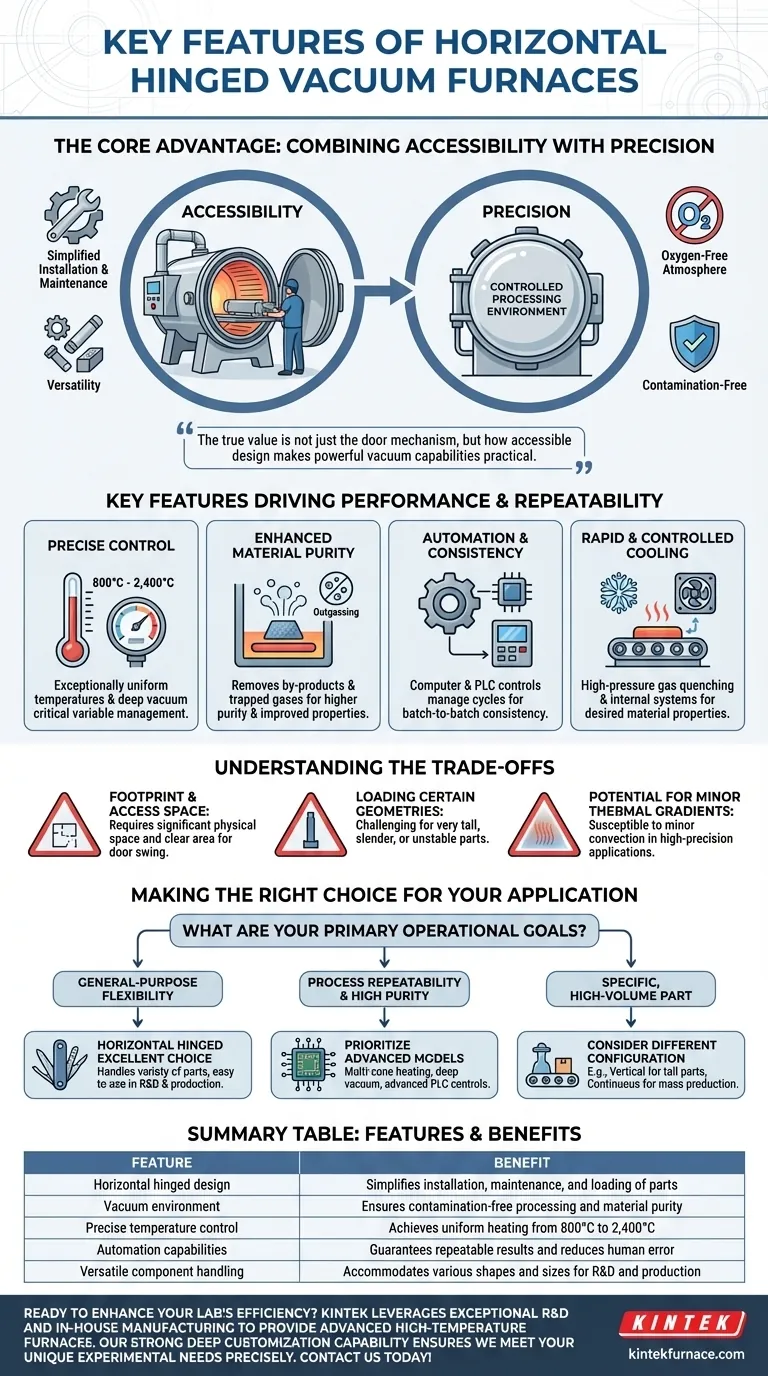
At their core, horizontal hinged vacuum furnaces are popular because they offer a highly effective balance between operational accessibility and advanced material processing capabilities. Their design simplifies installation, maintenance, and the loading of diverse parts, while the vacuum environment provides the precise, contamination-free conditions required for modern heat treatment.
The true value of a horizontal hinged vacuum furnace is not just the door mechanism itself, but how that accessible design makes the powerful capabilities of vacuum heat treatment practical for a wide range of industrial and laboratory applications.
