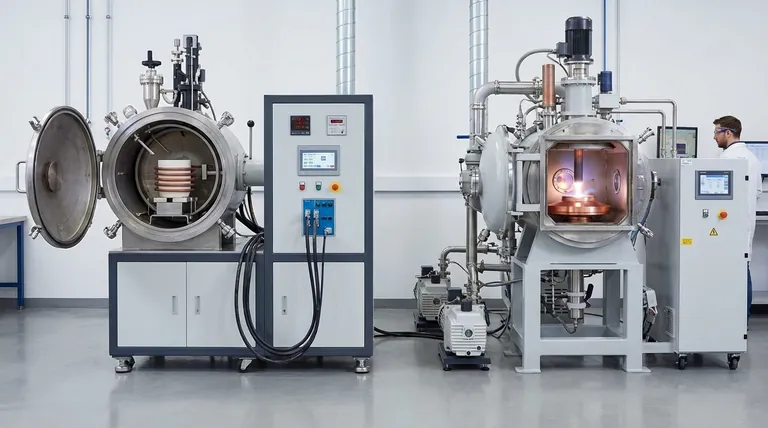
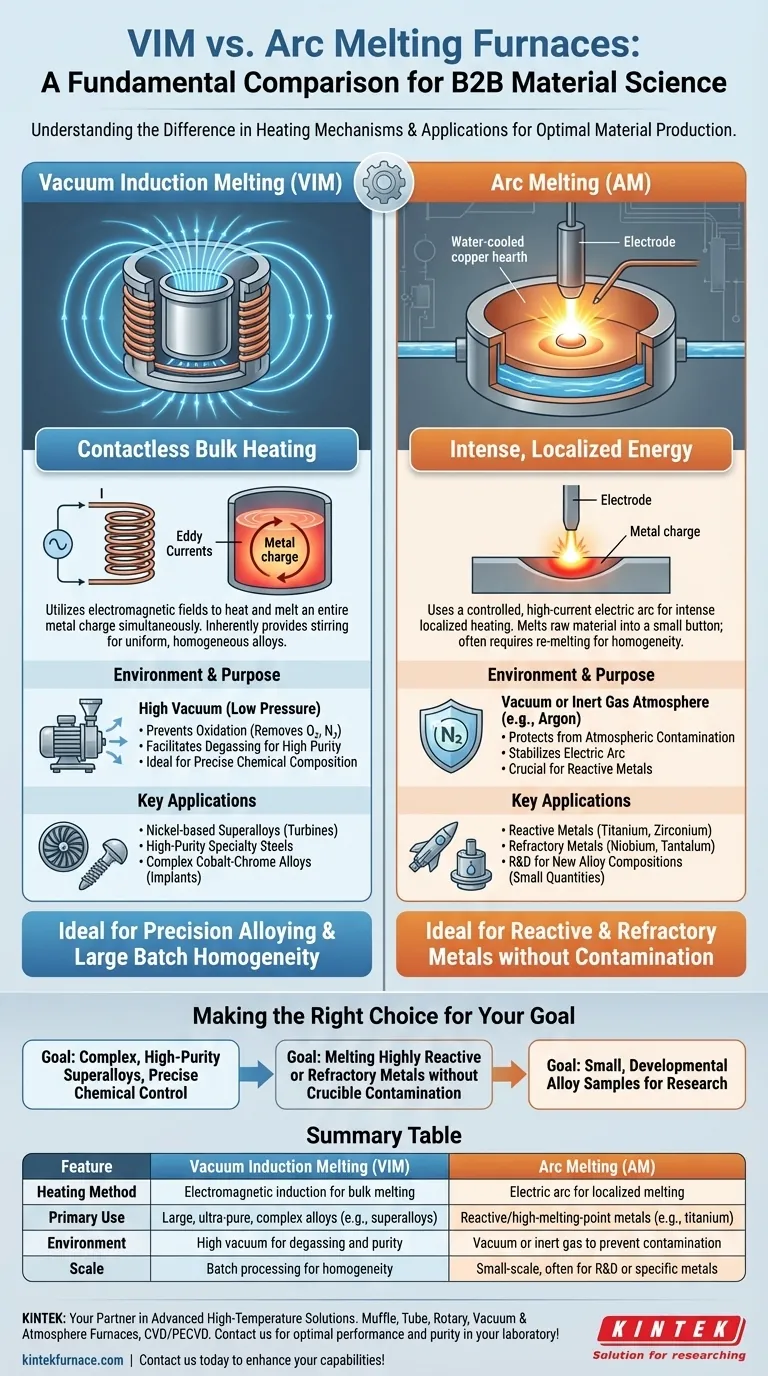
The fundamental difference between Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) and Arc Melting (AM) lies in their heating mechanisms and primary purpose. VIM uses electromagnetic fields to melt an entire batch of metal at once in a high vacuum, making it ideal for creating large, ultra-pure, complex alloys. In contrast, Arc Melting uses an intense electric arc for localized melting, a process essential for handling highly reactive or high-melting-point metals that would contaminate a traditional crucible.
