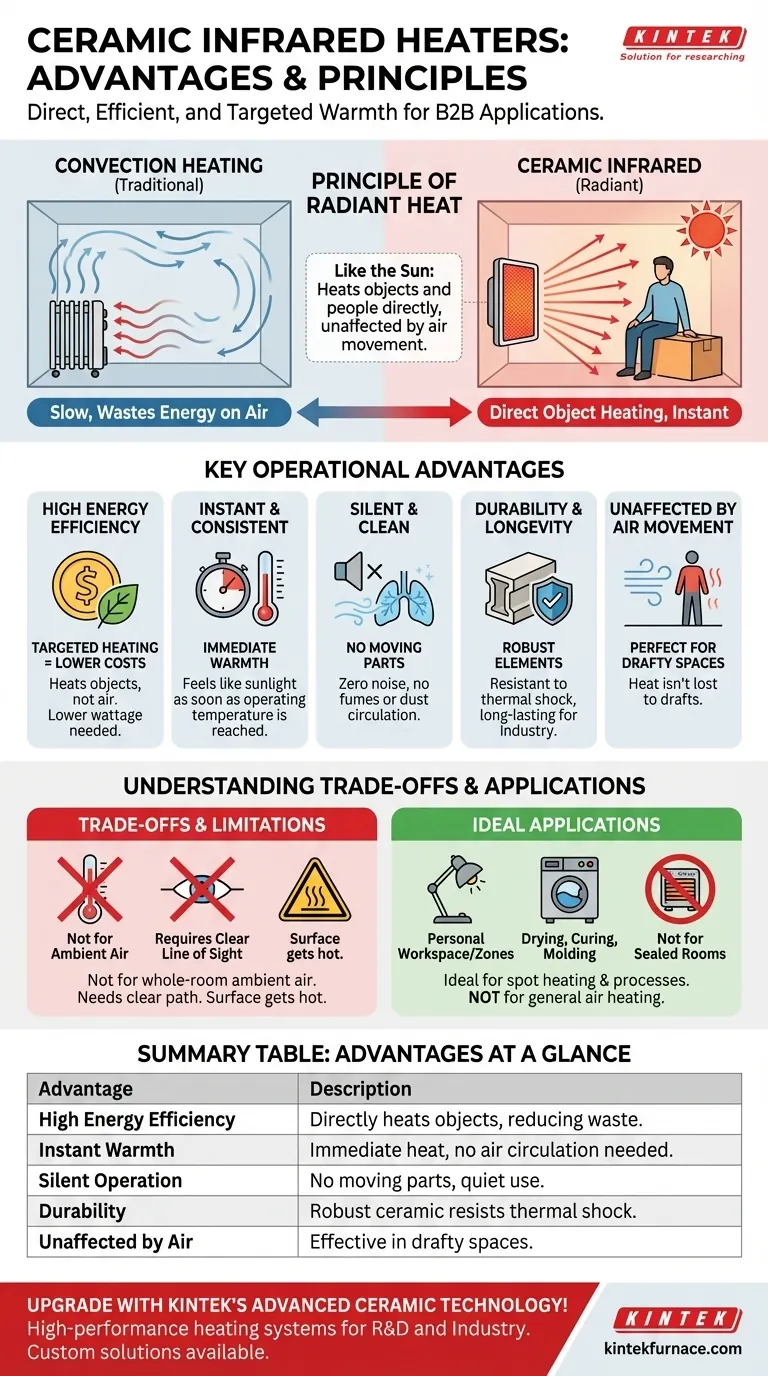
At their core, ceramic infrared heaters provide a distinct advantage by fundamentally changing how heat is delivered. Instead of slowly warming the air in a room, they emit infrared waves that directly heat objects and people in their path, resulting in near-instantaneous warmth, high energy efficiency, and a safer operational profile.
The true advantage of ceramic infrared technology lies not just in its efficiency, but in its method. By delivering radiant heat directly to you and your surroundings, it avoids wasting energy on heating the air, making it a targeted and effective solution for specific zones.

