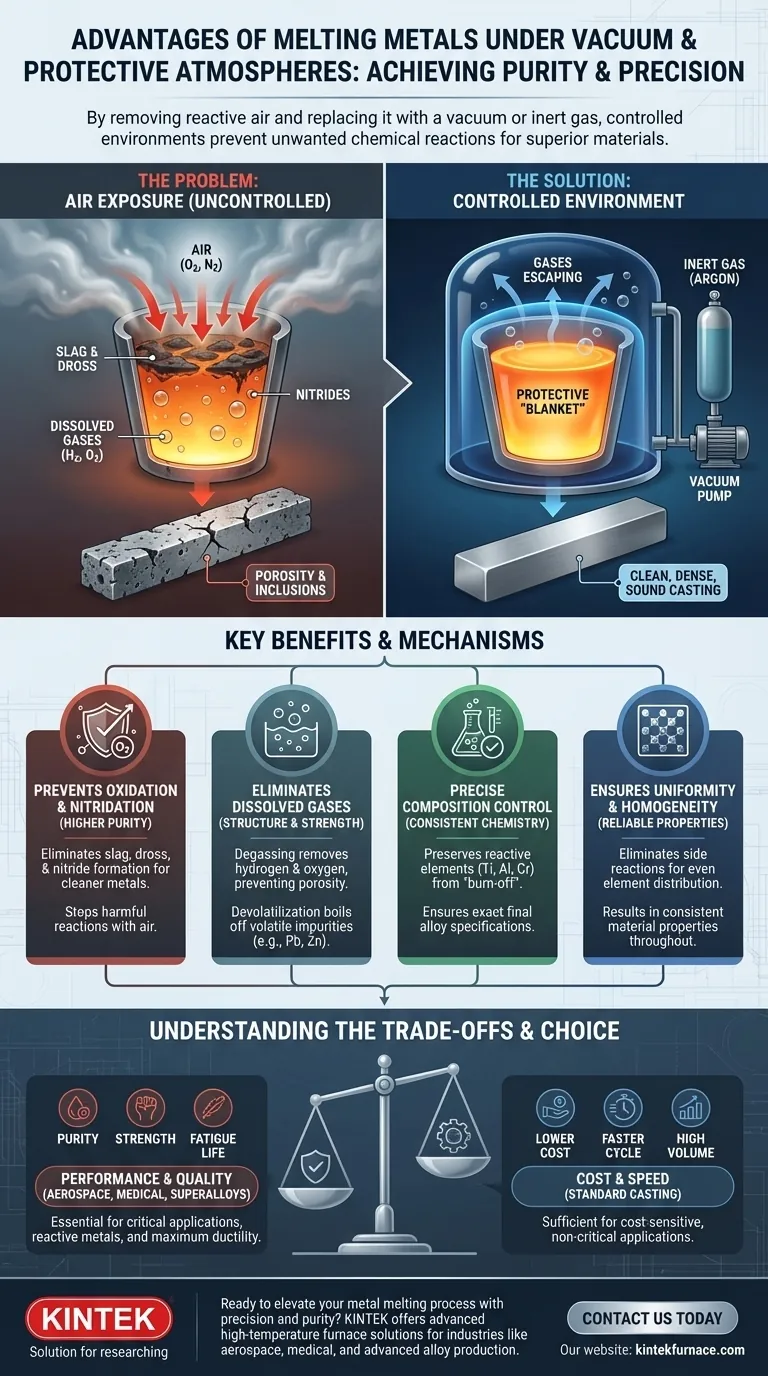
Melting metals in a controlled environment is fundamentally about achieving purity and precision. By removing reactive air and replacing it with a vacuum or an inert gas, the process prevents unwanted chemical reactions. This leads to cleaner, stronger, and more reliable materials by reducing oxidation, lowering dissolved gas content, removing volatile impurities, and ensuring precise control over the final alloy chemistry.
At its core, vacuum or protective atmosphere melting is a strategy to eliminate the uncontrolled chemical reactions that occur when molten metal is exposed to air. This control prevents contamination, removes impurities, and ensures the final material meets stringent performance and quality specifications.

The Foundation: Preventing Unwanted Reactions
The primary goal of controlled atmosphere melting is to isolate the molten metal from the chemically reactive gases in ambient air, primarily oxygen and nitrogen.
