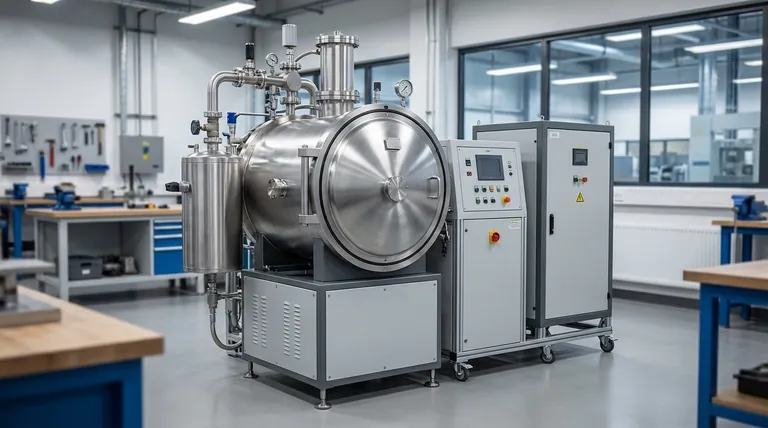
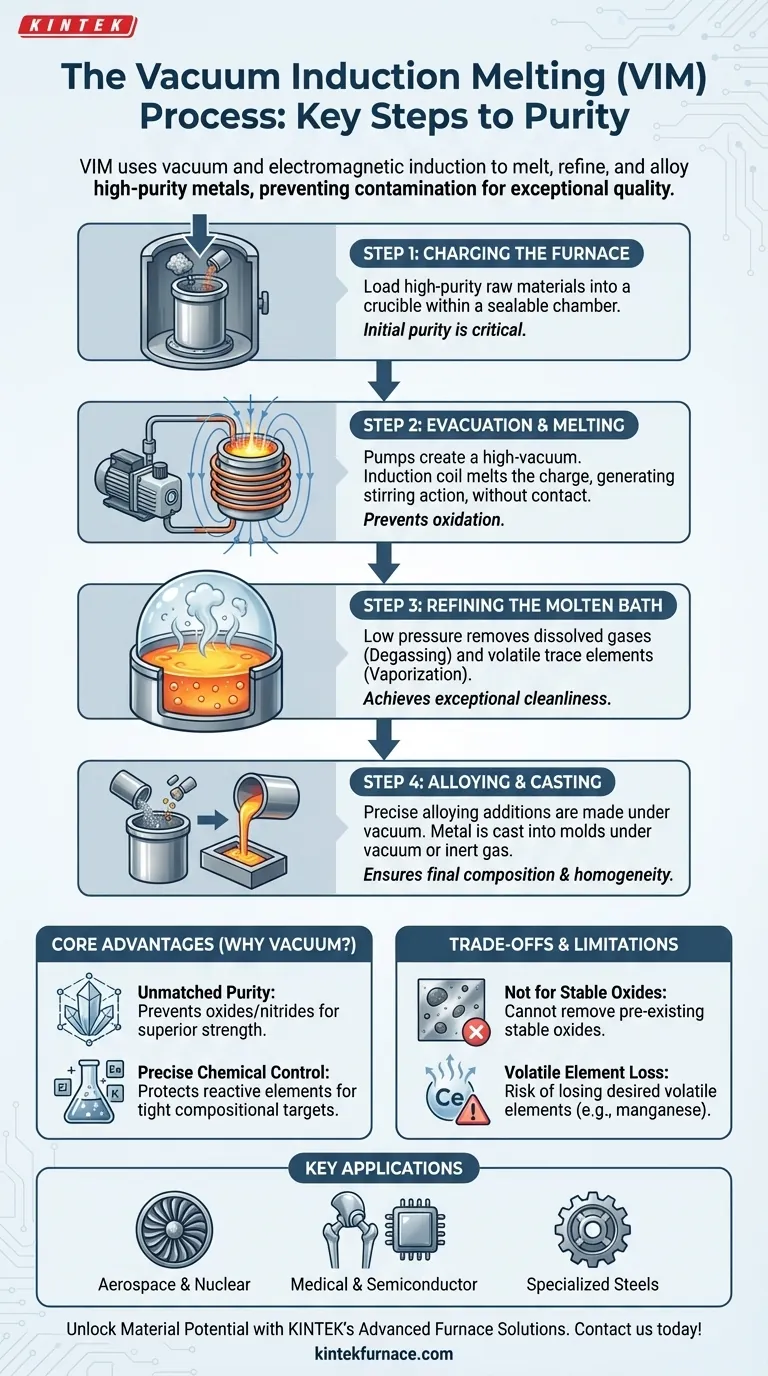
In short, the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process involves loading high-purity raw materials into a vacuum chamber, melting them using electromagnetic induction, refining the molten metal to remove gases and volatile elements, and precisely adjusting the final chemical composition before casting. This entire sequence is performed in a tightly controlled vacuum to prevent contamination from the atmosphere.
