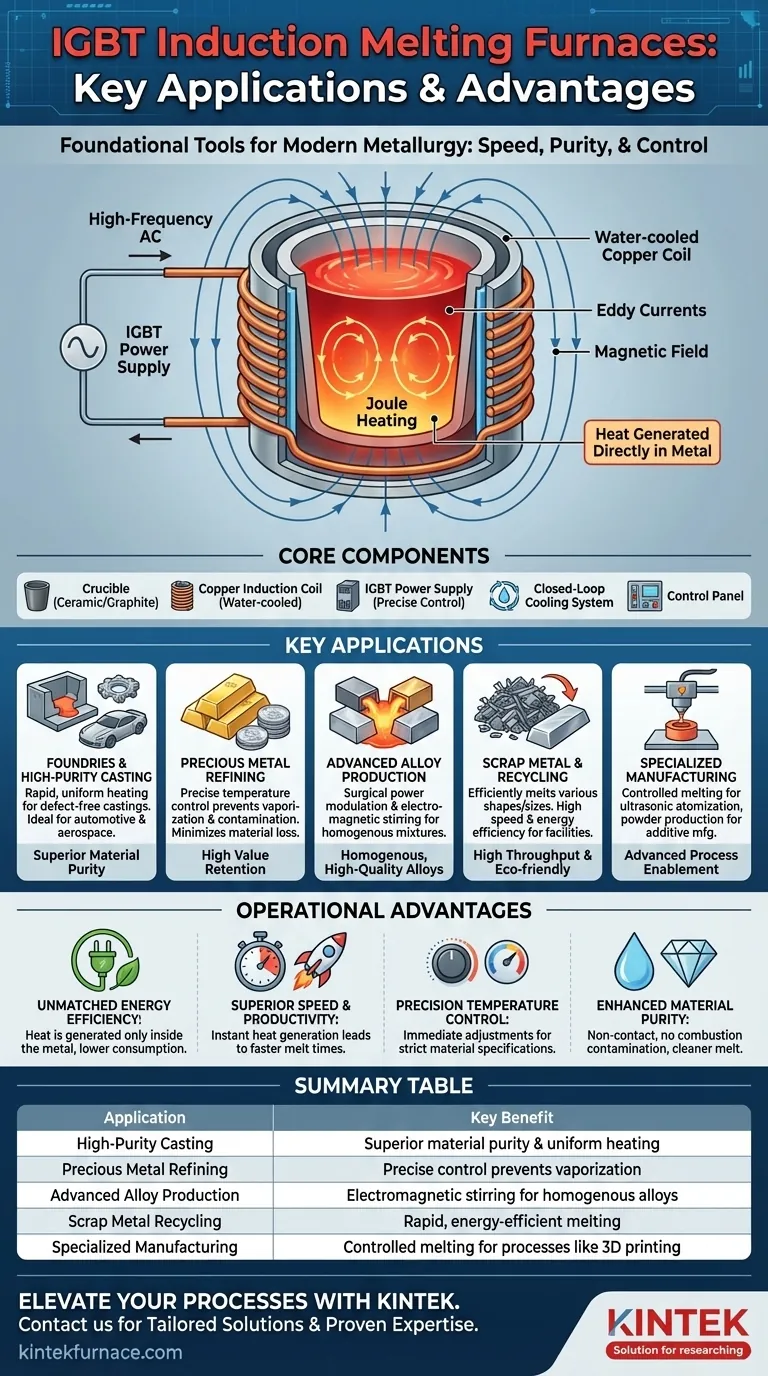
IGBT induction melting furnaces are foundational tools used across a spectrum of modern metallurgical processes. Their primary applications include the high-purity melting of both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, the creation of specialized alloys, the refining of precious metals like gold and silver, and the efficient recycling of scrap metal.
The core reason IGBT induction furnaces are so widely adopted is their method of non-contact heating. By using electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal itself, they provide a level of speed, purity, and temperature control that traditional fuel-fired furnaces cannot match.
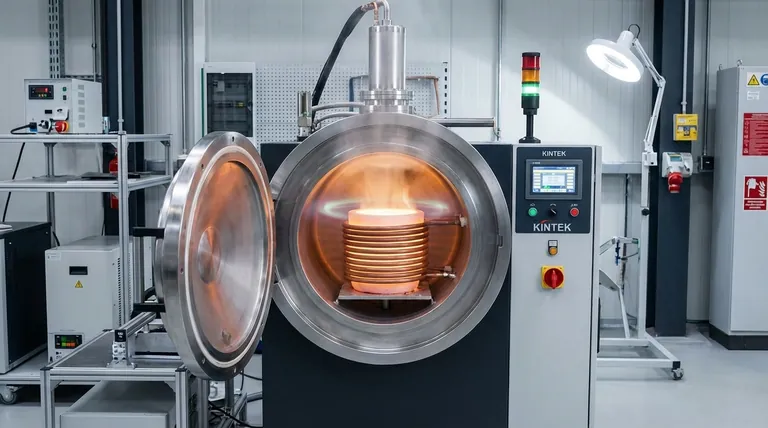

How Induction Melting Works: The Core Principle
To understand its applications, you must first understand how the technology operates. The process is elegant in its simplicity and effectiveness, relying on fundamental physics rather than combustion.
