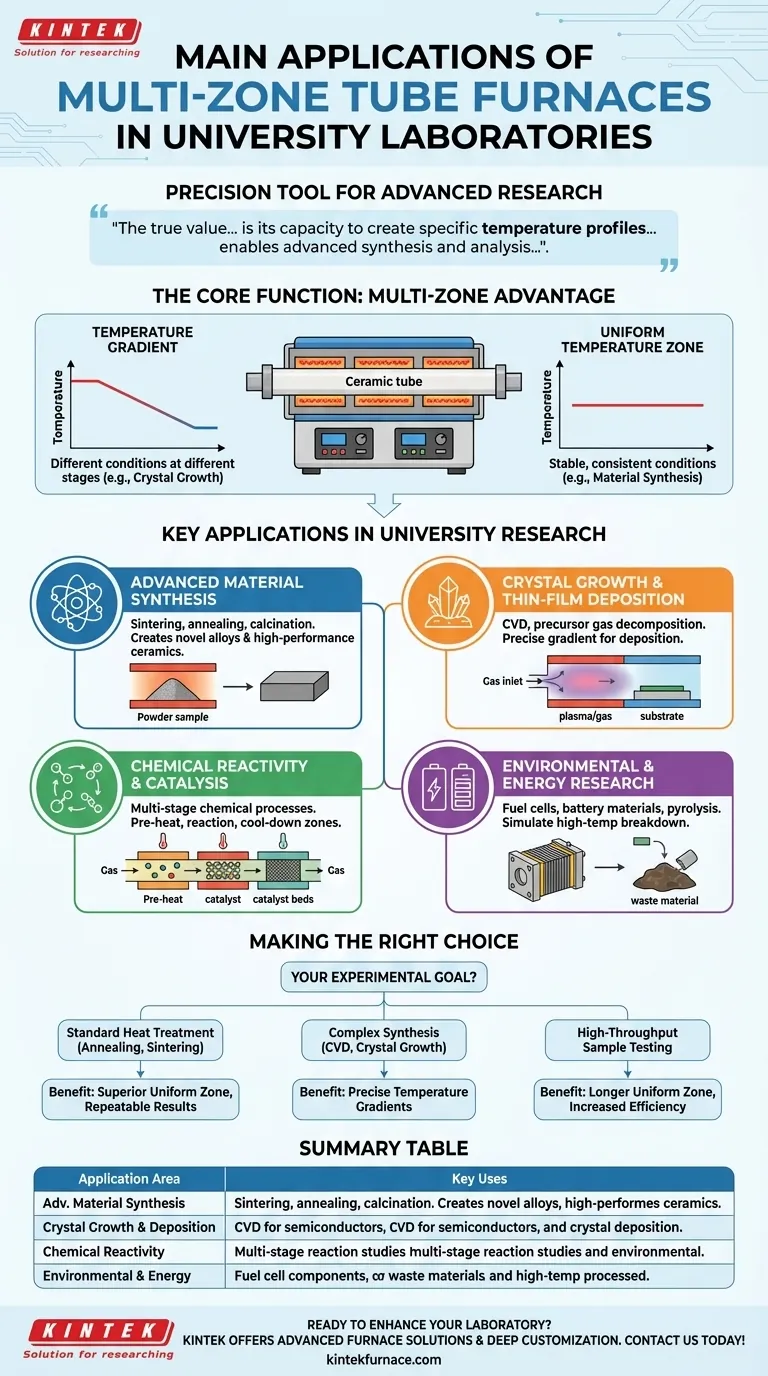
In a university laboratory, a multi-zone tube furnace serves as a precision tool for a wide range of advanced research applications. Its primary uses span material science, chemical synthesis, and energy research, where precise control over temperature across a sample's length is not just beneficial, but essential for achieving desired outcomes like crystal growth, thin-film deposition, and complex chemical reactions.
The true value of a multi-zone tube furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to create specific temperature profiles. This control—either a highly uniform temperature zone or a precise temperature gradient—is what enables advanced synthesis and analysis that single-zone furnaces cannot accomplish.

The Core Function: Precision Thermal Processing
A tube furnace is fundamentally a high-temperature heating device. However, the "multi-zone" capability elevates it from a simple oven to a sophisticated scientific instrument.
What is a Tube Furnace?
A tube furnace uses heating elements surrounding a ceramic or quartz tube. This tube acts as a reaction chamber, isolating the sample from the outside environment.
