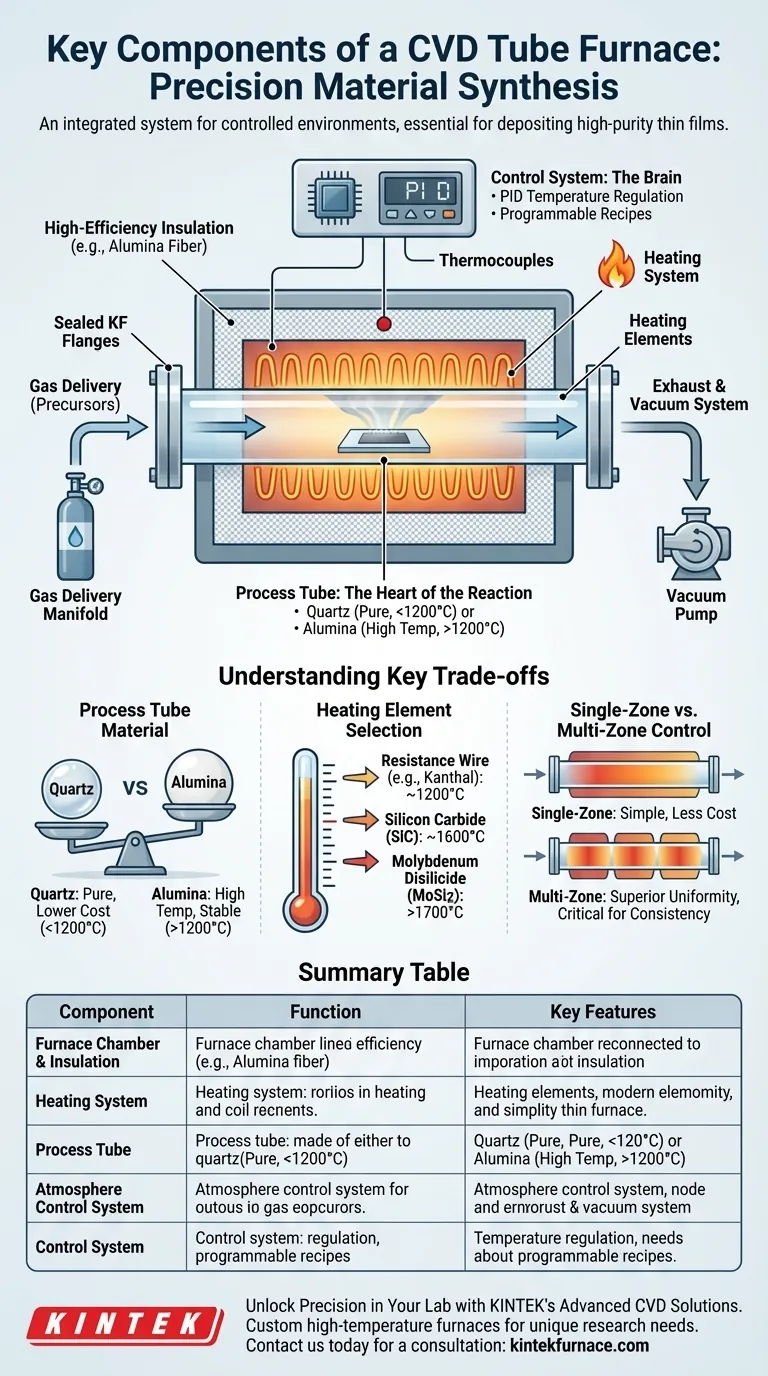
At its core, a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) tube furnace is an integrated system designed for one purpose: creating a highly controlled environment for material synthesis. The key components are the furnace chamber with its heating elements, a sealed process tube that acts as the reactor, a gas delivery and vacuum system to control the atmosphere, and a precision control system to orchestrate the entire process. These parts work in concert to deposit high-purity thin films onto a substrate.
The individual components of a CVD furnace are not as important as how they integrate. The true function of the furnace is to provide an operator with precise, repeatable control over temperature, pressure, and atmospheric composition—the fundamental variables that govern thin-film deposition.

The Anatomy of a CVD Furnace: A System-by-System Breakdown
To understand how a CVD furnace achieves this level of control, we must examine each of its core systems and the function they serve.
The Furnace Chamber and Insulation
The furnace chamber is the main structural body that houses the heating elements and the process tube. It is typically cylindrical or semi-cylindrical to promote even heating.