The Problem with Air: Oxidation and Nitridation
When hot, molten metal is exposed to air, it reacts aggressively with oxygen to form oxides, often seen as slag or dross on the surface.
Similarly, some metals can react with nitrogen to form hard, brittle particles called nitrides. These reactions degrade the final product.
How a Vacuum Removes Reactants
A vacuum physically removes the air from the melting chamber. By reducing the pressure, the number of oxygen and nitrogen molecules available to react with the melt is drastically decreased, effectively stopping these harmful reactions before they can start.
How a Protective Atmosphere Shields the Melt
A protective atmosphere works by replacing the air in the chamber with a non-reactive (inert) gas, most commonly argon. This inert gas forms a stable "blanket" over the molten metal, shielding it from any residual oxygen or other contaminants.
Achieving Higher Purity and Cleanliness
Beyond just preventing reactions, controlled atmospheres actively clean the metal itself, resulting in a superior final product.
Degassing: Eliminating Dissolved Gases
Molten metals can absorb significant amounts of gases like hydrogen and oxygen. As the metal cools and solidifies, the solubility of these gases drops, causing them to form bubbles that get trapped in the structure.
This creates a critical defect known as porosity, which severely weakens the material. The vacuum actively pulls these dissolved gases out of the liquid metal, a process called degassing, leading to a dense, sound casting.
Devolatilization: Boiling Off Impurities
A vacuum lowers the boiling point of all substances. This principle is used to remove undesirable trace elements with high vapor pressures (meaning they boil easily), such as lead, zinc, cadmium, or magnesium.
This purification step, known as devolatilization, is critical for high-purity alloys where even trace amounts of these elements can compromise performance.
Minimizing Non-Metallic Inclusions
The oxides and nitrides formed during air melting don't just disappear. They can become trapped within the solidified metal as non-metallic inclusions.
These microscopic particles act as stress concentration points, creating initiation sites for cracks and fatigue failure. By preventing oxidation in the first place, vacuum melting dramatically reduces the number of these harmful inclusions.
Gaining Precise Control Over Alloy Composition
For advanced alloys, the exact percentage of each element is critical to achieving the desired properties.
Preserving Reactive Alloying Elements
Many high-performance alloys rely on elements like titanium, aluminum, and chromium, which are extremely reactive with oxygen.
In an air melt, a significant and unpredictable amount of these expensive elements can be lost to oxidation. Melting in a vacuum prevents this "burn-off," ensuring the final composition is exactly what was intended and saving valuable material.
Ensuring Uniformity and Homogeneity
When side reactions are eliminated, the alloying elements can dissolve and mix into the base metal more evenly. This results in a highly homogeneous melt, ensuring that the material properties are consistent throughout the entire casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, this process is not the default choice for every application due to its inherent complexities.
Increased Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces and the associated control systems are significantly more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain than their air-melting counterparts.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to a deep vacuum and, if needed, backfilling it with an inert gas adds considerable time to each melt cycle. This reduces overall throughput compared to continuous air melting.
Unintentional Loss of Elements
The same devolatilization that removes impurities can also remove desirable alloying elements if they have a high vapor pressure. Controlling the process parameters to selectively remove only unwanted elements requires significant expertise.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use controlled atmosphere melting should be driven by the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is performance-critical applications (aerospace, medical): This process is essential for achieving the required purity, cleanliness, and mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is working with reactive metals (titanium, superalloys): This is the only way to prevent catastrophic loss of expensive alloying elements and ensure proper chemistry.
- If your primary focus is maximum fatigue life and ductility: The degassing effect of vacuum melting is critical for eliminating the porosity that limits these properties.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-sensitive casting (e.g., standard cast iron): Traditional air melting is often sufficient and more economical.
Ultimately, choosing this process is an investment in material integrity, ensuring the final component performs exactly as designed.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation and Nitridation | Eliminates slag, dross, and nitride formation for cleaner metals |
| Reduces Dissolved Gases | Removes hydrogen and oxygen to prevent porosity and enhance strength |
| Removes Volatile Impurities | Boils off elements like lead and zinc for higher purity alloys |
| Controls Alloy Composition | Preserves reactive elements like titanium and aluminum for precise chemistry |
| Ensures Homogeneity | Promotes uniform mixing for consistent material properties |
Ready to elevate your metal melting process with precision and purity? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like aerospace, medical, and advanced alloy production. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your material integrity and performance outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















