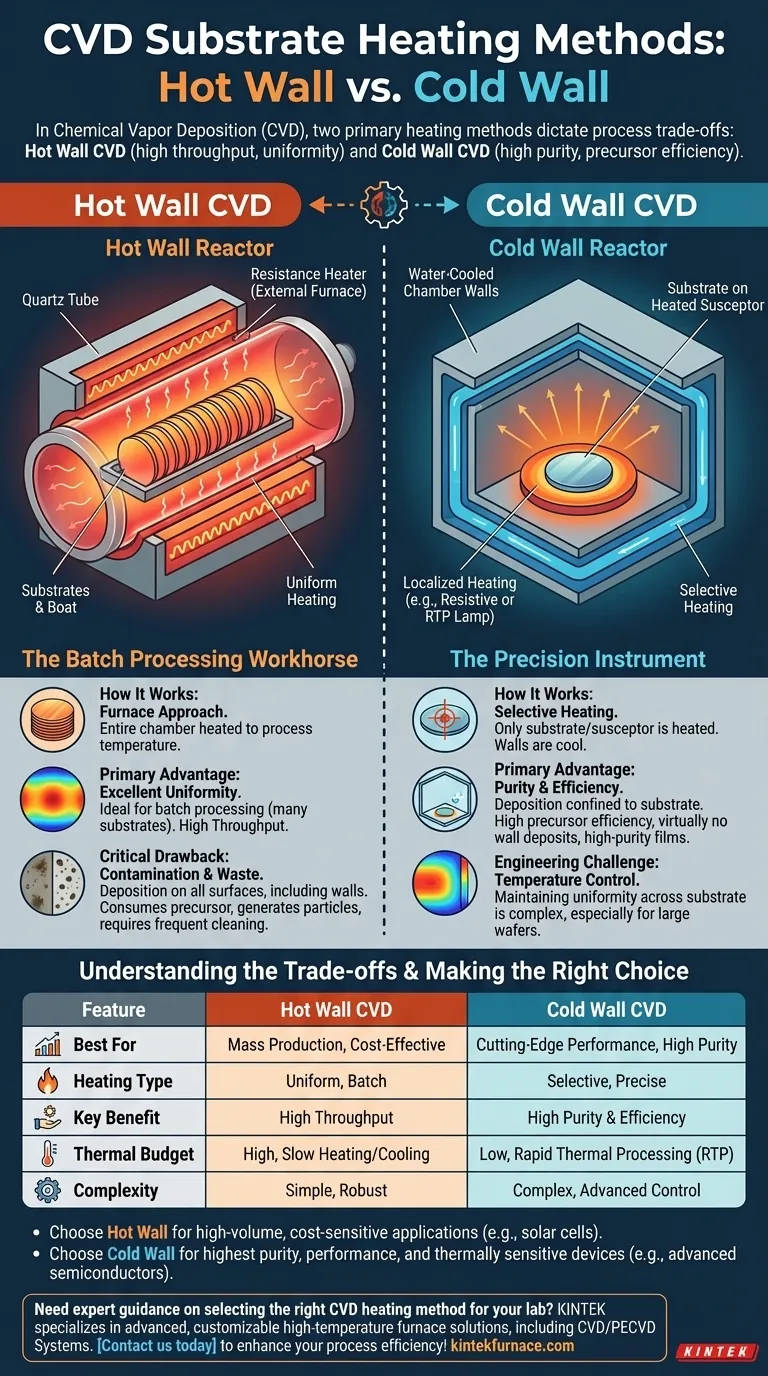
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), there are two fundamental methods for heating the substrate: Hot Wall CVD and Cold Wall CVD. In a hot wall system, the entire reaction chamber is heated externally, meaning the walls and the substrate are at the same high temperature. Conversely, in a cold wall system, energy is applied directly to the substrate or its holder, leaving the chamber walls intentionally cool.
The choice between a hot wall and cold wall reactor is a primary engineering decision. It dictates a fundamental trade-off between the high throughput and thermal uniformity of hot wall systems and the superior purity and precursor efficiency of cold wall systems.

Hot Wall CVD: The Batch Processing Workhorse
Hot wall CVD is a classic approach, widely used for its ability to process many substrates simultaneously with excellent temperature consistency.