Your choice between VIM and Arc Melting is not about which is superior, but which tool is right for the job. The decision hinges entirely on the type of metal you are working with and whether your goal is precision alloying of a large batch (VIM) or melting reactive metals without contamination (Arc Melting).

The Core Distinction: Heating Method and Scale
The way heat is introduced into the metal dictates the entire process, its advantages, and its ideal applications.
VIM: Contactless Bulk Heating
A VIM furnace operates like a powerful, highly controlled microwave for metal. An alternating current is passed through a copper coil, which generates a strong electromagnetic field.
This field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal charge placed inside a crucible. The metal's own electrical resistance causes it to heat up and melt from within.
Because the entire charge is heated simultaneously, this method produces an extremely uniform and homogeneous liquid melt. The electromagnetic field also creates a natural stirring action, ensuring all alloying elements are distributed evenly.
Arc Melting: Intense, Localized Energy
Arc Melting uses a controlled, high-current electric arc—like a miniature lightning strike—between an electrode and the raw material. This arc generates incredibly intense, localized heat, capable of melting metals with very high melting points.
This process is typically done in a shallow, water-cooled copper hearth. The raw material melts into a "button" or small ingot, solidifying where it contacts the cool copper without sticking or reacting.
Unlike VIM, arc melting does not heat the entire volume at once. To achieve a homogeneous melt, the resulting button often must be flipped and re-melted several times.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
While both processes often use a vacuum, they do so for slightly different but equally critical reasons.
Why VIM Requires a High Vacuum
The primary goal of VIM is to produce alloys with the highest possible purity and precise chemical composition. The high vacuum (low pressure) environment is essential for two reasons.
First, it prevents oxidation by removing atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen that would otherwise react with the molten metal.
Second, it facilitates degassing, pulling dissolved gases out of the melt. This refining step is critical for improving the mechanical properties, such as fatigue life, of high-performance alloys.
The Arc Melter's Controlled Atmosphere
Arc melters also operate in a vacuum or, more commonly, a backfilled environment of high-purity inert gas like argon.
The primary purpose here is to protect the melt from atmospheric contamination and to stabilize the electric arc. This is especially crucial when working with reactive metals like titanium or zirconium, which readily absorb oxygen and nitrogen, becoming brittle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
The differences in heating and environment lead to distinct industrial applications. Choosing the wrong one can lead to contaminated material or an inefficient process.
Application 1: Precision Alloying (VIM)
VIM is the workhorse for producing materials where exact chemical composition is non-negotiable. Its ability to create a large, homogeneous, and exceptionally clean batch of metal makes it the standard for a specific class of materials.
This includes nickel-based superalloys for jet engine turbines, high-purity specialty steels, and complex cobalt-chrome alloys for medical implants.
Application 2: Reactive & Refractory Metals (Arc Melting)
Arc Melting excels where VIM struggles: with metals that are highly reactive or have extremely high melting points.
Metals like titanium, zirconium, niobium, and tantalum will react with and destroy the ceramic crucibles used in VIM furnaces. The water-cooled copper hearth of an arc melter solves this by containing the melt without any chemical reaction. It is the go-to method for these materials and for R&D involving new alloy compositions in small quantities.
A Note on VAR: The Best of Both Worlds
In high-end applications, these processes are often used together. A large electrode may be first created in a VIM furnace. This electrode is then used as the consumable material in a Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) furnace, a specific type of arc process, to refine the grain structure and further improve cleanliness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material dictates the process. A simple analysis of your primary goal will lead you to the correct technology.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, high-purity superalloys or specialty steels with precise chemical control: VIM is the definitive industry standard for its bulk alloying and refining capabilities.
- If your primary focus is melting highly reactive metals (like titanium) or refractory metals (like tungsten) without crucible contamination: Arc melting is the only viable choice due to its use of a non-reactive copper hearth.
- If your primary focus is creating small, developmental alloy samples for research: A lab-scale arc melter is the most common and flexible tool for the job.
Ultimately, selecting the right melting technology begins with a deep understanding of your material's fundamental properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) | Arc Melting (AM) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic induction for bulk melting | Electric arc for localized melting |
| Primary Use | Large, ultra-pure, complex alloys (e.g., superalloys) | Reactive/high-melting-point metals (e.g., titanium) |
| Environment | High vacuum for degassing and purity | Vacuum or inert gas to prevent contamination |
| Scale | Batch processing for homogeneity | Small-scale, often for R&D or specific metals |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your metal melting needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Whether you're working with superalloys, reactive metals, or need deep customization for precise experimental control, our expertise ensures optimal performance and purity. Don't let furnace selection hold back your innovation—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and achieve your material goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















