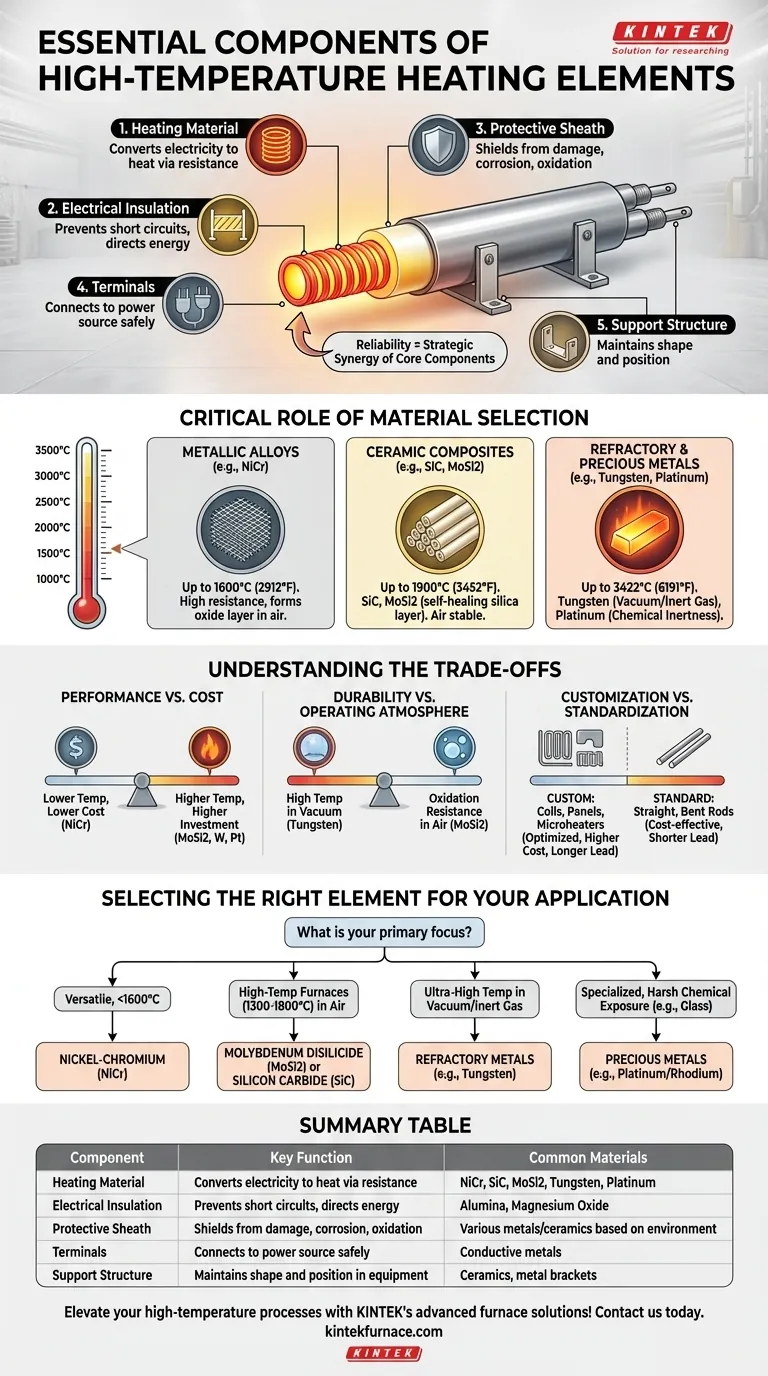
At their core, high-temperature heating elements are engineered systems built from five essential components. These include the active heating material that converts electricity to heat, electrical insulation to direct the current, a protective sheath to shield it from the environment, terminals for power connection, and a support structure to hold it in place.
The reliability of a high-temperature heating element is not defined by any single part, but by the strategic selection and synergy of its core components. The interplay between the heating material, insulation, and sheath is what ultimately determines its performance, lifespan, and suitability for a specific industrial environment.
Deconstructing the Core Components
To understand how these elements function under extreme stress, we must examine the role of each individual part.
