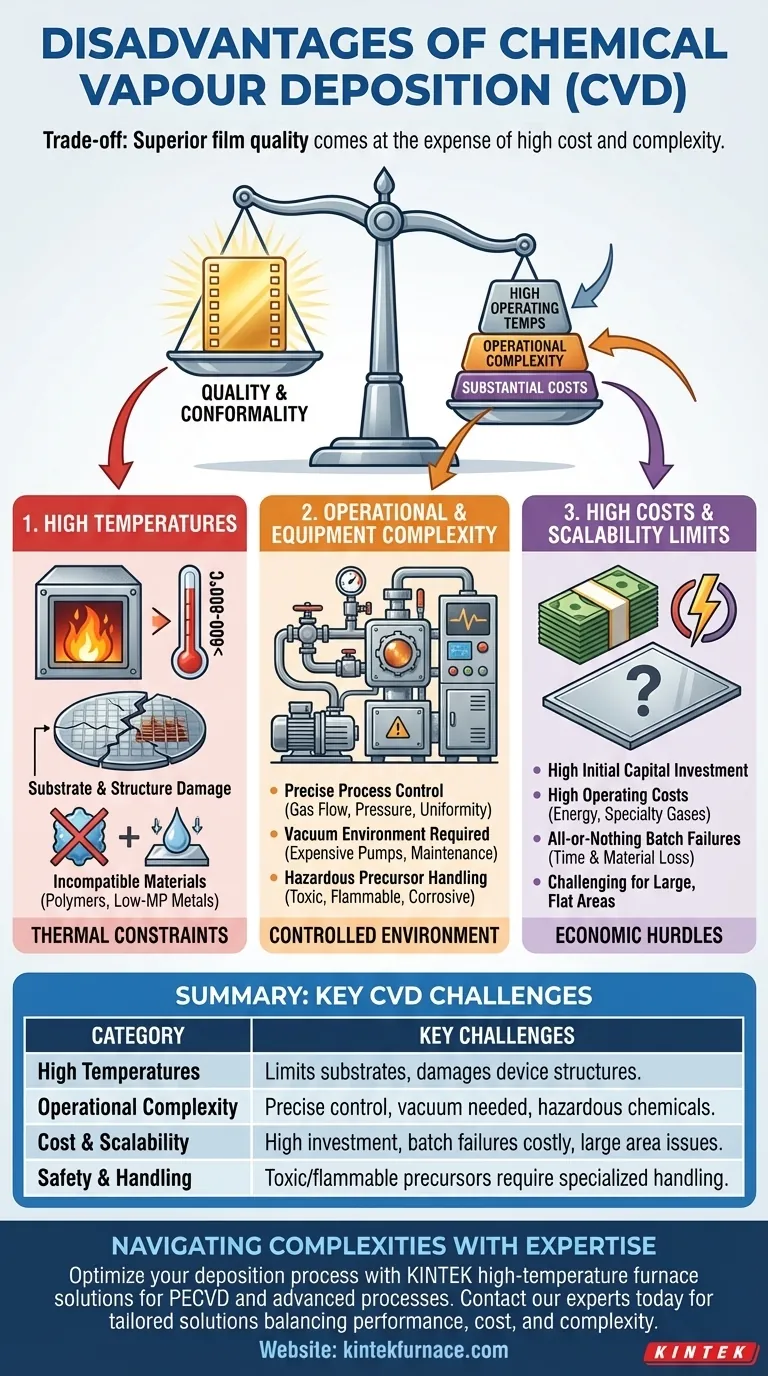
While an exceptional method for creating high-quality thin films, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not a universally ideal solution. Its primary disadvantages stem from high operating temperatures that limit compatible materials, significant equipment and process complexity, and substantial costs. These factors make it a specialized tool rather than a general-purpose coating technique.
The core trade-off of CVD is clear: you gain superior film quality, purity, and conformality at the expense of high energy consumption, operational complexity, and significant capital investment.

