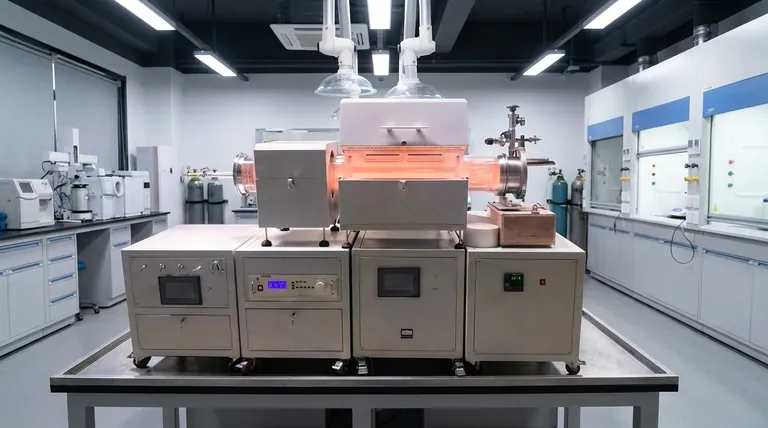
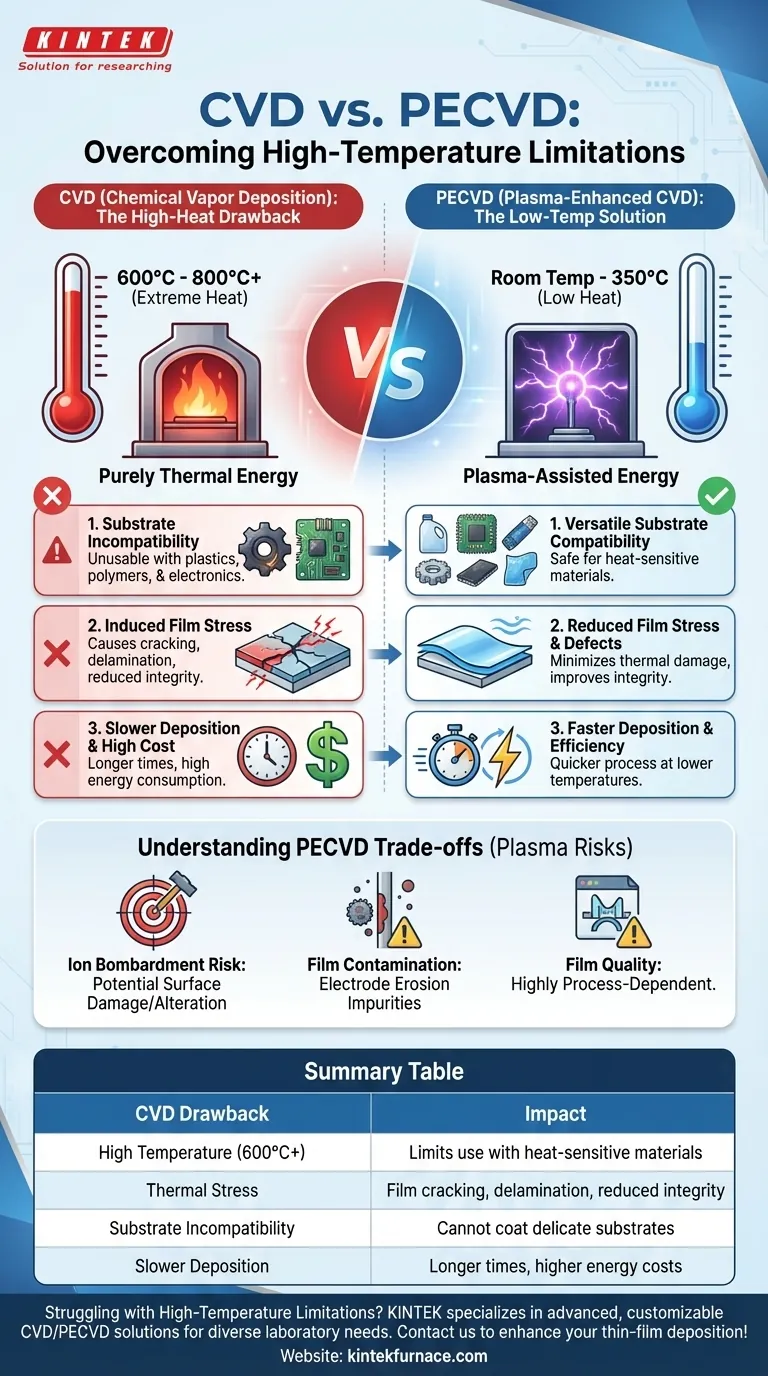
The single greatest drawback of traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) compared to Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is its reliance on extremely high temperatures. This fundamental requirement creates significant limitations, making it incompatible with heat-sensitive materials and introducing thermal stress into the deposited films. PECVD overcomes this by using plasma instead of heat, enabling a much more versatile, low-temperature process.
