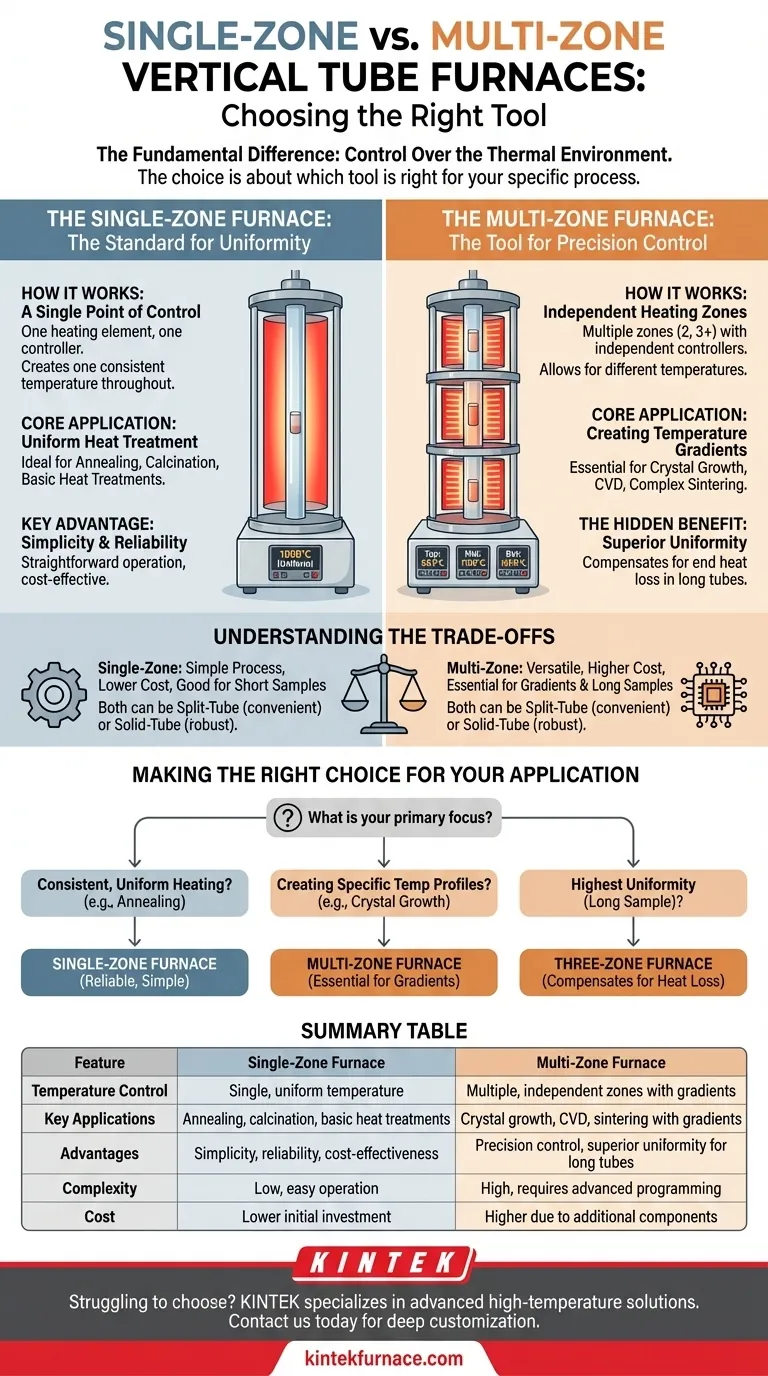
The fundamental difference between single-zone and multi-zone vertical tube furnaces lies in their control over the thermal environment. A single-zone furnace is designed to create one consistent temperature throughout its heating chamber. In contrast, a multi-zone furnace has multiple, independently controlled heating areas, which allows you to create precise temperature gradients or achieve superior temperature uniformity along the length of the tube.
The choice between a single-zone and multi-zone furnace is not about which is better, but which tool is right for your specific process. Your decision depends entirely on whether your application requires a single, stable temperature or a complex, tailored thermal profile.

