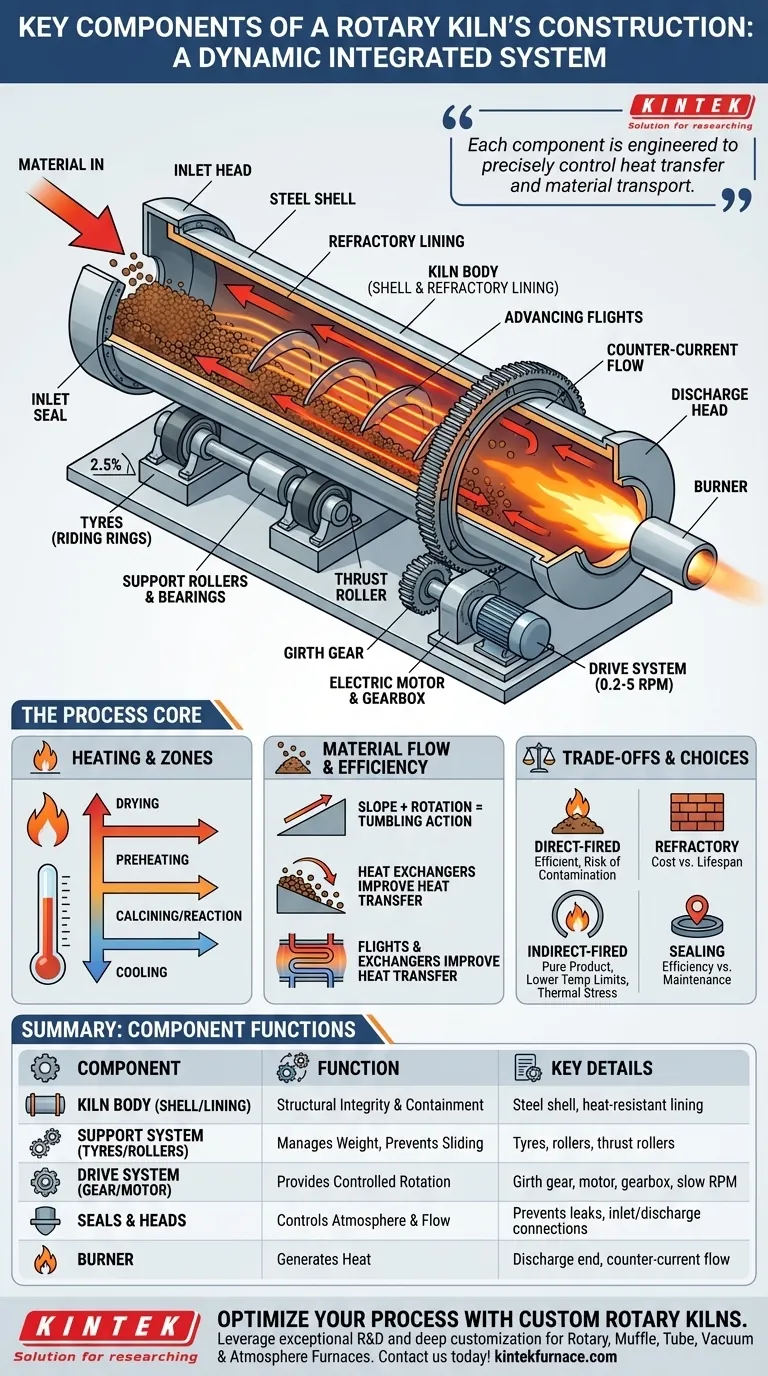
At its core, a rotary kiln is a deceptively simple machine. It consists of a large rotating cylinder, known as the kiln shell, which is inclined at a slight angle. This shell is supported by tyres (or riding rings) that rest on support rollers, and it is turned by a large drive gear. Inside, a refractory lining protects the steel shell from extreme temperatures generated by a burner, while seals at both ends contain heat and control the internal atmosphere.
A rotary kiln is not merely a collection of parts, but a dynamic, integrated system. Each component—from the structural shell and its refractory lining to the support, drive, and sealing mechanisms—is engineered to precisely control heat transfer and material transport for a specific chemical or physical transformation.

The Anatomy of a Rotary Kiln System
To understand a rotary kiln, it's best to break it down into its core functional groups: the body, the support system, the drive system, and the components that manage material and gas flow.
The Kiln Body: Shell and Lining
The most prominent feature is the kiln body, a long cylindrical drum made of a robust steel shell. This provides the structural integrity to span between supports and contain the process.
To withstand internal process temperatures that can exceed 1450°C (2640°F), the steel shell is protected by an internal refractory lining. This heat-resistant layer, made of specialized bricks or castable materials, is critical for both thermal efficiency and the kiln's operational lifespan.
