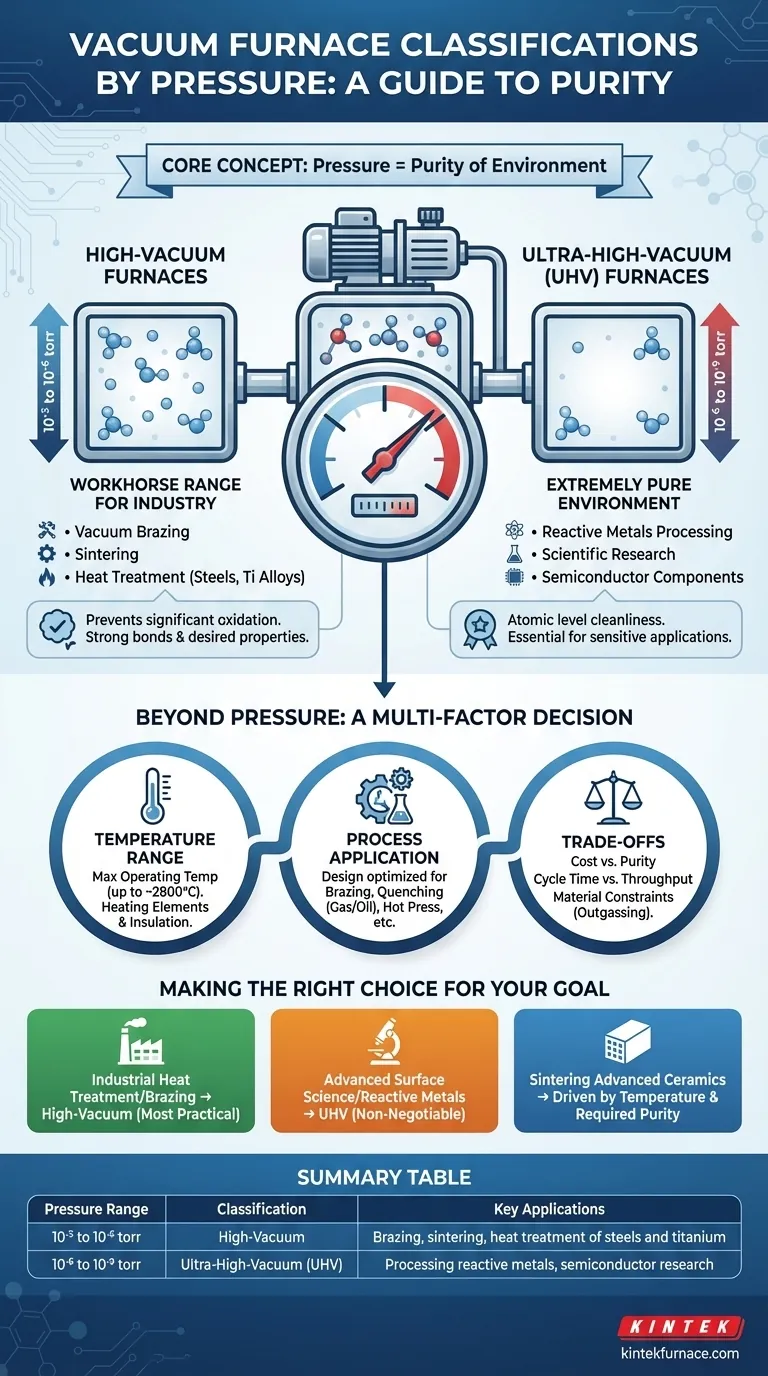
At its core, a vacuum furnace's classification by pressure defines the purity of its processing environment. Vacuum furnaces are divided into two primary categories based on this metric: high-vacuum furnaces, which operate between 10⁻³ and 10⁻⁶ torr, and ultra-high-vacuum (UHV) furnaces, which operate at pressures from 10⁻⁶ down to 10⁻⁹ torr. This distinction is critical as it directly impacts the types of materials and processes the furnace can handle.
The question of vacuum classification is not just about pressure ranges; it's about controlling contamination. Choosing between high-vacuum and ultra-high-vacuum is a decision about how completely you need to remove reactive atmospheric gases to achieve your desired material properties.

