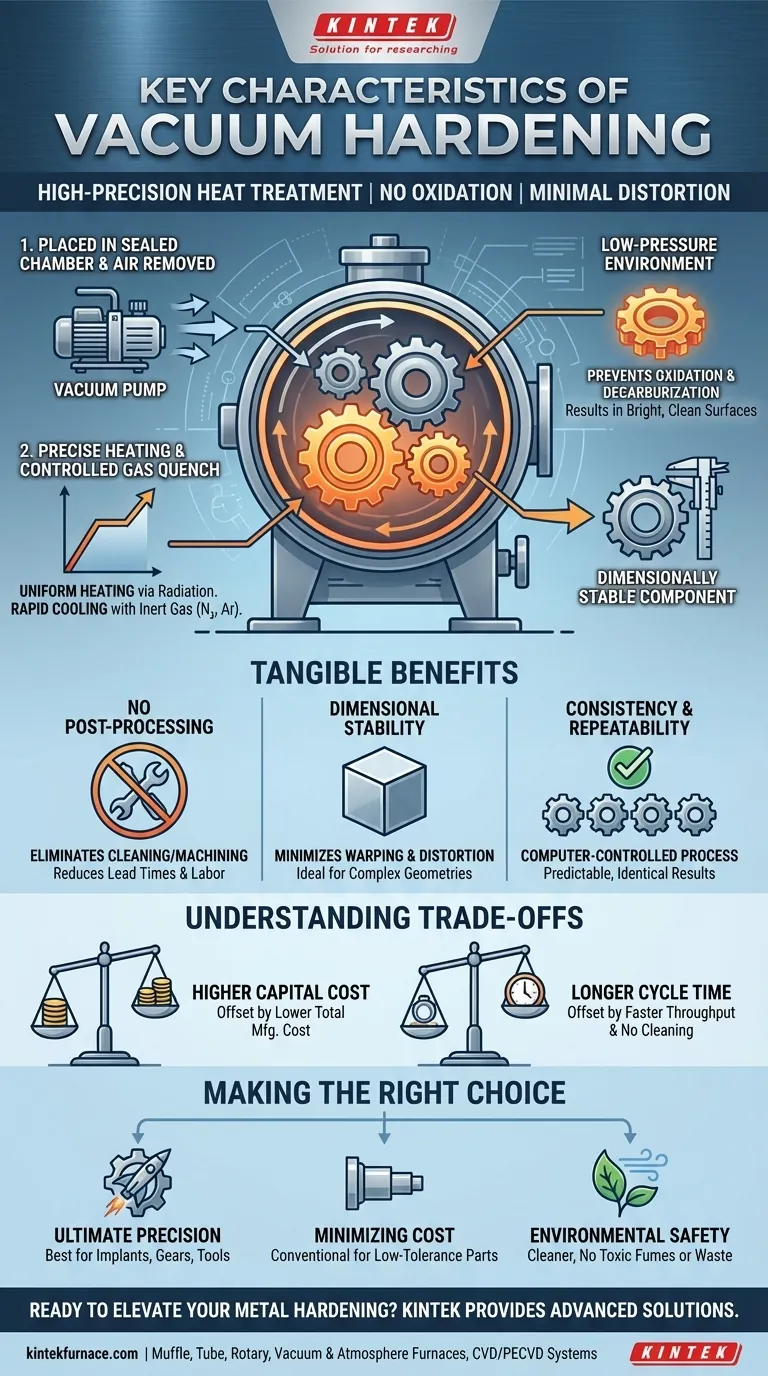
In essence, vacuum hardening is a high-precision heat treatment process defined by its ability to harden metals without causing surface oxidation or discoloration. It achieves this by heating the material in a controlled, low-pressure environment before rapidly cooling it, resulting in a clean, dimensionally stable component with enhanced mechanical properties.
The core value of vacuum hardening is not merely hardening the metal, but achieving that hardness with exceptional cleanliness, minimal distortion, and precise control, eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming secondary operations.