The Support System: Tyres, Rollers, and Bearings
The massive weight of the kiln is managed by the support system. Large steel bands, called tyres or riding rings, are attached to the outside of the shell.
These tyres ride on a set of support rollers (or trunnion wheels), which are heavy-duty assemblies with bearings that allow the kiln to rotate with minimal friction.
To prevent the inclined kiln from sliding downhill, thrust rollers are positioned to push against the side of the tyres, keeping the entire assembly in its correct longitudinal position.
The Drive System: Gear, Motor, and Control
Rotation is provided by the drive system. A large girth gear is mounted around the circumference of the kiln shell.
This gear is turned by a smaller pinion gear, which is connected to a powerful electric motor through a gearbox. The rotation speed is typically very slow and controllable, often ranging from just 0.2 to 5 revolutions per minute (rpm).
Material and Gas Flow: Slope, Seals, and Heads
Material moves through the kiln due to a combination of rotation and gravity. The kiln is installed at a slight downward slope, usually between 1% and 4% (1 to 4 cm of drop per meter of length).
As the kiln turns, material is lifted partway up the wall and then tumbles back down, slowly advancing toward the discharge end. This tumbling action ensures excellent mixing and uniform heat exposure.
Seals are installed at both the feed (inlet) and discharge ends. These are critical for preventing cold air from leaking in and hot process gas from escaping, which is essential for thermal efficiency and atmospheric control.
Finally, the inlet and discharge heads (or breeching) provide stationary connection points for feeding raw material into the kiln and for discharging the final product and exhaust gases.
The Process Core: Heating and Transformation
While the mechanical components provide the structure and motion, the process components create the conditions for transformation.
The Heat Source: Burners and Combustion
Heat is typically generated by a burner located at the discharge end of the kiln. This creates a counter-current flow, where the hot combustion gases travel up the kiln in the opposite direction of the material moving down.
This counter-flow design is highly efficient, as the hottest gases encounter the most processed material, and the cooler gases preheat the incoming raw feed.
Kiln Zones: From Drying to Cooling
The temperature gradient along the kiln's length naturally creates distinct process zones. Material entering the kiln is first dried, then preheated, before entering the high-temperature calcining or reaction zone where the primary transformation occurs.
Internal Design: Flights and Heat Exchangers
To improve efficiency, some kilns incorporate internal structures. Advancing flights or "lifters" are metal plates that help lift and shower the material through the gas stream, improving heat transfer.
More complex internal heat exchangers can be used to further enhance thermal efficiency by maximizing contact between the hot gases and the process material.
Understanding the System-Level Trade-offs
The selection and design of each component involves critical trade-offs that impact performance, cost, and maintenance.
Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The most fundamental design choice is the heating method. Direct-fired kilns, where the burner flame and combustion gases contact the material, are common and thermally efficient. However, they risk contaminating the product with byproducts of combustion.
Indirect-fired kilns heat the material by heating the outside of the kiln shell. This keeps the product pure but is less efficient, has lower temperature limits, and places immense thermal stress on the shell.
Refractory Selection and Lifespan
The choice of refractory material is a balance between cost, thermal insulation, and resistance to chemical attack and abrasion from the process material. A cheaper lining may reduce upfront cost but lead to more frequent and expensive shutdowns for replacement.
Sealing Efficiency vs. Maintenance
High-efficiency seals are complex and can be a significant maintenance point. However, failing to invest in good seals results in major energy losses as cold air infiltrates the system, and can lead to uncontrolled emissions. The cost of lost thermal efficiency often outweighs the maintenance cost of a good seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The final design of a rotary kiln is always tailored to its specific application.
- If your primary focus is high throughput: You will need a kiln with a large diameter, appropriate length, and a robust drive system capable of handling high material loads.
- If your primary focus is thermal efficiency: You will invest in high-performance refractory linings, advanced sealing systems, and potentially internal heat exchangers to minimize fuel consumption.
- If your primary focus is precise process control: You will require a variable-speed drive, a highly tunable burner system, and excellent seals to maintain a specific internal atmosphere and temperature profile.
Ultimately, a rotary kiln is a powerful tool because its individual components work together as a single, controllable processing machine.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Kiln Body | Structural integrity and process containment | Steel shell with refractory lining for high-temperature resistance |
| Support System | Manages weight and prevents sliding | Includes tyres, support rollers, and thrust rollers |
| Drive System | Provides rotation | Girth gear, motor, and gearbox for slow, controlled RPM |
| Seals and Heads | Controls atmosphere and material flow | Prevents leaks, with inlet and discharge heads for connections |
| Burner | Generates heat | Located at discharge end for counter-current flow efficiency |
Ready to Optimize Your Industrial Processes with a Custom Rotary Kiln?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're focused on high throughput, thermal efficiency, or precise process control, we can design a rotary kiln that precisely meets your experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your operations—Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















