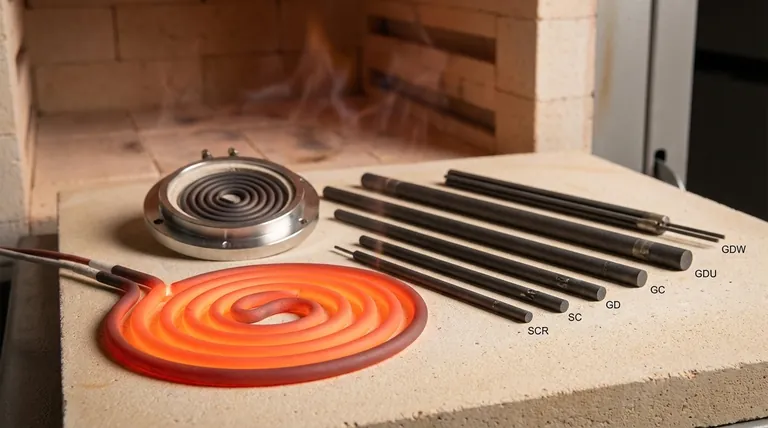
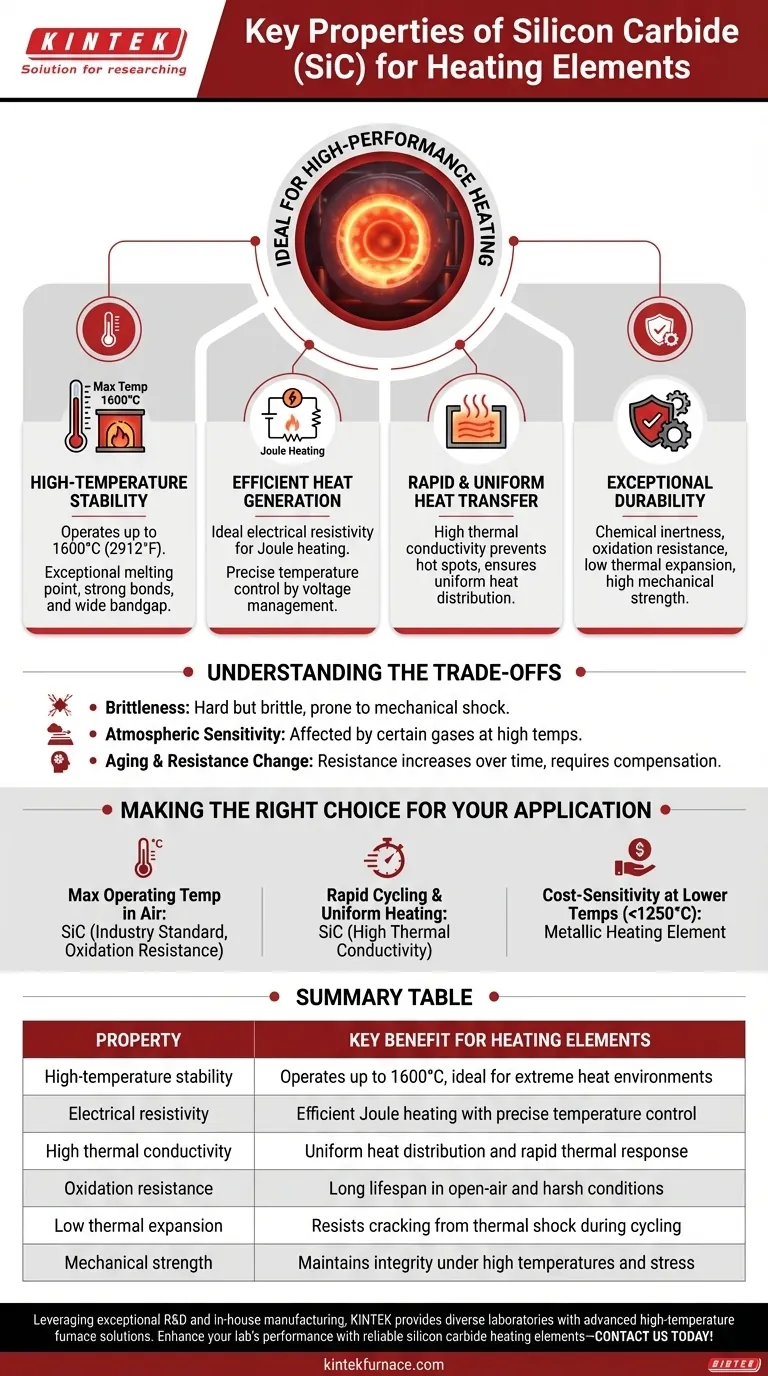
At its core, silicon carbide (SiC) is an ideal material for high-performance heating elements due to a unique combination of properties. Its ability to operate at extremely high temperatures, resist chemical attack and thermal shock, and efficiently convert electricity into usable heat makes it a superior choice for demanding industrial and laboratory furnaces.