How Vacuum Hardening Achieves Superior Results
To understand its key characteristics, you must first understand the principles that drive the process. The "vacuum" is the critical element that differentiates it from conventional methods.
The Role of the Vacuum Environment
The process begins by placing components inside a sealed furnace chamber and removing the atmosphere. This near-vacuum state is fundamental to the results.
By eliminating oxygen and other reactive gases, the process completely prevents oxidation and decarburization—the loss of carbon from the steel's surface—which can compromise performance.
This is why parts emerge from the furnace with a bright, clean, metallic surface, requiring no subsequent cleaning or grinding to remove scale.
Precision in Heating and Cooling
Vacuum furnaces allow for exceptionally uniform and precisely controlled heating cycles. The energy is transferred primarily through radiation, ensuring the entire component reaches the target temperature evenly.
After soaking at the austenitizing temperature, the parts are quenched (rapidly cooled) by introducing a high-purity inert gas like nitrogen or argon. The pressure and flow rate of this gas quench can be finely tuned.
This level of control over both the heating and cooling stages is what allows for the tailoring of specific material properties like hardness, toughness, and tensile strength.
The Tangible Benefits for Your Components
The controlled nature of the process translates directly into measurable advantages for the final product, influencing cost, performance, and manufacturing workflow.
Eliminating Post-Process Operations
Because parts come out clean and scale-free, you eliminate the need for secondary operations like sandblasting, chemical cleaning, or machining to correct surface imperfections.
This significantly reduces lead times, labor costs, and potential damage associated with post-heat-treat handling.
Ensuring Dimensional Stability
The uniform heating and controlled gas quenching minimize the thermal shock and internal stresses that cause warping and distortion in other methods like oil or salt bath quenching.
This is critical for complex geometries, thin-walled parts, or components with tight dimensional tolerances, as it ensures the part maintains its shape and accuracy.
Achieving Consistency and Repeatability
The entire vacuum hardening process is typically computer-controlled. Every variable—from the vacuum level and temperature ramp rates to the quench pressure—is monitored and executed precisely.
This guarantees that every part in a batch, and every subsequent batch, receives the exact same treatment, delivering highly predictable and repeatable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum hardening is not the universal solution for all applications. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its limitations.
Higher Process Cost
Vacuum furnace equipment is a significant capital investment, and the process itself can have a higher cost per part compared to conventional atmospheric hardening.
This cost is often justified by the elimination of secondary cleaning operations and the reduced scrap rate from distortion, but it must be factored into the total manufacturing cost analysis.
Cycle Time Considerations
The time required to pump the furnace down to the required vacuum level can extend the overall cycle time compared to some atmospheric processes.
However, this "slower" furnace time is often offset by the "faster" total throughput, as parts move directly to the next manufacturing step without needing to be cleaned.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct hardening method depends entirely on the specific requirements of your component and your overall project priorities.
- If your primary focus is ultimate precision and surface integrity: Vacuum hardening is the superior choice for parts like medical implants, aerospace gears, or injection molding tools where dimensional accuracy and a flawless finish are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost on low-tolerance parts: A conventional atmospheric or salt bath hardening process may be more cost-effective if some surface scaling and post-process cleaning are acceptable for the application.
- If your primary focus is environmental and operator safety: Vacuum hardening is an inherently cleaner process with no toxic fumes, hazardous waste disposal (from salts), or fire hazards associated with oil quenching.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum hardening is a decision to prioritize quality, precision, and a streamlined production workflow from the outset.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Oxidation Prevention | Eliminates surface oxidation and decarburization in a vacuum environment. |
| Dimensional Stability | Minimizes distortion with uniform heating and controlled gas quenching. |
| Precision Control | Allows tailored material properties via computer-monitored heating and cooling. |
| Process Cleanliness | Produces bright, scale-free surfaces, reducing need for secondary cleaning. |
| Consistency | Ensures repeatable results across batches for reliable performance. |
Ready to elevate your metal hardening process? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum hardening solutions can enhance your component quality, reduce costs, and streamline production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