The Single-Zone Furnace: The Standard for Uniformity
A single-zone furnace is the workhorse for many standard thermal processes. Its design prioritizes simplicity and consistency for applications that require the entire sample to be held at the same temperature.
How It Works: A Single Point of Control
The furnace features one continuous heating element (or a set of connected elements) that is governed by a single controller. You set one temperature, and the furnace works to maintain that temperature across the entire heated length of the chamber.
Core Application: Uniform Heat Treatment
This design is ideal for processes where temperature uniformity is the primary goal. Common applications include annealing, calcination, and other basic heat treatments that require a stable and consistent thermal environment for the entire sample.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Reliability
With fewer components and simpler programming, single-zone furnaces are straightforward to operate and are often a more cost-effective solution for routine, high-temperature work.
The Multi-Zone Furnace: The Tool for Precision Control
Multi-zone furnaces provide a level of control that is impossible to achieve with a single-zone design. They are essential for advanced materials science and complex process development.
How It Works: Independent Heating Zones
These furnaces are divided into two, three, or more distinct heating zones along the tube's length. Each zone has its own heating element and thermocouple, managed by an independent controller, allowing you to set a different temperature for each section.
Core Application: Creating Temperature Gradients
The ability to create a controlled temperature gradient is critical for sophisticated processes. This includes applications like crystal growth, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and certain types of sintering where different reactions must occur at different temperatures along the sample.
The Hidden Benefit: Superior Uniformity
Counterintuitively, a multi-zone furnace can also achieve better uniformity than a single-zone model, especially across longer tubes. By setting the outer zones to a slightly higher temperature, you can precisely compensate for the natural heat loss that occurs at the ends of the furnace tube, creating an exceptionally uniform flat zone in the center.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace requires a clear understanding of the compromises between simplicity, versatility, and cost.
Process Needs vs. Equipment Complexity
A single-zone furnace is simple: set the temperature and run the process. A multi-zone furnace offers immense versatility but requires more sophisticated programming and a deeper understanding of the thermal dynamics to use effectively.
Sample Length and Uniformity Goals
For short samples, a single-zone furnace often provides adequate uniformity. However, for longer samples or when exceptional uniformity is non-negotiable, a three-zone furnace is the superior technical choice to counteract heat loss at the tube ends.
Budget and Maintenance
Multi-zone furnaces are inherently more expensive due to the additional controllers, power supplies, and wiring. The increased number of components also means more potential points of failure and more complex troubleshooting.
Physical Access: Split-Tube vs. Solid-Tube
Both single and multi-zone furnaces can come in a split-tube design that hinges open for easy access to the chamber or a solid-tube design. Split-tube models are convenient for changing samples or process tubes quickly, while solid-tube furnaces can be more robust for certain high-pressure or atmospheric applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct furnace, align its capabilities directly with the requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is consistent, uniform heating for processes like annealing or basic material testing: A single-zone furnace offers a reliable, simple, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating specific temperature profiles for processes like crystal growth or CVD: A multi-zone furnace is essential for achieving the required temperature gradients.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperature uniformity across a long sample: A three-zone furnace, used to compensate for end-zone heat loss, is the superior technical choice.
Ultimately, understanding your process requirements is the key to selecting the furnace that will serve as a reliable tool rather than a source of experimental error.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single-Zone Furnace | Multi-Zone Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Single, uniform temperature | Multiple, independent zones with gradients |
| Key Applications | Annealing, calcination, basic heat treatments | Crystal growth, CVD, sintering with gradients |
| Advantages | Simplicity, reliability, cost-effectiveness | Precision control, superior uniformity for long tubes |
| Complexity | Low, easy operation | High, requires advanced programming |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher due to additional components |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature solutions tailored to your specific processes. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether you need simple uniform heating or complex thermal profiles. Don't let equipment limitations hold back your research—contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