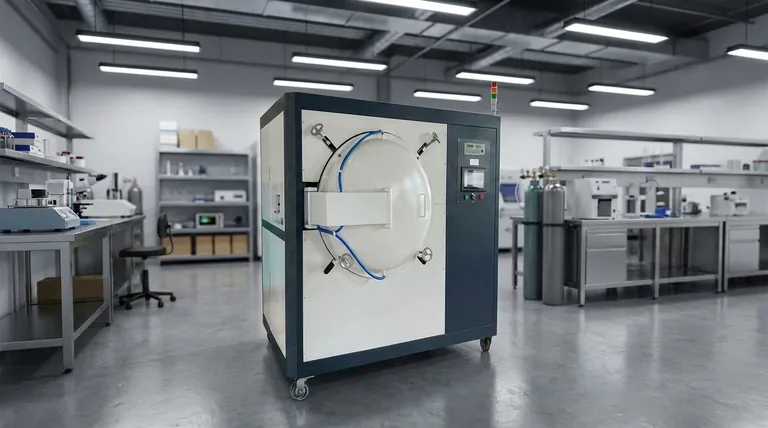

The Core Advantage: Combining Accessibility with Precision
The horizontal hinged configuration is a deliberate design choice that directly addresses the day-to-day realities of a production or research environment.
Simplified Installation and Maintenance
The furnace's horizontal orientation and hinged door provide direct, unobstructed access to the heating chamber. This straightforward design simplifies initial setup and makes routine maintenance, such as element replacement or chamber cleaning, significantly easier.
Versatility for Diverse Components
This design is exceptionally adaptable. It can accommodate components of almost any shape or size that fit within the chamber dimensions, making it a versatile workhorse for job shops, R&D labs, and facilities that handle a low-to-medium volume of varied parts.
The Foundation: A Controlled Processing Environment
The fundamental purpose of any vacuum furnace is to create a tightly controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere. By removing air and other gases, the furnace prevents oxidation and eliminates contaminants that could compromise material integrity during high-temperature processing.
Key Features Driving Performance and Repeatability
Beyond the physical design, the popularity of these furnaces is driven by their advanced technical capabilities that ensure high-quality, repeatable results.
Precise Temperature and Atmosphere Control
Modern vacuum furnaces offer exceptionally uniform temperatures, often ranging from 800°C to over 2,400°C. Combined with high-performance vacuum pumps that can achieve very low pressures, operators have precise control over the two most critical variables in heat treatment.
Enhanced Material Purity and Properties
Operating under a vacuum actively removes unwanted by-products and trapped gases from the material as it is heated. This process, known as outgassing, results in a final product with higher purity, improved structural integrity, and enhanced mechanical or electrical properties.
Automation for Consistent Results
These furnaces are highly integrated systems. Computer and PLC-based controls manage everything from pump-down cycles and temperature ramps to gas quenching. This automation ensures that every process is executed identically, eliminating human error and guaranteeing batch-to-batch consistency.
Rapid and Controlled Cooling
Many heat treatment processes require not only precise heating but also controlled cooling to achieve the desired material properties. Many furnaces incorporate features like high-pressure gas quenching or internal water-cooling systems to rapidly and uniformly cool the workload.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly versatile, the horizontal hinged design is not universally optimal. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Footprint and Access Space
The primary trade-off is physical space. The furnace itself has a significant footprint, and the hinged door requires a large, clear area to swing open. This can be a major constraint in smaller facilities compared to top-loading or vertical furnace designs.
Loading Certain Geometries
While versatile, loading very tall, slender, or unstable parts can be more challenging in a horizontal furnace. Gravity is not assisting with component stability as it would in a top-loading vertical furnace.
Potential for Minor Thermal Gradients
In some specific high-precision applications, the horizontal orientation can be more susceptible to minor thermal gradients caused by natural convection within the chamber. While modern designs with multiple heating zones mitigate this, it remains a consideration for processes with extreme temperature uniformity requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose flexibility: The horizontal hinged design is an excellent choice for its ability to handle a wide variety of parts and its ease of use in both R&D and production settings.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and high purity: Prioritize models with advanced PLC controls, multi-zone heating, and deep vacuum capabilities to ensure the most consistent and clean processing environment.
- If your primary focus is a specific, high-volume part: Consider if the part's geometry might be better suited to a different configuration, such as a vertical furnace for tall parts or a continuous furnace for mass production.
Ultimately, the horizontal hinged vacuum furnace remains a popular industry standard because it provides powerful, precise thermal processing within a practical and user-friendly framework.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Horizontal hinged design | Simplifies installation, maintenance, and loading of parts |
| Vacuum environment | Ensures contamination-free processing and material purity |
| Precise temperature control | Achieves uniform heating from 800°C to 2,400°C |
| Automation capabilities | Guarantees repeatable results and reduces human error |
| Versatile component handling | Accommodates various shapes and sizes for R&D and production |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a tailored vacuum furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs precisely. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can deliver superior performance and reliability for your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















