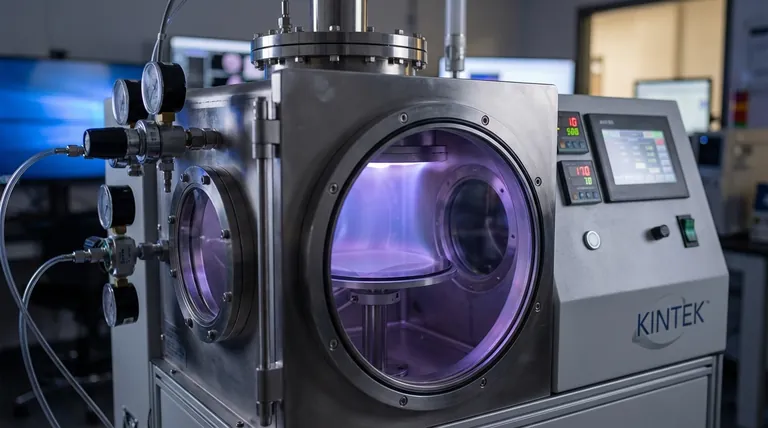
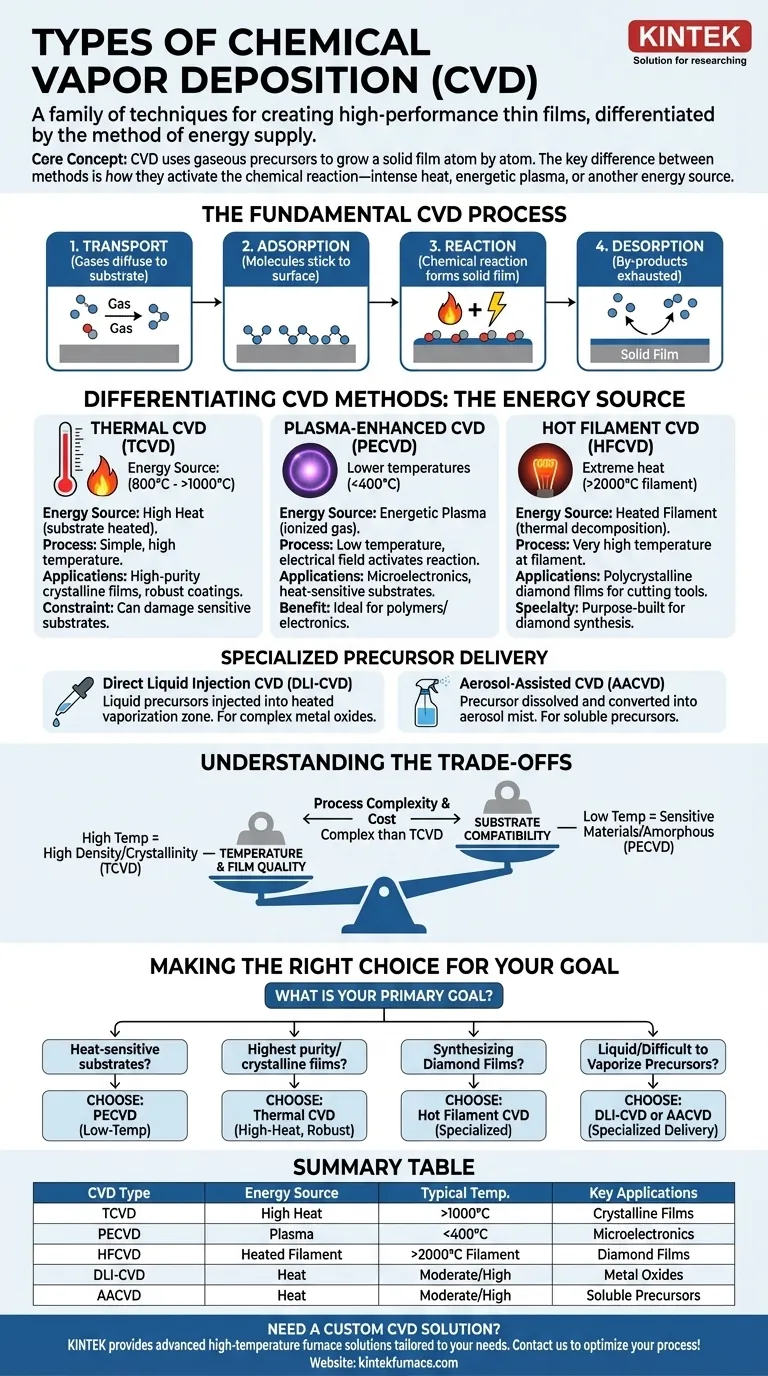
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not a single process but a family of techniques used to create high-performance thin films. The different types of CVD are distinguished primarily by the method used to supply energy to the precursor chemicals, which dictates the process temperature, the types of materials that can be deposited, and the substrates that can be coated. Key variations include high-temperature Thermal CVD, lower-temperature Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), and specialized methods like Hot Filament CVD.
