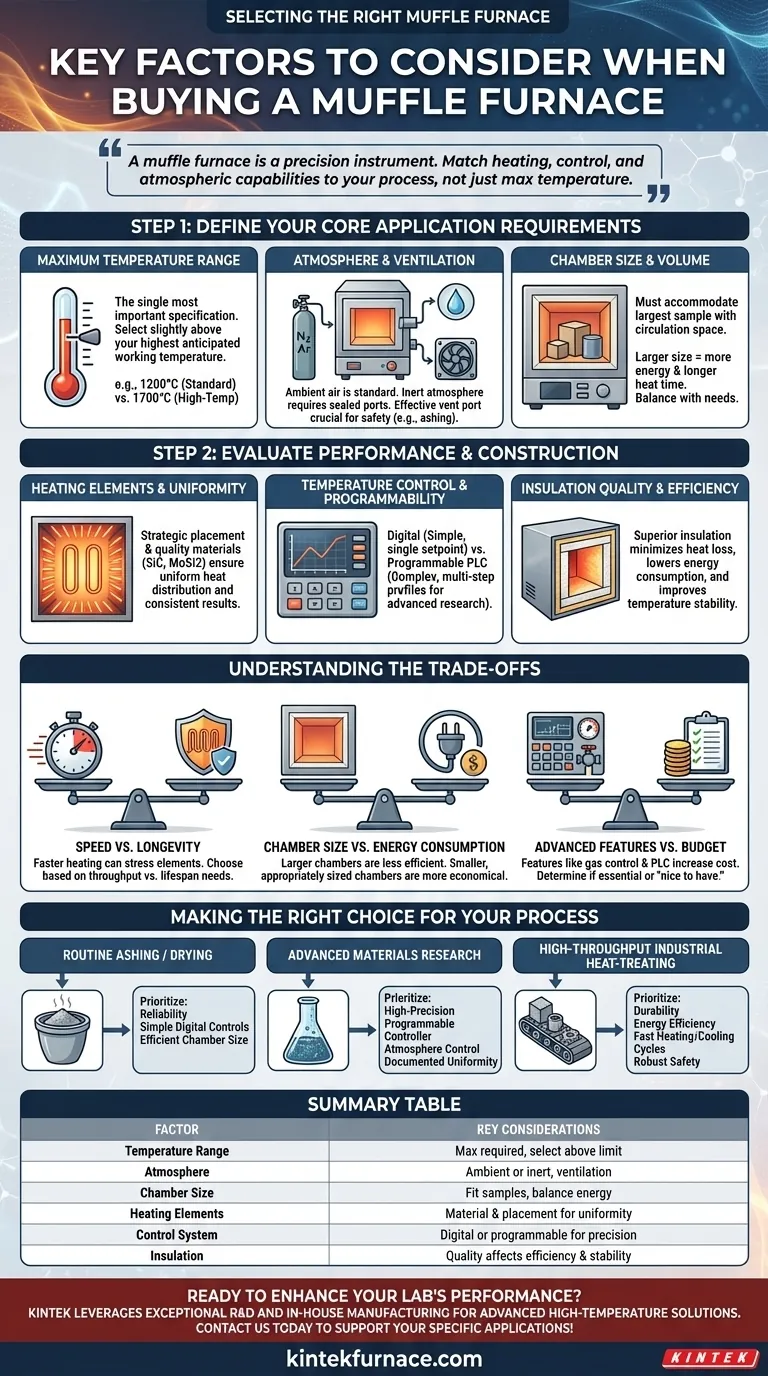
Selecting the right muffle furnace is a critical decision that directly impacts the accuracy of your results and the efficiency of your operations. The key factors to consider are your required temperature range, the physical size of your samples, the atmospheric conditions needed for your process, and the level of temperature control your application demands.
A muffle furnace is more than just a high-temperature oven; it is a precision instrument. The most common mistake is focusing on maximum temperature alone, when the true goal is to select a furnace whose heating, control, and atmospheric capabilities are perfectly matched to your specific scientific or industrial process.