The core purpose of VIM is not just to melt metal, but to achieve an exceptional level of purity and chemical precision. By performing the process in a vacuum, it eliminates atmospheric contamination, which is the primary source of impurities in conventional melting.

A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the VIM Process
To truly understand VIM, it's best to view it as a sequence of deliberate stages, each designed to protect and enhance the quality of the final alloy.
Step 1: Charging the Furnace
The process begins by loading a crucible with a "charge" of carefully selected raw materials. Because VIM is not effective at removing certain stable impurities, the initial purity of the raw materials is critical. The charge is placed inside a large, sealable chamber.
Step 2: Evacuation and Melting
Once the chamber is sealed, powerful pumps remove the air to create a high-vacuum environment. This prevents the hot, reactive metal from reacting with oxygen and nitrogen in the air.
With the vacuum established, power is sent to an induction coil that surrounds the crucible. This generates a powerful magnetic field that induces electrical currents within the metal charge, rapidly heating and melting it without any direct contact. This induction also creates a natural stirring action, which helps ensure the melt is uniform in temperature and composition.
Step 3: Refining the Molten Bath
This is where the vacuum environment performs its most important work. The low pressure dramatically lowers the boiling point of certain elements and compounds.
This vacuum refining achieves two goals:
- Degassing: Dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen, which can cause defects and embrittlement, are pulled out of the liquid metal.
- Vaporization: Undesirable trace elements with high vapor pressure (like lead, bismuth, and cadmium) are boiled off and removed.
Step 4: Alloying and Casting
With the base melt purified, final alloying additions are introduced into the furnace through a vacuum-sealed charging system. This allows for extremely precise control over the final chemistry, especially for reactive elements like titanium and aluminum that would be lost in an air melt.
After a final stir to ensure homogeneity, the molten metal is poured, or "tapped," into molds. This is also done under vacuum or in a backfilled inert gas (like argon) atmosphere to prevent any re-contamination before the metal solidifies.
Why Use a Vacuum? The Core Advantages of VIM
Using a vacuum is more complex and expensive than melting in air, but it's essential for producing high-performance alloys for demanding applications.
Unmatched Purity
The primary benefit is preventing the formation of oxides and nitrides. These non-metallic inclusions act as stress points within the final material, reducing its strength, ductility, and fatigue life. VIM produces exceptionally "clean" metal.
Precise Chemical Control
In air melting, highly reactive but essential alloying elements like titanium and aluminum can burn off unpredictably. The vacuum in VIM protects these elements, allowing metallurgists to hit extremely tight compositional targets, which is critical for the performance of superalloys and other advanced materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, VIM is not a universal solution. It has specific limitations that are important to recognize.
Not Ideal for Stable Oxide Removal
The vacuum is excellent for removing gases and volatile elements, but it cannot remove stable oxides (like silica or alumina) that were present in the initial raw materials. This is why starting with high-purity inputs is non-negotiable for VIM. For removing these, a secondary process like electroslag remelting (ESR) is often required.
Loss of Desired Volatile Elements
The same principle that removes undesirable volatile impurities can also remove desirable alloying elements with high vapor pressure, such as manganese. The process parameters must be carefully controlled to minimize the loss of these essential elements during the refining stage.
Key Applications for VIM Technology
The decision to specify a VIM-produced material is driven by the need for ultimate performance and reliability.
- If your primary focus is mission-critical components (Aerospace & Nuclear): VIM is chosen for its ability to produce clean superalloys and reactive metal alloys with the superior fatigue life and high-temperature strength these applications demand.
- If your primary focus is high-purity materials (Medical & Semiconductor): The process is essential for creating biocompatible implants and materials with specific electronic properties, free from detrimental impurities that could cause failure.
- If your primary focus is specialized tool and stainless steels: VIM is used when standard air-melted grades cannot meet extreme requirements for performance, cleanliness, or specific mechanical properties.
Ultimately, choosing Vacuum Induction Melting is a deliberate engineering decision for applications where material integrity and chemical precision are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Charging the Furnace | Load high-purity raw materials into a crucible to ensure initial cleanliness. |
| 2 | Evacuation and Melting | Create a vacuum and use induction heating to melt metal without atmospheric contamination. |
| 3 | Refining the Molten Bath | Remove gases and volatile impurities through degassing and vaporization under vacuum. |
| 4 | Alloying and Casting | Add precise alloying elements and cast under vacuum or inert gas to prevent re-contamination. |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Materials with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for precision and purity. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you're in aerospace, medical, semiconductor, or tool steel industries.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your VIM processes and deliver superior results for your mission-critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