The true value of silicon carbide is not a single attribute, but its rare synthesis of properties. It simultaneously generates intense heat, survives extreme conditions, and transfers that heat effectively, a combination that few other materials can offer.

The Core Principles of SiC Heating Elements
To understand why SiC is so effective, we must look at how its individual properties work together to solve the core challenges of high-temperature heating.
High-Temperature Stability
Silicon carbide elements can operate at surface temperatures up to 1600°C (2912°F). This capability is rooted in its fundamental material science.
SiC has an exceptionally high melting point and strong atomic bonds. Its wide bandgap energy also allows it to remain electrically stable at temperatures and voltages that would cause other materials to break down.
Efficient Heat Generation (Electrical Properties)
A heating element works by resisting the flow of electricity, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. SiC possesses an ideal level of electrical resistivity for this purpose.
It is conductive enough to allow a current to flow easily but resistive enough to convert that electrical energy into heat efficiently. This allows for precise temperature control by simply managing the voltage supplied to the element.
Rapid and Uniform Heat Transfer (Thermal Conductivity)
Once heat is generated within the element, it must be delivered to the furnace and the product. SiC has a high thermal conductivity for a ceramic material.
This property allows the heat to move quickly away from the element's core, preventing destructive hot spots and ensuring the heat is distributed uniformly throughout the furnace chamber.
Exceptional Durability (Chemical & Mechanical Stability)
An element's lifespan is determined by its ability to withstand its harsh operating environment. SiC excels due to its chemical inertness and mechanical robustness.
It has a natural resistance to oxidation, allowing for a long operational life in open-air furnaces.
Furthermore, its low thermal expansion minimizes internal stress as the element heats up and cools down. This resistance to thermal shock prevents cracking and failure during rapid temperature cycles.
Finally, SiC maintains high mechanical strength even when glowing hot, preventing it from sagging, stretching, or breaking under its own weight.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While silicon carbide is a premier heating element material, it's important to understand its limitations to ensure proper application.
Brittleness
Like most ceramics, SiC is hard but brittle. It cannot be drawn into a wire like metallic elements (e.g., Kanthal) and is susceptible to fracture from mechanical impact or shock. Care must be taken during installation and maintenance.
Atmospheric Sensitivity
While highly resistant to oxidation, the performance and lifespan of SiC elements can be affected by different furnace atmospheres. It is exceptionally strong in reducing atmospheres but may interact with certain reactive gases at very high temperatures.
Aging and Resistance Change
Over hundreds or thousands of hours of use at high temperatures, the electrical resistance of a silicon carbide element will gradually increase. Modern power control systems can often compensate for this, but it is a factor in the element's lifecycle and requires consideration for long-term process stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element technology depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum operating temperature in air: SiC is an industry standard, offering a superb combination of heat capability and long life through oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling and uniform heating: SiC's high thermal conductivity makes it ideal for applications requiring fast thermal response and precise temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitivity at lower temperatures (below 1250°C): A metallic heating element may offer a more economical solution, provided it meets the temperature and atmospheric requirements.
Ultimately, silicon carbide's unique blend of thermal, electrical, and mechanical resilience makes it the definitive material for reliable heating in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit for Heating Elements |
|---|---|
| High-temperature stability | Operates up to 1600°C, ideal for extreme heat environments |
| Electrical resistivity | Efficient Joule heating with precise temperature control |
| High thermal conductivity | Uniform heat distribution and rapid thermal response |
| Oxidation resistance | Long lifespan in open-air and harsh conditions |
| Low thermal expansion | Resists cracking from thermal shock during cycling |
| Mechanical strength | Maintains integrity under high temperatures and stress |
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Enhance your lab's performance with reliable silicon carbide heating elements—contact us today to discuss how we can tailor solutions for your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















