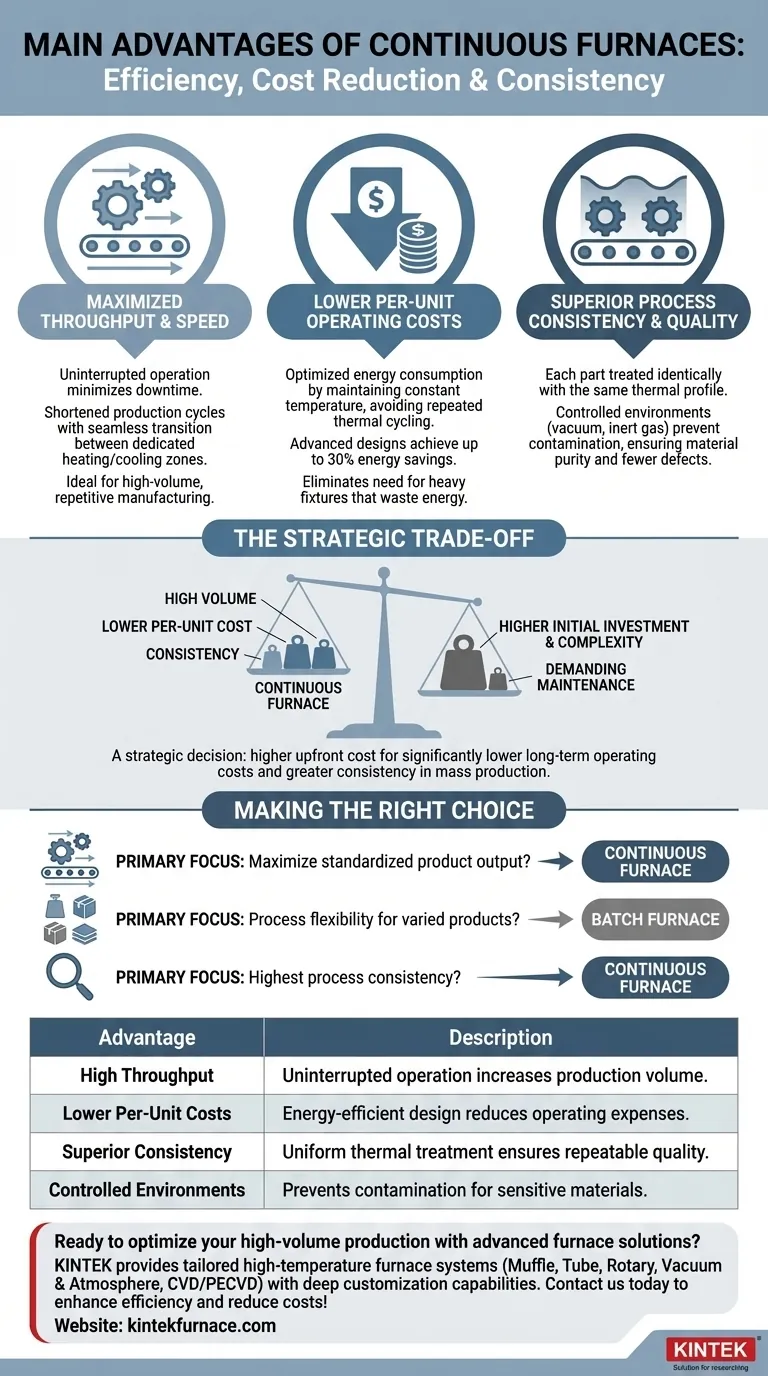
The primary advantages of a continuous furnace center on high-volume production efficiency, lower per-unit operating costs, and superior process consistency. Unlike batch furnaces that process materials in discrete loads, a continuous furnace moves products through various heating and cooling zones in an uninterrupted flow, making it ideal for large-scale, repetitive manufacturing.
While continuous furnaces provide unmatched throughput and energy efficiency for mass production, their value is directly tied to process stability. They represent a strategic trade-off: a higher initial investment in exchange for significantly lower operating costs and greater consistency on a per-unit basis.

Maximizing Throughput and Production Speed
The core design principle of a continuous furnace is to eliminate the start-and-stop nature of batch processing, which unlocks significant gains in production volume.
The Power of Continuous Operation
A continuous furnace operates without interruption. This design minimizes downtime associated with loading, unloading, heating up, and cooling down an entire chamber, maximizing a facility's total throughput.
Shortened Production Cycles
These systems are engineered with dedicated heating and cooling sections. As parts move through the furnace, they transition seamlessly between zones, which dramatically reduces the total time required to process each individual item.
Driving Down Per-Unit Operating Costs
For a consistent product line, the operational model of a continuous furnace is inherently more efficient than its batch counterpart.
Optimizing Energy Consumption
Because the furnace maintains a constant temperature in its various zones, it avoids the energy-intensive cycle of repeatedly heating a large thermal mass from a lower temperature. Furthermore, many designs eliminate the need for heavy fixtures like baskets or racks, which would otherwise absorb and waste thermal energy.
Some advanced designs, such as atmosphere furnaces, can achieve up to 30% energy savings compared to conventional methods by optimizing heat retention and distribution.
Enhancing Process Consistency
A continuous furnace treats every part identically. Each item is individually exposed to the same thermal profile as it moves through the system, ensuring a level of uniformity and repeatability that is difficult to achieve in a large batch process.
Controlled Environments for Purity
Many continuous furnaces operate with a controlled environment, such as a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere. This prevents oxidation, contamination, and other undesirable chemical reactions, leading to improved material properties and fewer rejected parts. This is critical in sensitive industries where cleanliness and material integrity are paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Continuous vs. Batch
Choosing a continuous furnace is a significant engineering and financial decision. Its advantages are clear, but they come with important trade-offs that make it unsuitable for certain applications.
Higher Initial Investment and Complexity
Continuous furnaces are generally more complex and carry a significantly higher upfront cost for installation compared to batch furnaces. Their intricate design requires more sophisticated control systems and a larger physical footprint.
Demanding Maintenance Requirements
The continuous nature of these systems means that any downtime is extremely costly. They demand a rigorous and frequent maintenance schedule to ensure optimal performance and prevent unplanned production stoppages.
When a Batch Furnace Is Superior
A batch furnace remains the better choice for operations that require flexibility. If you need to process a wide range of products, run different cycle times, or require varying temperatures, a batch furnace's ability to be easily reconfigured between loads is a decisive advantage. They are also the clear choice for smaller production runs or when initial capital cost is the primary constraint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision between a continuous and a batch furnace hinges entirely on your specific production goals and operational realities.
- If your primary focus is maximizing output for a standardized product: A continuous furnace is purpose-built for this role, delivering the lowest cost-per-unit at scale.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility for varied products or batch sizes: A batch furnace offers the versatility to adapt to changing requirements with a much lower initial investment.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest level of process consistency in mass production: The repeatable thermal treatment of a continuous furnace provides unmatched quality control.
Ultimately, the best choice aligns the furnace's fundamental operational strengths with your specific production volume and process needs.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Throughput | Uninterrupted operation increases production volume by minimizing downtime. |
| Lower Per-Unit Costs | Energy-efficient design reduces operating expenses for large-scale runs. |
| Superior Consistency | Uniform thermal treatment ensures repeatable quality and fewer defects. |
| Controlled Environments | Vacuum or inert atmospheres prevent contamination for sensitive materials. |
Ready to optimize your high-volume production with advanced furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and reduce costs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency



