While both methods deposit thin films, the core trade-off is between temperature and process complexity. CVD's high heat limits its applications but offers a purely thermal reaction, whereas PECVD's low-temperature plasma process provides versatility at the cost of potential plasma-induced side effects.

The Fundamental Difference: Heat vs. Plasma
The drawbacks of CVD stem directly from how it initiates chemical reactions. Understanding this core difference is key to choosing the right process for your application.
The CVD Method: Purely Thermal Energy
Traditional CVD uses high heat, typically between 600°C and 800°C or even higher, to break down precursor gases. The substrate itself is heated, providing the thermal energy needed for the chemical reaction to occur on its surface.
The PECVD Method: Plasma-Assisted Energy
PECVD uses plasma—an ionized gas containing high-energy electrons, ions, and free radicals—to provide the energy for the reaction. This allows deposition to occur at much lower temperatures, often from room temperature to 350°C.
How CVD's High Temperature Becomes a Drawback
The reliance on intense heat is not just a process detail; it has direct, practical consequences that limit the use of conventional CVD.
Substrate Incompatibility
The most significant drawback is the inability to coat temperature-sensitive substrates. Materials like plastics, polymers, or electronic components with pre-existing circuitry would be damaged or destroyed by the high temperatures required for CVD.
PECVD’s low-temperature nature makes it the clear choice for these applications, as it avoids thermal damage.
Induced Film Stress and Defects
High heat can create significant thermal stress in the deposited film as it cools. This occurs due to a mismatch in thermal expansion between the film and the substrate, which can lead to cracking, delamination, or reduced film integrity.
Because PECVD operates at lower temperatures, it significantly reduces thermal stress and the risk of heat-induced defects like lattice mismatch.
Slower Deposition and Higher Costs
While not always the case, traditional CVD can involve longer deposition times and higher costs related to energy consumption for heating and expensive precursors. PECVD can often achieve faster deposition speeds at lower temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PECVD Is Not a Perfect Solution
To make an objective decision, you must also understand the potential drawbacks introduced by PECVD's plasma-based process. These are the trade-offs for its low-temperature advantage.
The Risk of Ion Bombardment
In some PECVD setups (like direct, capacitively coupled reactors), the substrate is directly exposed to the plasma. This can lead to ion bombardment, where high-energy ions physically strike the substrate surface, potentially causing damage or altering its properties.
Potential for Film Contamination
The electrodes used to generate the plasma can erode over time. This erosion can introduce contaminants from the electrode material directly into the deposited film, compromising its purity.
Film Quality Is Process-Dependent
While PECVD produces films with good density and fewer pinholes, the quality is highly dependent on the plasma parameters. Certain film properties, such as wear resistance or barrier performance, may be inferior to those achieved with other methods depending on the specific materials and process conditions used.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the primary constraints and goals of your specific project.
- If your primary focus is substrate integrity: PECVD is the necessary choice for any temperature-sensitive material, including most electronics, plastics, and components with existing circuitry.
- If your primary focus is avoiding plasma-induced effects: Conventional CVD is the better option, provided your substrate is robust enough to handle temperatures exceeding 600°C without damage.
- If your primary focus is film quality and density at low temperatures: PECVD offers an excellent balance, producing high-quality, uniform films without the thermal stress inherent in high-temperature processes.
Ultimately, your choice depends on balancing the need for low-temperature processing against the potential risks introduced by a plasma environment.
Summary Table:
| Drawback | Impact |
|---|---|
| High Temperature (600°C+) | Limits use with heat-sensitive materials like plastics and electronics |
| Thermal Stress | Can cause film cracking, delamination, and reduced integrity |
| Substrate Incompatibility | Inability to coat temperature-sensitive substrates without damage |
| Slower Deposition | May lead to longer process times and higher energy costs |
Struggling with high-temperature limitations in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems, tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Enhance your thin-film deposition processes—contact us today to discuss how our Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and more can benefit your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What is plasma-deposited silicon nitride, and what are its properties? Discover Its Role in Solar Cell Efficiency
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- What are the advantages of using CVD? Achieve High-Purity, Conformal Thin Films for Your Applications



