The Role of Electromagnetic Induction
An IGBT power supply sends a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a water-cooled copper coil. This generates a powerful, rapidly changing magnetic field around and within the furnace's crucible.
When a conductive material (like metal) is placed inside this field, the magnetic forces induce electrical currents within it, known as eddy currents. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, precise heat through a process called Joule heating, causing it to melt from the inside out.
The Importance of Non-Contact Heating
Because the heat is generated directly within the metal charge, there is no physical contact with a heating element or flame. This is a critical advantage, as it completely eliminates contamination from combustion byproducts, ensuring a much higher level of material purity in the final product.
Key Components of a Modern System
A typical IGBT induction furnace consists of a few core components working in concert:
- A crucible (often ceramic or graphite) to contain the molten metal.
- The water-cooled copper induction coil that generates the magnetic field.
- An IGBT power supply that converts mains electricity into the necessary high-frequency AC.
- A closed-loop cooling system to manage the heat generated in the coils.
- A control panel for precise regulation of power, temperature, and melt time.
A Breakdown of Key Applications
The unique advantages of induction heating make it the superior choice for industries where quality, speed, and control are paramount.
Foundries and High-Purity Casting
For both ferrous (iron, steel) and non-ferrous (aluminum, copper) metals, induction furnaces provide rapid and uniform heating. This ensures the entire melt reaches a consistent temperature, which is critical for producing high-quality, defect-free castings in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Precious Metal Refining
In the processing of gold, silver, and platinum, even minor material loss or contamination is costly. Induction furnaces offer the precise temperature control needed to prevent overheating and vaporization. The non-contact process guarantees the final product's purity and value.
Advanced Alloy Production
Creating specialized alloys requires exact ratios and specific temperature profiles. The precise power modulation of an IGBT supply allows metallurgists to control the melt with surgical accuracy. The inherent electromagnetic stirring action within the melt also promotes a more homogenous mixture, resulting in a higher-quality alloy.
Scrap Metal and Recycling
Induction furnaces can efficiently melt scrap metal of various sizes and shapes. Their high speed and energy efficiency make them an economically and environmentally sound choice for recycling facilities, turning waste material back into valuable raw stock.
Specialized Manufacturing Processes
The technology's precision has opened doors to advanced applications. This includes processes like ultrasonic atomization, where a controlled stream of molten metal is used to create fine metal powders essential for additive manufacturing (3D printing) and thermal spray coatings.
Understanding the Operational Advantages
The adoption of IGBT induction furnaces is driven by several clear, measurable benefits over older technologies.
Unmatched Energy Efficiency
Unlike fuel-fired furnaces that lose significant heat to the surrounding environment, induction furnaces generate heat only where it is needed: inside the metal. This results in dramatically lower energy consumption and a cooler, safer working environment.
Superior Speed and Productivity
The ability to generate heat instantly within the charge leads to significantly faster melt times compared to conventional methods. For a foundry or recycling plant, this translates directly to higher throughput and increased productivity per shift.
Precision Temperature Control
The solid-state IGBT power supply allows for immediate and precise adjustments to the power output. This gives operators unparalleled control over the melting process, which is essential for meeting the strict specifications of advanced materials and alloys.
Enhanced Material Purity
By eliminating combustion, you eliminate a primary source of contamination. The resulting melt is cleaner, with fewer impurities and oxides. This leads to better mechanical properties in the final cast product and less refinement needed for precious metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an IGBT induction furnace should be aligned with your specific operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is material purity and value: Induction is the definitive choice for precious metals, medical-grade alloys, and aerospace components where contamination is unacceptable.
- If your primary focus is production volume and speed: The rapid melt cycles of induction furnaces are ideal for high-throughput foundries and recycling operations looking to maximize output.
- If your primary focus is creating specialized materials: The precise temperature control offered by IGBT systems is essential for research and development and the production of advanced alloys with specific properties.
Ultimately, adopting IGBT induction technology is a strategic decision to prioritize control, quality, and efficiency in your metallurgical processes.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-Purity Casting | Superior material purity & uniform heating for defect-free castings |
| Precious Metal Refining | Precise temperature control prevents vaporization & contamination |
| Advanced Alloy Production | Electromagnetic stirring ensures homogenous, high-quality alloys |
| Scrap Metal Recycling | Rapid, energy-efficient melting for high throughput |
| Specialized Manufacturing | Controlled melting for processes like ultrasonic atomization & 3D printing |
Ready to elevate your metallurgical processes with precision and efficiency?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our IGBT induction melting furnaces are designed to meet the demanding needs of foundries, precious metal refiners, alloy producers, and recycling facilities.
We offer:
- Tailored Solutions: Strong deep customization capabilities to precisely match your unique operational requirements.
- Proven Expertise: Expertise in Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems.
- Unmatched Support: End-to-end support from installation to maintenance.
Contact us today to discuss how our IGBT induction furnaces can enhance your productivity, purity, and profitability.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