How It Works: The Furnace Approach
A hot wall reactor typically consists of a quartz tube placed inside a larger resistance-heated furnace. The furnace heats the entire tube and everything inside it to the required process temperature.
This design ensures that the gas molecules and all internal surfaces, including the substrates, are in thermal equilibrium.
Primary Advantage: Excellent Uniformity
Because the entire chamber acts as a uniform heat source, hot wall systems provide exceptional temperature stability and uniformity across a large area. This makes them ideal for batch processing, where dozens or even hundreds of wafers can be coated at once.
The Critical Drawback: Contamination and Waste
The main disadvantage is that deposition occurs everywhere, not just on the substrates. Material deposits on the chamber walls, consuming expensive precursor gases and flaking off as particles that can contaminate the substrates. This also necessitates frequent, time-consuming cleaning cycles.
Cold Wall CVD: The Precision Instrument
Cold wall CVD was developed to overcome the purity and efficiency limitations of the hot wall design. It is the dominant method for manufacturing high-performance semiconductor devices.
How It Works: Selective Substrate Heating
In a cold wall reactor, only the substrate and its holder (known as a susceptor) are heated. The chamber walls are kept near room temperature, often with active water-cooling.
Heating can be achieved through several methods, such as passing an electric current through the susceptor (resistive heating) or using high-intensity lamps to heat the substrate directly (radiant or RTP heating).
Primary Advantage: Purity and Efficiency
Because the chamber walls are cool, chemical reactions and deposition are confined almost exclusively to the hot substrate surface. This drastically improves precursor efficiency and virtually eliminates particle contamination from wall deposits, leading to higher-purity films.
The Engineering Challenge: Temperature Control
The primary challenge in a cold wall system is maintaining perfect temperature uniformity across the entire substrate, especially as wafer sizes increase. Temperature gradients can lead to variations in film thickness and properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is universally superior; the optimal choice depends entirely on the process goals and economic constraints.
Throughput vs. Purity
Hot wall CVD excels at high-volume, cost-sensitive applications where absolute film purity is secondary. Think of coatings for solar cells or basic semiconductor layers.
Cold wall CVD is essential for applications demanding the highest purity and performance, such as advanced logic and memory chips, where even minimal contamination can cause device failure.
Thermal Budget and Process Speed
Cold wall systems have a much lower thermal mass, allowing for very rapid heating and cooling. This enables Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP), which minimizes the total time a substrate spends at high temperatures—a critical factor for sensitive, multi-layered devices. Hot wall furnaces, by contrast, take hours to heat up and cool down.
Complexity and Cost
A simple hot wall tube furnace is a relatively straightforward and robust piece of equipment. Cold wall systems are inherently more complex, requiring sophisticated heating elements, cooling channels, and advanced temperature monitoring to manage uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct heating strategy, you must first define your primary objective for the deposition process.
- If your primary focus is mass production and cost-effectiveness: Hot wall CVD is almost always the superior choice for its unparalleled batch processing capability.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge device performance and film purity: Cold wall CVD provides the essential control over contamination and process efficiency.
- If you are working with thermally sensitive materials: A cold wall system offers precise control over the thermal budget, protecting delicate structures from prolonged heat exposure.
Ultimately, choosing your heating method is the first step in defining your process's balance between manufacturing scale and film quality.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Wall CVD | Uniform heating, batch processing, lower cost | High-throughput applications like solar cells |
| Cold Wall CVD | High purity, precise control, rapid heating | High-performance devices like semiconductors |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right CVD heating method for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, with deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is MPCVD considered a cornerstone of modern materials science and engineering? Unlock High-Purity Materials for Innovation
- What are the two main methods of synthetic diamond production? Discover HPHT vs. CVD for Lab-Grown Gems
- How is MPCVD used in manufacturing polycrystalline diamond optical components? Achieve Superior Optical Performance
- Who should perform maintenance on MPCVD equipment? Trust Certified Experts for Safety and Precision
- What are the key advantages of MPCVD in diamond synthesis? Achieve High-Purity, Scalable Diamond Production



