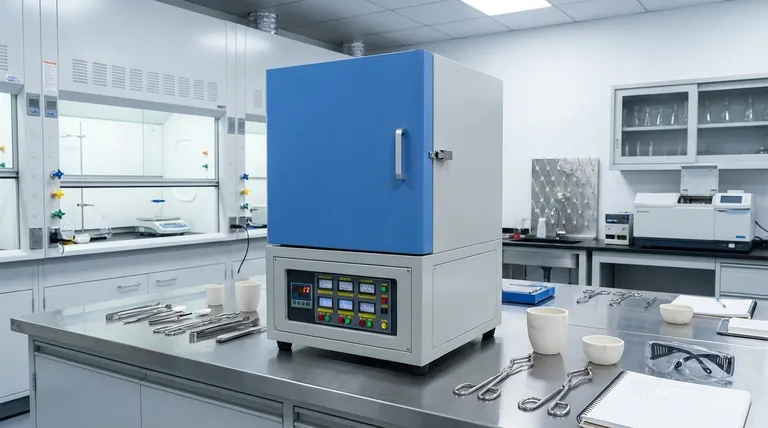

Step 1: Define Your Core Application Requirements
Before evaluating any specific model, you must first define the non-negotiable parameters of your work. This ensures you are comparing options that are truly suitable for your needs.
What is your maximum required temperature?
The temperature range is the single most important specification. A furnace rated for 1200°C is fundamentally different from one designed for 1700°C.
Always select a furnace with a maximum temperature slightly above your highest anticipated working temperature to avoid running the unit at its absolute limit, which can shorten its lifespan.
What atmosphere will you be working in?
Most basic muffle furnaces operate in ambient air. If your process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, you must select a furnace with sealed gas ports.
Proper ventilation is also crucial, especially for processes like ashing that produce smoke or fumes. Ensure the furnace has an effective vent port to exhaust byproducts safely.
What are the size and volume of your samples?
The furnace's internal chamber size must accommodate your largest sample or crucible, with adequate clearance for air circulation to ensure uniform heating.
Consider both the dimensions (width, height, depth) and the total capacity. A larger chamber is not always better, as it consumes more energy and takes longer to heat.
Step 2: Evaluate Furnace Performance and Construction
Once you have defined your core needs, you can assess the technical specifications that determine a furnace's performance, accuracy, and efficiency.
Heating Elements and Temperature Uniformity
High-quality heating elements (like silicon carbide or molybdenum disilicide for higher temperatures) and their strategic placement are essential for uniform heat distribution. Poor uniformity can lead to inconsistent results across your sample.
The heating rate determines how quickly the furnace reaches its setpoint. While a faster rate can improve throughput, it may also place more stress on the heating elements.
Temperature Control and Programmability
The controller is the brain of the furnace. A simple digital controller allows you to set a single temperature, which is sufficient for many basic applications.
For more complex processes, a programmable logic controller (PLC) offers the ability to create multi-step temperature profiles, control heating and cooling rates, and program thermal gradients. This precision is vital for materials science and advanced research.
Insulation Quality and Energy Efficiency
The quality of the insulation (typically ceramic fiber) dictates the furnace's energy efficiency and external surface temperature.
Superior insulation minimizes heat loss, which lowers energy consumption and improves temperature stability within the chamber, saving on long-term operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace involves balancing competing factors. Being aware of these trade-offs is key to making a wise investment.
Speed vs. Element Longevity
Furnaces capable of extremely fast heating rates often achieve this by pushing their heating elements harder. This can be ideal for high-throughput environments but may lead to a shorter element lifespan compared to a furnace with a more moderate heating rate.
Chamber Size vs. Energy Consumption
A large chamber provides versatility but is inherently less energy-efficient. It requires more power and time to heat and stabilize, increasing operational costs. If your samples are consistently small, choosing a smaller, appropriately sized chamber is more economical.
Advanced Features vs. Budget
Features like gas atmosphere control and advanced PLC programming significantly increase the cost of a furnace. It is crucial to determine if these capabilities are essential for your work or simply "nice to have." Over-investing in features you will never use is a common pitfall.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Use your specific application as the ultimate guide to filter your options and identify the ideal furnace configuration.
- If your primary focus is routine ashing or drying: Prioritize reliability, simple digital controls, and a chamber size that efficiently matches your typical sample volume.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research: Prioritize a high-precision programmable controller, options for atmosphere control, and documented temperature uniformity.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial heat-treating: Emphasize durability, energy efficiency, fast heating/cooling cycles, and robust safety features.
By systematically aligning the furnace's capabilities with your specific application, you invest in an instrument that delivers reliable, accurate results for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Maximum required temperature, select slightly above working limit |
| Atmosphere | Ambient air or inert gases, ventilation for safety |
| Chamber Size | Dimensions and volume to fit samples, balance with energy use |
| Heating Elements | Material and placement for uniform heating and longevity |
| Control System | Digital or programmable for precision and complex profiles |
| Insulation | Quality affects energy efficiency and temperature stability |
Ready to enhance your lab's performance with a custom muffle furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