The crucial insight is that selecting a CVD "type" is a strategic choice driven by your substrate's heat tolerance and the desired film properties. The fundamental difference between methods lies in how they activate the chemical reaction—be it with intense heat, energetic plasma, or another energy source.

The Fundamental CVD Process
Before exploring the variations, it's essential to understand the universal steps that define all CVD processes. This is a surface-based technique where a solid film is grown atom by atom from gaseous precursors.
The Four Core Stages
The deposition process consistently follows four main stages:
- Transport: Precursor gases are introduced into a chamber and diffuse toward the substrate surface.
- Adsorption: The precursor gas molecules stick to the substrate surface.
- Reaction: With sufficient energy (from heat or plasma), a chemical reaction occurs on the surface, decomposing the precursors and forming the solid film.
- Desorption: Gaseous by-products from the reaction detach from the surface and are exhausted from the chamber.
Differentiating CVD Methods: The Energy Source
The "type" of CVD is defined by how it supplies the energy needed for the surface reaction in stage three. This choice has profound implications for the entire process.
Thermal CVD (TCVD)
Thermal CVD is the classic and most straightforward form. The energy required to break down the precursor gases comes directly from high temperatures, typically by heating the substrate itself to several hundred or even over a thousand degrees Celsius.
This method is robust and capable of producing very high-purity, crystalline films. Its primary limitation is the extreme heat, which can damage or destroy thermally sensitive substrates like plastics or certain electronic components.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
PECVD overcomes the temperature limitations of TCVD. Instead of relying solely on heat, this method uses an electrical field to generate plasma (an ionized gas) inside the reaction chamber.
This highly energetic plasma provides the activation energy to drive the chemical reaction. This allows for deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures, making PECVD ideal for coating heat-sensitive materials. It is a cornerstone of modern microelectronics for depositing materials like silicon nitride.
Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD)
HFCVD is a specialized form of thermal CVD. It uses an electrically heated metal filament (often tungsten) placed near the substrate to thermally decompose the precursor gases.
The filament reaches very high temperatures (over 2000°C), creating highly reactive chemical species. This method is particularly dominant in the synthesis of high-quality polycrystalline diamond films for cutting tools and thermal management applications.
Specialized Precursor Delivery Methods
Some CVD techniques are defined by how they introduce precursors that aren't naturally gases at room temperature.
- Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLI-CVD): This method is designed for liquid precursors. The liquid is precisely injected into a heated vaporization zone, where it turns into a gas before reaching the substrate. It is often used for depositing complex metal oxides.
- Aerosol-Assisted CVD (AACVD): In this technique, the precursor is first dissolved in a solvent and then converted into a fine mist or aerosol. This aerosol is then transported into the heated reaction chamber, where the solvent evaporates and the precursor deposits.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD method involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" type; the optimal choice depends entirely on the application's specific constraints.
Temperature vs. Film Quality
The most significant trade-off is between processing temperature and the resulting film's properties. High-temperature methods like TCVD often produce films with higher density and crystallinity. Low-temperature PECVD allows for coating sensitive materials but may result in films with different structural properties, such as being amorphous rather than crystalline.
Substrate Compatibility
The substrate's material properties are a hard constraint. If your substrate cannot withstand 800°C, TCVD is not a viable option, making a low-temperature process like PECVD the only choice.
Process Complexity and Cost
Generally, TCVD systems are simpler and less expensive than PECVD systems, which require sophisticated RF power supplies and plasma control hardware. Specialized methods like DLI-CVD add further complexity related to liquid handling and vaporization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary requirement will guide your selection of a CVD method.
- If your primary focus is depositing on heat-sensitive substrates like polymers or complex electronics: PECVD is your ideal starting point due to its low-temperature processing capabilities.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest-purity crystalline films and your substrate can withstand intense heat: Thermal CVD offers a robust and often simpler path to superior material properties.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing synthetic diamond films: Hot Filament CVD is the purpose-built and industry-standard method for this specific application.
- If your primary focus is using precursors that are liquid or difficult to vaporize: Look to specialized delivery systems like DLI-CVD or AACVD to enable your process.
Ultimately, understanding the different types of CVD is about understanding how to best deliver energy to drive a reaction for your specific material and substrate.
Summary Table:
| CVD Type | Energy Source | Typical Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD (TCVD) | High Heat | Several hundred to >1000°C | High-purity crystalline films, robust coatings |
| Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Plasma | Low temperatures (e.g., <400°C) | Microelectronics, heat-sensitive substrates |
| Hot Filament CVD (HFCVD) | Heated Filament | Filament >2000°C, substrate varies | Diamond films for cutting tools, thermal management |
| Direct Liquid Injection CVD (DLI-CVD) | Heat (vaporization) | Moderate to high | Complex metal oxides, liquid precursors |
| Aerosol-Assisted CVD (AACVD) | Heat (evaporation) | Moderate to high | Soluble precursors, specialized coatings |
Need a Custom CVD Solution for Your Lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're working with heat-sensitive substrates or aiming for high-purity films, we can help optimize your process. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















