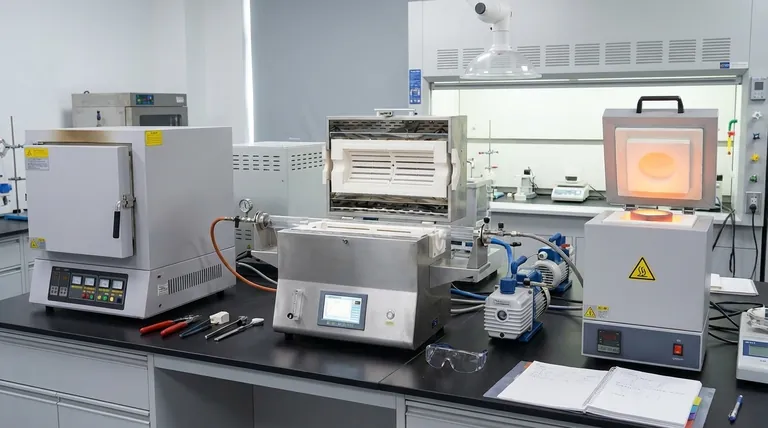
Based on physical shape and appearance, muffle furnaces are primarily categorized into three distinct types: box furnaces, tube furnaces, and crucible furnaces. Each design is purpose-built, with its form directly enabling a specific set of laboratory or industrial functions, from general-purpose heating to precision processing in controlled atmospheres.
The shape of a muffle furnace is not an aesthetic choice; it is the most critical indicator of its intended function. Understanding the differences between box, tube, and crucible designs is essential for selecting the right instrument for your specific heating application.

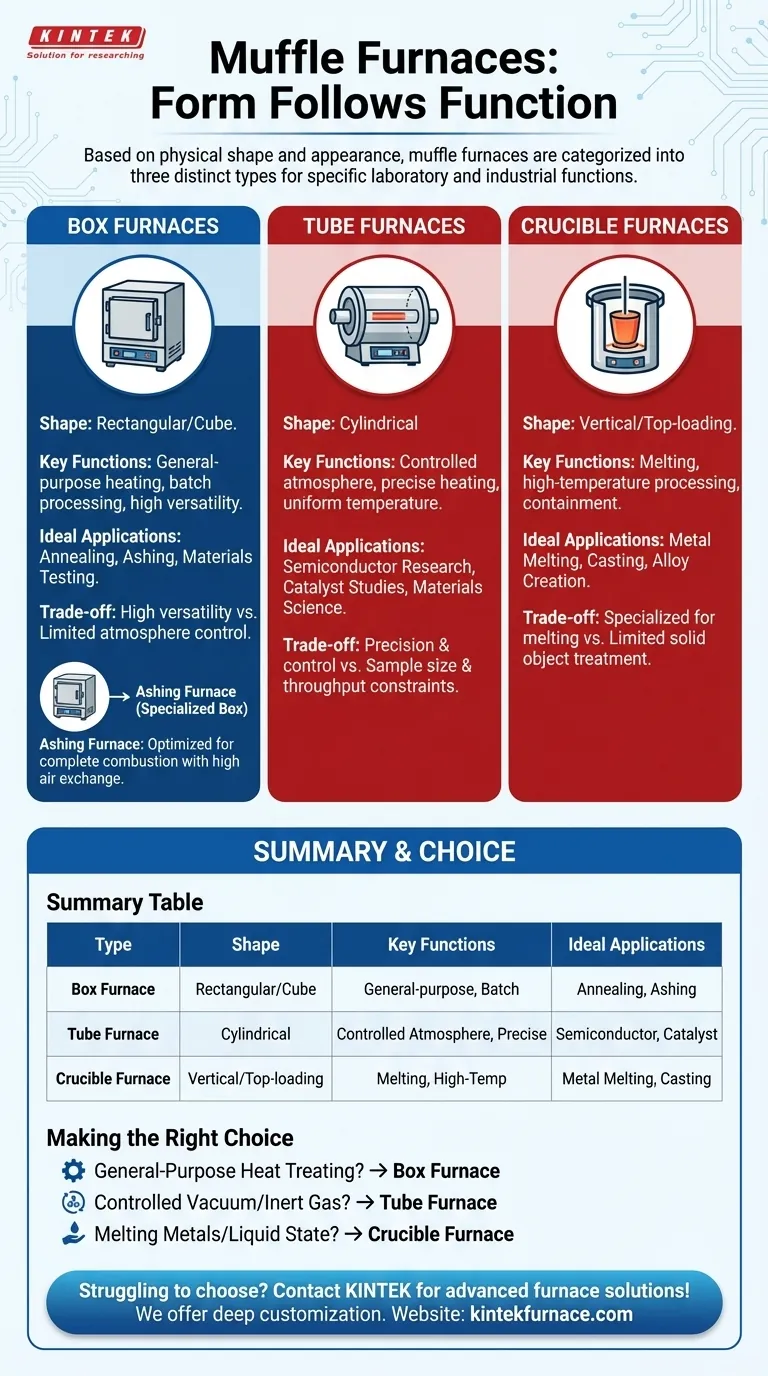
The Primary Furnace Shapes: Form Follows Function
The physical construction of a furnace dictates how it can be used. The chamber's shape determines how samples are loaded, how heat is distributed, and whether the internal atmosphere can be effectively controlled.