The Heating Material: The Engine of Heat Generation
This is the most critical component, responsible for resistive heating. When electrical current passes through it, the material's resistance causes it to heat up. The choice of material dictates the element's maximum operating temperature and overall performance.
Electrical Insulation: Containing and Directing Energy
Materials like alumina or magnesium oxide serve as high-temperature electrical insulators. Their purpose is to prevent the electrical current from short-circuiting to the equipment or the element's sheath, ensuring all energy is converted into usable heat within the heating wire.
The Protective Sheath: A Shield Against the Environment
The sheath encases the heating material and insulation, protecting them from physical damage, corrosion, and oxidation. The material used for the sheath must be able to withstand the application's specific chemical and thermal conditions.
Terminals and Support Structures: The Essential Framework
Terminals provide a safe and reliable point of connection to the power source. Support structures, such as ceramic holders or metal brackets, ensure the element maintains its shape and position within the furnace or equipment, preventing contact that could lead to failure.
The Critical Role of Material Selection
The heart of a heating element's capability lies in its primary heating material. Different materials are chosen for distinct temperature ranges and atmospheric conditions.
Metallic Alloys (e.g., Nickel-Chromium)
Nickel-chromium (NiCr) alloys are the workhorses of industrial heating. They are valued for their high resistance and ability to form a protective oxide layer that prevents degradation in air. They are suitable for applications up to approximately 1600°C (2912°F).
Ceramic Composites (e.g., SiC, MoSi2)
For even higher temperatures in air, ceramic composites are required. Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are common choices. MoSi2, capable of reaching 1900°C (3452°F), is particularly notable for its self-healing properties, where it forms a protective silica layer at high temperatures.
Refractory & Precious Metals (e.g., Tungsten, Platinum)
For the most extreme applications, refractory and precious metals are used. Tungsten can operate up to 3422°C (6191°F) but requires a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere to prevent rapid oxidation. Platinum and its alloys are used in specialized fields like glass manufacturing due to their exceptional chemical resistance, despite their high cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element involves balancing competing priorities. An ideal choice in one scenario may be a poor fit for another.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between an element's maximum operating temperature and its cost. Standard NiCr elements are cost-effective for many applications, while high-performance MoSi2, Tungsten, or Platinum elements represent a significant investment reserved for processes that demand their unique capabilities.
Durability vs. Operating Atmosphere
An element's lifespan is critically dependent on its environment. Tungsten offers the highest temperature ceiling but will fail almost instantly in an oxygen-rich atmosphere. Conversely, the self-healing antioxidant function of MoSi2 relies on the presence of oxygen to form its protective layer.
Customization vs. Standardization
Heating elements can be fabricated in custom shapes—such as coils, panels, or microheaters—to optimize heat transfer for a specific piece of equipment. While this customization enhances thermal efficiency, it often involves higher upfront costs and longer lead times compared to standardized straight or bent rod elements.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated by the specific demands of your process. Use these guidelines to inform your decision.
- If your primary focus is versatile industrial heating below 1600°C: Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) alloys offer an excellent balance of reliable performance and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature furnaces (1300°C - 1800°C) in air: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are the standard due to their stability and resistance to oxidation.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperature in a vacuum or inert gas: Refractory metals like Tungsten are required, as they can withstand extreme heat but degrade rapidly in oxygen.
- If your primary focus is specialized processes with harsh chemical exposure, like glass: Precious metals like Platinum/Rhodium alloys are necessary for their extreme chemical inertness, despite their high cost.
Understanding these components and their material trade-offs empowers you to select a heating element that ensures efficiency, reliability, and success in your specific high-temperature application.
Summary Table:
| Component | Key Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Material | Converts electricity to heat via resistance | NiCr, SiC, MoSi2, Tungsten, Platinum |
| Electrical Insulation | Prevents short circuits, directs energy | Alumina, Magnesium Oxide |
| Protective Sheath | Shields from damage, corrosion, oxidation | Various metals/ceramics based on environment |
| Terminals | Connects to power source safely | Conductive metals |
| Support Structure | Maintains shape and position in equipment | Ceramics, metal brackets |
Elevate your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored heating elements and systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency, reliability, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific application and drive success in your industrial heating projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions



