The Challenge of High Temperatures
The "chemical" aspect of CVD relies on thermally driven reactions, which introduces a major constraint.
Substrate Material Limitations
Most traditional CVD processes operate at very high temperatures, often exceeding 600-800°C. This heat is necessary to provide the activation energy for precursor chemicals to react and form the desired film on the substrate surface.
This immediately disqualifies substrates with low melting points or that undergo undesirable phase changes, such as polymers, certain plastics, and many types of metals.
Impact on Device Structures
Even for substrates that can withstand the heat, like silicon wafers, the high temperature can be problematic. Pre-existing structures or doped regions on the wafer can be damaged or altered during a high-temperature CVD step, complicating multi-stage fabrication processes.
Operational and Equipment Complexity
CVD is far from a simple "plug-and-play" process, demanding a controlled and costly environment.
Intricate Process Control
Achieving a high-quality, uniform film requires precise, simultaneous control over multiple variables. These include gas flow rates for each precursor, chamber pressure, and temperature uniformity across the entire substrate.
A minor deviation in any of these parameters can lead to defects, poor film quality, or complete failure of the deposition run.
The Need for a Vacuum Environment
CVD is performed in a vacuum chamber to prevent contamination from atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, which could cause unwanted reactions. This necessitates expensive and high-maintenance vacuum pumps, seals, and monitoring equipment.
Handling of Precursor Chemicals
The chemicals used as precursors in CVD are often hazardous. Many are toxic, flammable, or corrosive, requiring specialized storage, delivery systems, and exhaust gas treatment (abatement) to ensure operator safety and environmental compliance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use CVD involves weighing its superior results against significant practical and financial hurdles.
High Initial and Ongoing Costs
The combination of a high-temperature furnace, a robust vacuum system, precise mass flow controllers, and safety equipment makes CVD reactors very expensive to purchase and install.
Furthermore, the process consumes large amounts of energy and requires specialty gases and regular maintenance, leading to high operating costs.
The "All-or-Nothing" Nature
CVD processes can be lengthy, sometimes taking hours to deposit a film of the desired thickness. If a problem occurs midway through—such as a temperature fluctuation or gas flow issue—the entire batch of substrates may be ruined.
This makes process failures extremely costly in terms of both materials and lost production time.
Limitations on Substrate Geometry
While CVD offers excellent conformal coating (uniform coating over 3D structures), scaling the process to coat very large, flat surfaces uniformly can be challenging and economically uncompetitive compared to other methods like sputtering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating these disadvantages against your specific needs is the key to an effective thin-film strategy.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible film purity and crystal quality: CVD is often the superior choice, provided your substrate can tolerate the heat and the budget allows for the cost.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials: You must explore lower-temperature alternatives like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), or Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
- If your primary focus is low cost and high throughput for large areas: CVD is likely unsuitable, and you should investigate methods like sputtering, screen printing, or slot-die coating.
Ultimately, knowing the limitations of CVD is just as important as knowing its strengths, empowering you to select the most effective deposition technology for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| High Temperatures | Limits substrate materials (e.g., polymers), can damage pre-existing device structures. |
| Operational Complexity | Requires precise control of gas flow, pressure, and temperature; needs a vacuum environment. |
| Cost & Scalability | High initial investment and operating costs; batch failures are costly; challenging for large, flat surfaces. |
| Safety & Handling | Involves toxic, flammable, or corrosive precursor chemicals requiring specialized handling and abatement. |
Navigating the complexities of thin-film deposition requires a partner with deep expertise. While CVD has its disadvantages, the right high-temperature furnace solution is critical for successful PECVD or other advanced processes.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements and overcome the limitations of standard equipment.
Let us help you optimize your deposition process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover a tailored solution that balances performance, cost, and complexity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do CVD tube furnace sintering systems play in 2D material synthesis? Enabling High-Quality Atomic Layer Growth
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis



















