At its core, a vacuum system for heat treatment is a coordinated series of pumps designed to remove atmosphere from a sealed chamber. The primary components are a backing (or roughing) pump, a vacuum booster, and a high-vacuum pump, such as a diffusion pump. These work in sequence to reduce the internal pressure, creating the necessary environment for processing materials without oxidation or contamination.
A vacuum furnace is more than just its pumps. It is a precisely engineered ecosystem where the chamber, heating elements, pump train, and cooling system work in concert to control the material's environment, ensuring predictable and superior metallurgical outcomes.

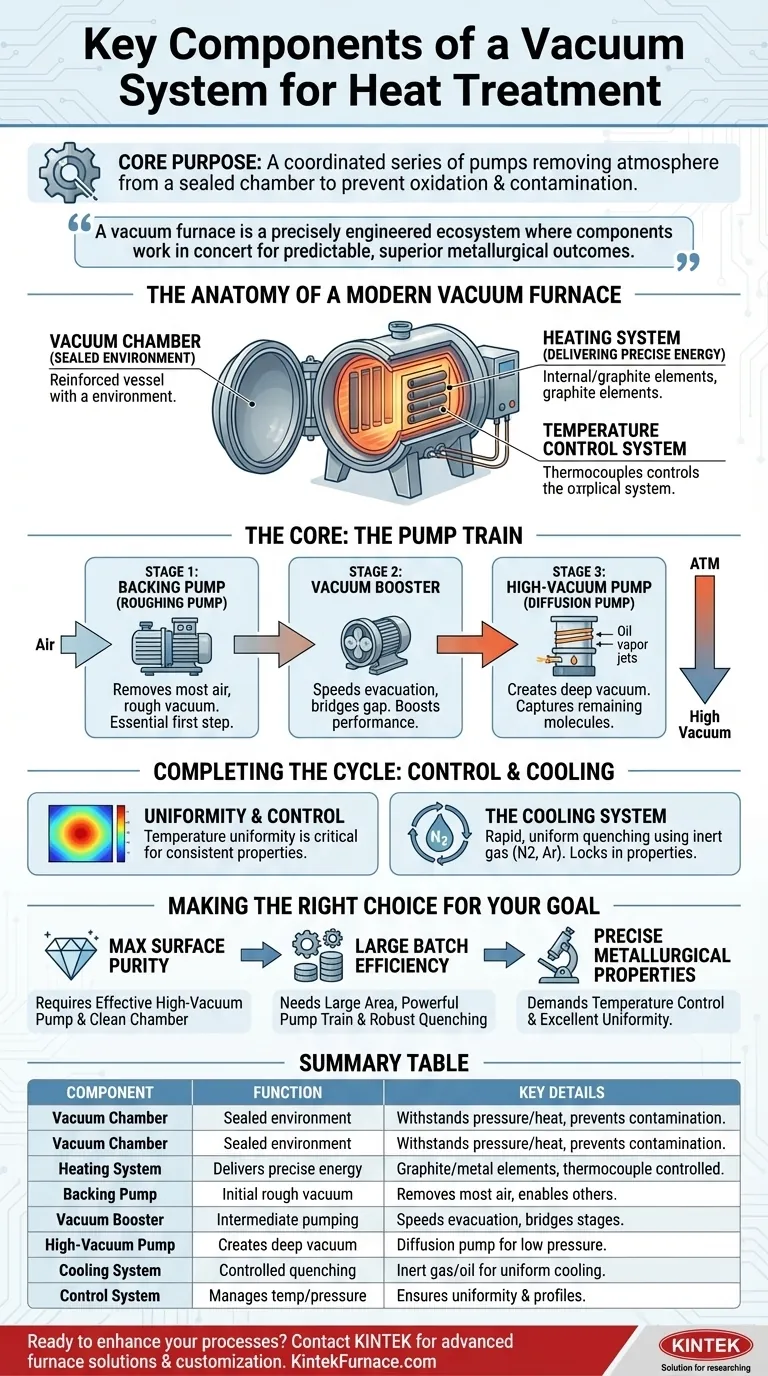
The Anatomy of a Modern Vacuum Furnace
To understand the vacuum system, you must first see it within the context of the entire furnace. Each part has a distinct and critical function.