By controlling the atmosphere inside the tube—whether it's a vacuum, an inert gas like argon, or a reactive gas—researchers can perform thermal processes without unwanted contamination or oxidation.
The "Multi-Zone" Advantage: Gradients and Uniformity
The key innovation of a multi-zone furnace is its independent heating zones, typically two or three, arranged along the length of the tube. This allows for two critical functionalities.
First, it enables the creation of a temperature gradient, where each end of the furnace is held at a different temperature. This is crucial for processes that require different thermal conditions at different stages.
Second, by working in concert, the zones can create a longer and more stable uniform temperature zone in the center of the furnace than a single-zone furnace could achieve. This ensures larger samples or multiple small samples are processed under identical conditions.
Key Applications in University Research
The ability to manipulate the temperature profile makes multi-zone furnaces indispensable for several cutting-edge research areas.
Advanced Material Synthesis
Processes like sintering, annealing, and calcination are fundamental to materials science. They are used to create novel alloys, high-performance ceramics, and precisely structured powders.
A multi-zone furnace's long, uniform temperature zone ensures that these heat treatments are applied consistently across the entire sample, preventing defects and ensuring reliable material properties.
Crystal Growth and Thin-Film Deposition
This is where temperature gradients become critical. In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), a precursor gas is introduced into the tube.
A multi-zone furnace can create a hot zone to decompose the gas and a cooler zone downstream for the desired material to deposit as a thin film or crystal. This precise control is essential for manufacturing semiconductors and other electronic materials.
Chemical Reactivity and Catalysis Studies
Researchers can use different zones to simulate multi-stage chemical processes. The first zone might pre-heat a reactant gas, the central zone hosts the catalytic reaction at a specific temperature, and a final zone can cool the products.
This allows for detailed study of reaction kinetics and catalyst performance under highly controlled conditions.
Environmental and Energy Research
Multi-zone furnaces are used to develop materials for new energy technologies, such as synthesizing components for solid-oxide fuel cells or advanced batteries.
They are also used in environmental science to simulate the high-temperature breakdown of pollutants or to convert waste materials into safer, less toxic substances through processes like pyrolysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a multi-zone furnace is not always the necessary choice. Understanding its limitations is key to proper application.
Complexity and Cost
The added controllers and power electronics make a multi-zone furnace significantly more expensive and complex to operate than a single-zone model. Programming and stabilizing a specific temperature gradient requires expertise and time.
Sample Size Limitations
Like all lab-scale tube furnaces, these are designed for processing small samples, typically for research and development purposes. They are not intended for high-throughput or large-scale industrial production.
Atmosphere Control is a Separate System
The furnace provides the heat, but not the atmosphere. The researcher is responsible for designing and implementing the system of vacuum pumps, gas lines, and flanges needed to create the controlled environment inside the tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Your specific experimental goal should dictate your need for a multi-zone furnace.
- If your primary focus is standard heat treatment (annealing, sintering): A multi-zone furnace provides a superior uniform temperature zone, leading to more repeatable results, especially for larger samples.
- If your primary focus is complex synthesis (CVD, crystal growth): A multi-zone furnace is often essential for creating the precise temperature gradients required for these processes.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput sample testing: The longer uniform zone allows you to process more samples simultaneously under identical conditions, increasing efficiency.
Ultimately, the multi-zone tube furnace is a cornerstone of modern materials research, empowering scientists to build new materials from the atom up.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Sintering, annealing, calcination for alloys and ceramics |
| Crystal Growth & Thin-Film Deposition | CVD for semiconductors and electronic materials |
| Chemical Reactivity & Catalysis | Multi-stage reaction studies and catalyst performance |
| Environmental & Energy Research | Fuel cell components, battery materials, pyrolysis |
Ready to enhance your university laboratory with precision thermal processing? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for materials science, chemistry, and energy research. Our product line, including Multi-Zone Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can drive your research forward with superior temperature control and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How does a multi-zone tube furnace achieve precise temperature gradient control? Master MoS2 Isotope Monolayer Synthesis
- What are the benefits of integrating multiple heating zones in a tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control
- What are the advantages of individually temperature-controlled zones in multi-zone furnaces? Unlock Precision Thermal Gradients
- How do multi zone tube furnaces improve laboratory efficiency? Boost Throughput with Parallel Processing
- What advantages do multi zone tube furnaces offer for chemical reaction studies? Achieve Precise Thermal Control



















