At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process that transforms gases into a solid, high-purity thin film on a surface. The fundamental steps involve introducing reactive precursor gases into a chamber, using energy like heat to trigger a chemical reaction on or near a substrate, and allowing the resulting solid material to deposit and build up as a film, atom by atom. Unwanted chemical by-products are then removed as gases.
Chemical Vapor Deposition is not a single action but a highly controlled sequence of physical transport and chemical reactions. Mastering CVD means mastering the flow of gases, the application of energy, and the removal of waste to precisely engineer a solid material from a gaseous state.

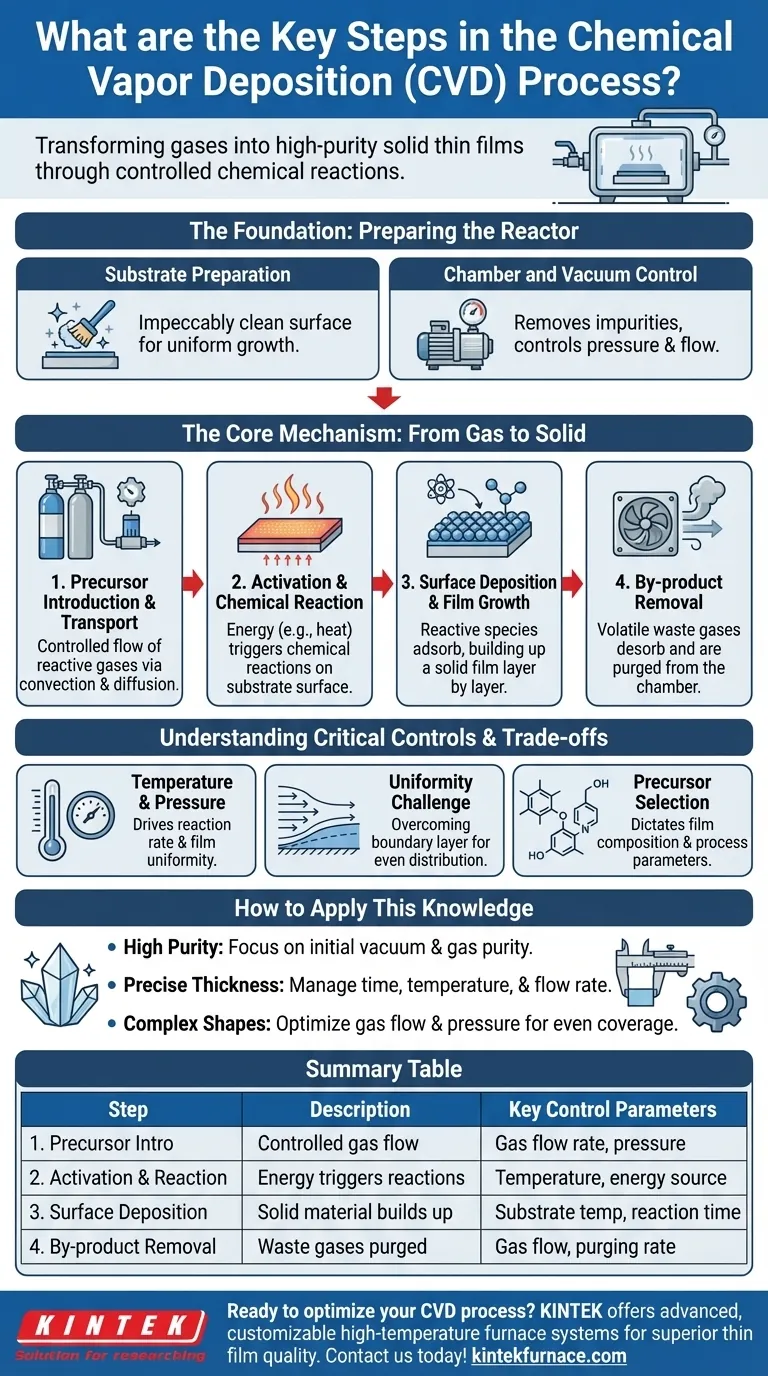
The Foundation: Preparing the Reactor
Before any deposition can begin, the environment must be meticulously prepared. This stage is critical for ensuring the purity and quality of the final film.