Box-Type Furnaces: The General-Purpose Workhorse
A box furnace is the most common type, characterized by a rectangular or cube-shaped chamber with a front-loading door. This design provides maximum versatility.
Its open, accessible chamber is ideal for processing multiple samples of various sizes and shapes simultaneously. This makes it the standard choice for general lab work, materials testing, annealing, and ashing processes.
Tube-Type Furnaces: Precision and Controlled Atmospheres
A tube furnace features a cylindrical heating chamber. A process tube, typically made of ceramic or quartz, is placed inside, and samples are loaded into the tube.
This design excels at creating a tightly controlled atmosphere. The tube can be easily sealed and purged with inert gas or connected to a vacuum system, preventing oxidation and contamination. This makes it essential for sensitive processes in semiconductor, materials science, and catalyst research.
Crucible Furnaces: For Melting and High-Volume Processing
Crucible furnaces are typically top-loading vertical chambers designed specifically to hold a crucible, which is a container used for melting metals, alloys, and other materials.
Their primary function is to contain and heat liquid materials to very high temperatures safely. Unlike box furnaces designed for heat-treating solid objects, crucible furnaces are optimized for melting and casting applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace shape involves balancing versatility against specialization. No single design is superior for all tasks; each comes with inherent strengths and limitations.
Box Furnace: Versatility vs. Atmosphere Control
The key strength of a box furnace is its flexibility to handle diverse sample loads.
However, its large front door and chamber volume make it difficult and inefficient to maintain a high-purity vacuum or a perfectly controlled inert gas atmosphere compared to a sealed tube furnace.
Tube Furnace: Precision vs. Sample Constraints
The tube furnace offers unparalleled control over temperature uniformity and atmosphere. This precision is critical for advanced applications.
The trade-off is sample size and throughput. You are strictly limited by the diameter of the process tube, making it impractical for large components or high-volume batch processing of irregularly shaped items.
Ashing Furnace: A Specialized Box Design
An ashing furnace is a specific variant of a box furnace designed for loss-on-ignition testing.
It is engineered with a high rate of air exchange to completely combust organic materials, leaving only inorganic ash. While shaped like a box furnace, its specialized airflow system makes it unsuitable for applications requiring a static or controlled atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements should be the sole driver of your decision. Consider the material, the process, and the desired outcome to select the appropriate furnace geometry.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating, ashing, or drying various samples: A box-type furnace offers the greatest versatility and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is processing materials under a vacuum or specific inert gas: A tube-type furnace is the only design that can reliably provide the required atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or holding materials in a liquid state: A top-loading crucible furnace is specifically engineered for this high-temperature task.
By understanding that a furnace's shape is defined by its intended function, you can select the precise tool required for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Type | Shape | Key Functions | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Box Furnace | Rectangular/Cube | General-purpose heating, batch processing | Annealing, ashing, materials testing |
| Tube Furnace | Cylindrical | Controlled atmosphere, precise heating | Semiconductor research, catalyst studies |
| Crucible Furnace | Vertical/Top-loading | Melting, high-temperature processing | Metal melting, casting |
Struggling to choose the right muffle furnace for your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your experimental requirements—whether you need versatile box furnaces, precise tube furnaces, or specialized crucible designs. Don't let equipment limitations hold you back; contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