This chamber is lined with high-efficiency insulation, often made from high-purity alumina fiber. This material minimizes heat loss, which allows for faster heating/cooling cycles and reduces overall energy consumption.
The Heating System: Generating Extreme Temperatures
The heating system is responsible for bringing the substrate up to the critical temperature required for the chemical reaction to occur.
Different heating elements are used depending on the target temperature range:
- Resistance Wire (e.g., Kanthal): Common for temperatures up to ~1200°C.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Used for higher temperatures, typically up to 1600°C.
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2): Capable of reaching the highest temperatures, often 1700°C or more.
Many advanced furnaces feature multi-zone control, where several independent heating zones are managed along the length of the tube. This ensures exceptional temperature uniformity, which is critical for consistent film growth over a large area.
The Process Tube: The Heart of the Reaction
The process tube is the sealed, inert container where the deposition actually happens. A substrate is placed inside, and precursor gases are flowed through it.
The material of this tube is critical and is chosen based on the process temperature:
- Quartz Tubes: Used for processes typically below 1200°C. They offer high purity but will soften and deform at higher temperatures.
- Alumina Tubes: Required for high-temperature applications (above 1200°C) due to their excellent thermal and chemical stability.
The ends of the tube are sealed with vacuum-tight flanges, such as stainless steel KF flanges, which provide ports for gas inlet, outlet, and vacuum pumping.
The Atmosphere Control System
This system manages the environment inside the process tube. It is responsible for introducing gaseous chemical precursors and removing unreacted gases and byproducts.
It consists of vacuum pumps to evacuate the chamber and a gas delivery manifold to introduce precise amounts of one or more precursor gases. This control is essential for creating the specific chemical environment needed for the desired film to form.
The Control System: The Brain of the Operation
The entire process is managed by a microprocessor-based controller, which acts as the furnace's brain. This system uses a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) algorithm for extremely precise temperature regulation.
High-resolution thermocouples placed near the process tube continuously measure the temperature and provide feedback to the controller. This allows the system to execute fully programmable recipes, including rapid heating ramps, controlled dwell times at specific temperatures, and programmed cooling phases.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing or designing a CVD furnace involves balancing performance requirements with practical constraints. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for selecting the right tool for the job.
Process Tube Material: Quartz vs. Alumina
The choice between a quartz and an alumina tube is a primary consideration. Quartz is often preferred for its high purity and lower cost in low-to-medium temperature applications. However, its temperature limitation is a hard ceiling. Alumina is mandatory for high-temperature work but can be more expensive and brittle.
Heating Element Selection: Temperature vs. Lifespan
The heating elements directly dictate the furnace's maximum operational temperature. While MoSi2 elements enable the highest temperatures, they may require more careful operational procedures compared to robust SiC or resistance wire elements used in lower-temperature regimes.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Control
A single-zone furnace is simpler and less expensive but may have slight temperature variations along its length. Multi-zone control offers superior temperature uniformity, which is critical for industrial production or research requiring highly consistent film properties, but it adds to the system's cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific research or production goal will determine the most critical components and features for your CVD furnace.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature synthesis (>1500°C): Prioritize a furnace equipped with an alumina process tube and either SiC or MoSi2 heating elements.
- If your primary focus is high-purity electronic or optical films: Emphasize a system with a high-purity quartz tube and a sophisticated gas delivery system for precise precursor control.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and scaling: Look for a furnace with multi-zone heating control and a fully programmable PID controller with advanced safety interlocks.
By understanding how these core components function together, you can effectively control the complex environment required for chemical vapor deposition.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace Chamber & Insulation | Houses heating elements and process tube | High-efficiency insulation, cylindrical design |
| Heating System | Generates required temperatures | Multi-zone control, elements like SiC or MoSi2 |
| Process Tube | Sealed reactor for deposition | Materials: quartz (<1200°C) or alumina (>1200°C) |
| Atmosphere Control System | Manages gas and vacuum | Precise gas delivery, vacuum pumps |
| Control System | Orchestrates temperature and process | PID controllers, programmable recipes |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's Advanced CVD Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on high-temperature synthesis, high-purity films, or scalable processes, we deliver reliable, tailored systems that enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Ready to elevate your material synthesis? Contact us today for a consultation and discover how our expertise can drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- Why is the tube design important in CVD furnaces? Ensure Uniform Deposition for High-Quality Films
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- What types of atmosphere control does a CVD Tube Furnace support? Master Vacuum and Gas Control for Precision



















