avoiding the intense hot spots that can occur with direct flame impingement in direct-fired systems.
Material Limitations
In an indirect kiln, the maximum achievable process temperature is limited by the metallurgical properties of the rotating shell itself, as it must withstand both the high heat and the mechanical stresses of rotation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific processing objective dictates whether an indirect-fired kiln is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials: An indirect-fired kiln is essential to protect your product from combustion gases and maintain a controlled, inert atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is calcining or roasting minerals without chemical alteration: The indirect method is superior for applications like converting gypsum to plaster or processing bauxite and silica sand.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise, uniform heating: The indirect method offers unparalleled temperature control and uniformity, which is critical for high-value or thermally sensitive products.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput at the lowest capital cost: A direct-fired kiln may be more suitable, provided your material is not harmed by direct contact with flue gases.
Understanding these core components and their interplay empowers you to select the precise thermal processing tool for your specific objective.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Drum (Kiln Shell) | Houses material for processing; rotates to move material | Refractory lining, advancing flights for even heating |
| External Furnace and Burner System | Heats the kiln shell externally | Burners, gas/air piping; prevents contamination |
| Drive and Support System | Rotates the drum at controlled speeds | Electric motor, riding rings, trunnions; 0.2-5 rpm |
| Sealing System | Controls internal atmosphere | High-temperature air seals; maintains inert gas environment |
| Material Handling and Exhaust | Manages material input/output and gas venting | Inlet/discharge breeching; separate kiln and furnace exhausts |
Unlock precise thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, enhanced by deep customization capabilities to meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our indirect-fired rotary kilns can optimize your material processing with superior atmosphere control and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