The Vacuum Chamber: The Sealed Environment
The vacuum chamber, or vessel, is the heart of the furnace. It is a sealed container designed to withstand both extreme external atmospheric pressure when a vacuum is pulled and the intense internal temperatures of the heat treatment cycle.
Its integrity is paramount; any leaks compromise the entire process by allowing contaminants like oxygen and nitrogen to enter.
The Heating System: Delivering Precise Energy
Inside the chamber are the heating elements, typically made of graphite or refractory metals. These elements generate the heat required for the process.
This is governed by a temperature control system, which uses thermocouples to monitor the temperature within the chamber and adjust power to the elements, ensuring the material follows a precise heating profile.
The Core of the Vacuum: The Pump Train
No single pump can efficiently take a furnace from atmospheric pressure down to a deep vacuum. Instead, a series of pumps, known as a "pump train," work together in stages.
Stage 1: The Backing Pump
The backing pump (also called a roughing pump) does the initial heavy lifting. It removes the vast majority of the air from the chamber, taking the pressure from atmospheric levels down to a "rough" vacuum.
This pump cannot create the high vacuum needed for treatment, but it's the essential first step and provides the necessary low-pressure environment for the other pumps to operate.
Stage 2: The Vacuum Booster
A vacuum booster acts as an intermediate stage. It "boosts" the performance of the backing pump, helping to move a large volume of gas molecules more quickly.
It bridges the operational gap between the roughing pump and the high-vacuum pump, significantly reducing the time it takes to reach the target pressure.
Stage 3: The High-Vacuum Pump
Once the booster and backing pump have lowered the pressure sufficiently, the high-vacuum pump takes over. The most common type in this application is the diffusion pump.
This pump works by using a high-velocity jet of oil vapor to capture remaining air molecules and drag them out of the chamber. This is what creates the extremely low-pressure environment required to prevent oxidation and ensure surface purity.
Completing the Cycle: Control and Cooling
Creating the vacuum is only part of the process. The material properties are locked in during the cooling phase.
Uniformity and Control
The performance of a furnace is not just measured by its ultimate vacuum level. The uniformity of temperature across the effective working area is a critical indicator of quality.
Poor uniformity leads to inconsistent material properties, rendering the process unreliable for high-stakes applications like aerospace or medical components.
The Cooling System
After the heating cycle, the material must be cooled at a controlled rate. This is done by a cooling system, which often uses high-pressure inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) to rapidly and uniformly quench the parts inside the chamber.
Other methods, such as vacuum oil quenching, exist for specific applications, but gas quenching is common for its cleanliness and control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how these components contribute to the final result allows you to select the right process for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface purity and brightness: Your process must utilize an effective high-vacuum pump (like a diffusion pump) and a meticulously clean chamber to minimize any contamination.
- If your primary focus is processing large batches efficiently: A furnace with a large effective working area, a powerful pump train for fast evacuation, and a robust gas quenching system for rapid cooling are essential.
- If your primary focus is achieving precise metallurgical properties: The most critical components are the temperature control system and the furnace's ability to maintain excellent temperature uniformity across the entire workload.
By understanding each component's function, you gain direct control over the quality and consistency of your heat-treated product.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed environment | Withstands pressure and heat, prevents contamination |
| Heating System | Delivers precise energy | Uses graphite/metal elements, controlled by thermocouples |
| Backing Pump | Initial rough vacuum | Removes most air, enables other pumps |
| Vacuum Booster | Intermediate pumping | Speeds evacuation, bridges rough to high vacuum |
| High-Vacuum Pump | Creates deep vacuum | Often a diffusion pump for low-pressure environments |
| Cooling System | Controlled quenching | Uses inert gas or oil for uniform cooling |
| Control System | Manages temperature and pressure | Ensures uniformity and precise heating profiles |
Ready to enhance your heat treatment processes with reliable vacuum systems? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for superior metallurgical outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your laboratory efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control



