Why Pressure Level is a Critical Specification
The primary purpose of a vacuum is to create a controlled, inert environment. At the high temperatures used in heat treating, brazing, and sintering, materials become highly reactive with atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. The vacuum level determines just how "clean" this environment is.
The Role of Vacuum: More Than Just Empty Space
A vacuum is a space with gas pressure far below atmospheric pressure. By removing air, you remove the molecules that can cause unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation, on the surface of your material.
A lower pressure number means fewer residual gas molecules and, therefore, a purer environment for your process.
High-Vacuum Furnaces (10⁻³ to 10⁻⁶ torr)
This is the workhorse range for a vast number of industrial applications. It provides an environment clean enough for processes like vacuum brazing, sintering, and the bright heat treatment of most tool steels, stainless steels, and titanium alloys.
This level of vacuum is sufficient to prevent significant oxidation and ensure clean, strong bonds and desired metallurgical properties for many common materials.
Ultra-High-Vacuum (UHV) Furnaces (10⁻⁶ to 10⁻⁹ torr)
The UHV range represents an extremely pure environment, reserved for the most sensitive applications. These furnaces are used for processing highly reactive metals or for scientific research where surface cleanliness at the atomic level is paramount.
Achieving UHV requires more advanced pumping systems, specialized construction materials, and longer pump-down times. It is essential for advanced materials science, semiconductor components, and certain high-purity alloy development.
Beyond Pressure: A Multi-Factor Decision
While pressure is a key classifier, selecting the right furnace involves a holistic look at several interconnected specifications. The pressure range you need is often dictated by these other factors.
Temperature Range: The Second Key Axis
Furnaces are also classified by their maximum operating temperature, which is determined by the heating elements and insulation used.
- Low-Temperature (up to ~1000°C): Often use nickel-chromium heating elements.
- Medium-Temperature (up to ~1600°C): Typically use molybdenum or silicon carbide elements.
- High-Temperature (up to ~2800°C): Require graphite or tungsten elements.
The temperature required for your process (e.g., sintering a ceramic vs. brazing an aluminum part) is a primary factor that will narrow your furnace choices.
Process Application and Quenching Method
Different applications require different furnace designs. For example, a vacuum brazing furnace is optimized for joining components, while a gas quenching furnace is designed to rapidly cool parts with high-pressure inert gas to achieve specific hardness.
Other specialized types include oil quenching furnaces for specific steels and vacuum hot press furnaces for sintering powders under simultaneous heat and pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a vacuum level is a balance of technical requirements and practical constraints. Over-specifying your vacuum needs can lead to unnecessary costs and process inefficiencies.
Cost vs. Purity
Achieving a lower pressure is exponentially more expensive. UHV systems require multi-stage pumping systems (e.g., turbomolecular and ion pumps), superior seals, and more rigorous manufacturing, all of which dramatically increase cost.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Pumping down to UHV levels takes significantly more time than reaching a high-vacuum state. For industrial production, a longer cycle time means lower throughput. Often, the most economical choice is a furnace that provides a vacuum level that is "good enough" for the process, not the absolute purest possible.
Material and Process Constraints
The materials being processed can also limit the achievable vacuum. Some materials can "outgas" at high temperatures, releasing trapped gases and making it difficult to reach or maintain a deep vacuum. The furnace design must account for this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be guided by the specific demands of your material and process, not by pursuing the lowest possible pressure.
- If your primary focus is industrial heat treatment or brazing of standard alloys: A high-vacuum furnace (10⁻³ to 10⁻⁶ torr) is almost always the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive materials or conducting advanced surface science: An ultra-high-vacuum (UHV) system is non-negotiable to achieve the required purity.
- If your primary focus is sintering advanced ceramics or composites: Your decision will be driven first by the required temperature range, then by the vacuum level needed to prevent contamination for that specific material.
Ultimately, selecting the right vacuum furnace is about precisely matching the environment's purity and temperature to your material's processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Pressure Range | Classification | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 10⁻³ to 10⁻⁶ torr | High-Vacuum | Brazing, sintering, heat treatment of steels and titanium |
| 10⁻⁶ to 10⁻⁹ torr | Ultra-High-Vacuum (UHV) | Processing reactive metals, semiconductor research |
Need a custom vacuum furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise matching to your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior material processing results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