Substrate Preparation
The process starts with the substrate, which is the material to be coated. This surface must be impeccably clean, as any contaminants or imperfections can disrupt the uniform growth of the film.
Chamber and Vacuum Control
The entire process takes place in a sealed reaction chamber. Air is pumped out to create a vacuum, which serves two purposes: it removes atmospheric impurities that could contaminate the film and allows for precise control over the pressure and flow of the precursor gases.
The Core Mechanism: From Gas to Solid
This is the heart of the CVD process, where the controlled transformation from gas to solid film occurs in a precise sequence.
Step 1: Precursor Introduction and Transport
Once the chamber is prepared, one or more precursor gases are introduced in a controlled flow. These gases contain the atoms required for the final film. They are transported toward the substrate through physical processes like convection (the bulk movement of the gas) and diffusion (movement from high to low concentration).
Step 2: Activation and Chemical Reaction
The chamber is heated to a specific temperature, providing the energy needed to "activate" the precursors. This energy causes the gas molecules to undergo chemical reactions. These reactions can occur in the gas phase above the substrate or, more importantly, directly on the hot substrate surface itself.
Step 3: Surface Deposition and Film Growth
The chemical reactions produce the desired solid material as a reactive species. This species adsorbs (sticks) to the substrate's surface and arranges itself into a stable, solid structure. The film grows layer by layer, sometimes atom by atom, resulting in a highly ordered and dense coating.
Step 4: By-product Removal
The chemical reactions also create volatile by-products that are not part of the film. These gaseous waste products desorb (detach) from the surface and are continuously flushed out of the chamber by the gas flow, a process often called purging. This prevents them from interfering with the film's growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Controls
The quality of a CVD film is not accidental; it is the direct result of managing a delicate balance of competing factors.
The Role of Temperature and Pressure
Temperature is the primary driver of the chemical reaction rate. Too low, and the reaction won't occur; too high, and unwanted gas-phase reactions can create particles that rain down as defects on the film. Pressure influences the concentration of precursors and the distance they can travel, affecting film uniformity.
The Challenge of Uniformity
A key goal of CVD is to create a film with the same thickness everywhere. However, a "boundary layer" of slower-moving gas naturally forms just above the substrate. Ensuring that fresh precursor gases can diffuse evenly through this layer to all parts of the substrate is a significant engineering challenge.
Precursor Selection is Paramount
The choice of precursor gases dictates everything. It determines the composition of the final film (e.g., metal, ceramic, diamond), the required process temperature, and the nature of the volatile by-products that must be removed.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding these steps allows you to troubleshoot the process and tailor it to specific outcomes.
- If your primary focus is achieving high purity: Your control over the initial vacuum and the purity of your precursor gases is the most critical factor.
- If your primary focus is precise thickness control: You must meticulously manage reaction time, substrate temperature, and the flow rate of the precursor gases.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex, three-dimensional shape: The gas-phase nature of CVD is an advantage, but you must optimize gas flow and pressure to ensure reactants reach all surfaces evenly.
By viewing CVD as a controllable sequence of transport and reaction, you can move from simply following a recipe to truly engineering advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Step | Description | Key Control Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Precursor Introduction and Transport | Controlled flow of reactive gases into the chamber. | Gas flow rate, pressure |
| 2. Activation and Chemical Reaction | Energy application (e.g., heat) triggers reactions on the substrate. | Temperature, energy source |
| 3. Surface Deposition and Film Growth | Solid material adsorbs and builds up layer by layer. | Substrate temperature, reaction time |
| 4. By-product Removal | Volatile waste gases are purged from the chamber. | Gas flow, purging rate |
Ready to optimize your CVD process with precision-engineered solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace systems, including CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements, delivering superior thin film quality and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our products can enhance your material engineering projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth



