The Principle of Radiant Heat: Why It Matters
The primary benefits of ceramic infrared heaters stem from their use of radiant heat, which operates differently from the convection heat used by most traditional space heaters.
Direct Object Heating vs. Air Convection
A conventional heater warms the air, which then circulates to transfer warmth. This process, known as convection, is slow and inefficient in large or drafty spaces.
Infrared heaters work like the sun. They emit infrared radiation that travels unimpeded through the air until it is absorbed by solid objects—like you, the furniture, or the floor—warming them directly.
Immediate and Consistent Warmth
Because radiant heat doesn't rely on air circulation, you feel its effects almost instantly. As soon as the ceramic element reaches its operating temperature, it begins projecting warmth to anything in its line of sight.
Unaffected by Air Movement
In spaces like garages, workshops, or large open-plan offices, convection heat is easily lost to drafts or simply dissipates. Infrared heat is unaffected by air currents, making it exceptionally effective for spot heating in these challenging environments.
Key Operational Advantages
The unique heating method of ceramic infrared elements translates into several practical benefits for both commercial and personal use.
High Energy Efficiency
By heating only the necessary objects and zones, very little energy is wasted. This targeted approach means a lower-wattage infrared heater can often provide the same level of comfort as a higher-wattage convection heater, leading to lower electricity consumption.
Clean and Silent Operation
Ceramic infrared heaters have no moving parts like fans, so they operate in complete silence. Furthermore, because they do not burn fuel or circulate air with dust and allergens, they produce no toxic emissions or fumes, ensuring better indoor air quality.
Durability and Longevity
The ceramic elements used in these heaters are robust and resistant to thermal shock. This inherent durability makes them a long-lasting heating solution, particularly in demanding industrial applications like drying, curing, or molding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, ceramic infrared technology is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Not Ideal for Raising Ambient Air Temperature
The core strength of an infrared heater is also its main trade-off. It is designed to heat objects, not the air itself. If your goal is to raise the overall ambient temperature of a small, well-insulated room, a traditional convection heater may feel more effective.
Requires a Clear Line of Sight
Infrared radiation travels in straight lines. Any physical obstruction between the heater and the target object will block the heat, creating "shadows." This requires careful placement to ensure effective coverage of the desired zone.
Surface Temperature Considerations
While modern units are equipped with many safety features, the emitting surface of the heater can become very hot. Proper clearance from combustible materials and caution during operation are always necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To leverage the advantages of a ceramic infrared heater, you must match the technology to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is heating a personal workspace or a specific zone: Ceramic infrared is the ideal choice for delivering fast, efficient, and direct warmth exactly where you need it.
- If your primary focus is an industrial process like drying or curing: The clean, controllable, and intense radiant heat is perfectly suited for applications requiring precise thermal energy without air disturbance.
- If your primary focus is raising the overall air temperature in a sealed room: A convection-based heater may be a more suitable tool for achieving a uniform ambient temperature.
Ultimately, choosing the right heater is about understanding that you are not just buying a device, but selecting the right method for transferring energy.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| High Energy Efficiency | Directly heats objects, reducing wasted energy and lowering electricity costs. |
| Instant and Consistent Warmth | Provides immediate heat without relying on air circulation, ideal for spot heating. |
| Silent and Clean Operation | No moving parts or emissions, ensuring quiet use and better indoor air quality. |
| Durability and Longevity | Robust ceramic elements resist thermal shock, suitable for demanding applications. |
| Unaffected by Air Movement | Effective in drafty or large spaces, as heat is not lost to air currents. |
Upgrade your heating solutions with KINTEK's advanced ceramic infrared technology! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories and industries with high-performance heating systems. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and process needs. Experience enhanced efficiency and reliability—contact us today to discuss how we can tailor our solutions for you!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















