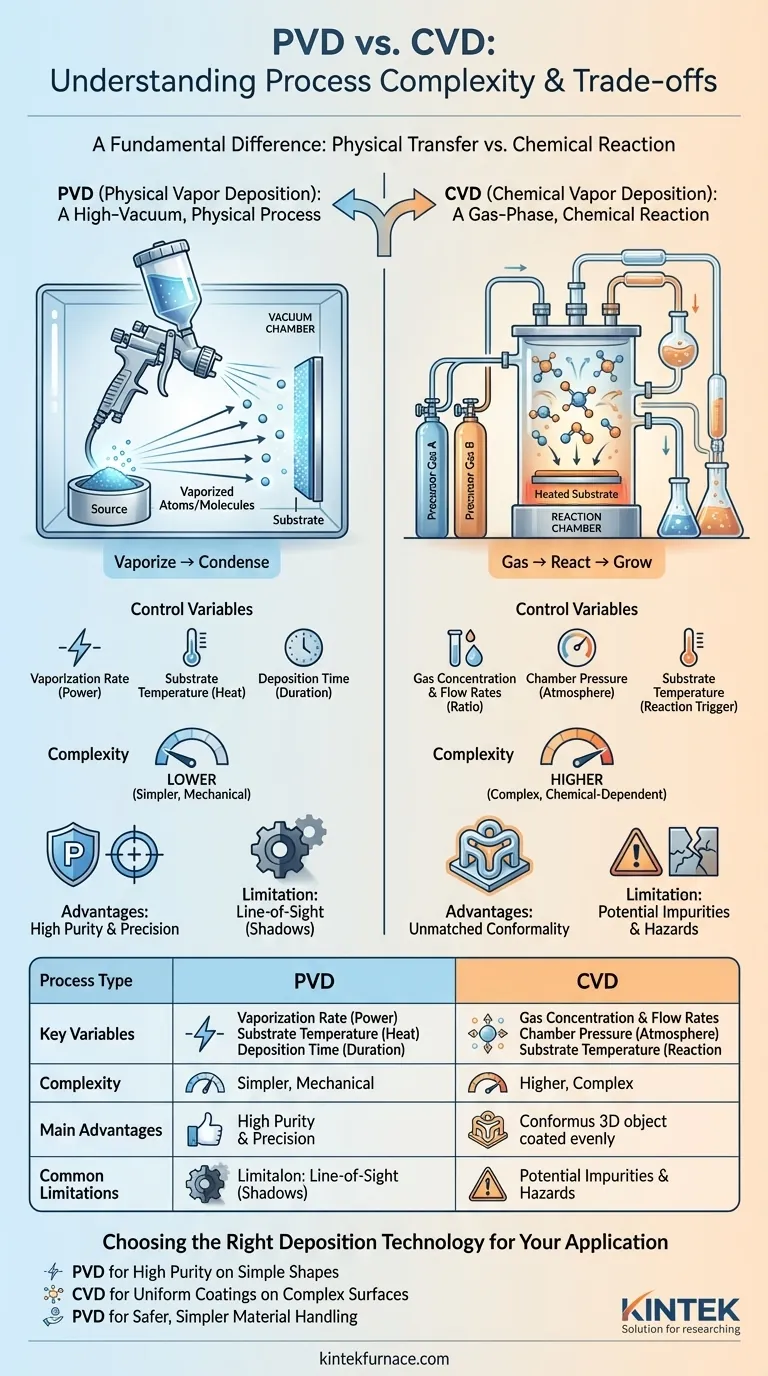
In essence, the complexity difference between PVD and CVD is fundamental, stemming from the very nature of each process. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a comparatively simpler, mechanical-like process that physically transfers a solid material onto a surface in a vacuum. In contrast, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is an inherently more complex process that uses chemical reactions between precursor gases to grow a new material directly on the substrate.
The decision between PVD and CVD is not about choosing the "simpler" option, but about aligning your goals with the right set of process controls. PVD's simplicity offers purity and precision, while CVD's complexity is necessary to achieve superior coating uniformity on intricate geometries.

The Core Difference: Physical vs. Chemical Deposition
To understand the complexity, we must first look at the mechanism. The two methods build thin films in fundamentally different ways, which dictates every other aspect of the process.
PVD: A High-Vacuum, Physical Process
PVD operates on a straightforward principle: vaporize and condense. A solid source material is vaporized into atoms or molecules inside a high-vacuum chamber.
These vaporized particles then travel in a straight line—often called "line-of-sight"—until they strike the substrate, where they condense to form a thin film. The process is analogous to spray painting, but on an atomic level.
CVD: A Gas-Phase, Chemical Reaction
CVD is a process of synthesis. It introduces one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing the substrate.
Through heat, light, or plasma, these gases react or decompose on the substrate's surface, forming a solid film of a new material. The process doesn't just move material; it creates it on-site through a controlled chemical reaction.
A Breakdown of Process Complexity
The difference between a physical transfer and a chemical reaction creates a significant gap in the number and sensitivity of the variables that must be controlled.
Control Variables in PVD
Controlling a PVD process is more direct. The primary variables are:
- Vaporization Rate: How quickly the source material is turned into vapor.
- Substrate Temperature: Influences the film's adhesion and structure.
- Deposition Time: Directly controls the final thickness.
While precision is crucial, these parameters are largely physical and more intuitive to manage.
Control Variables in CVD
CVD requires managing a delicate chemical environment. The key variables include:
- Gas Concentration and Flow Rates: The precise ratio of precursor gases is critical to the chemical reaction.
- Chamber Pressure: Affects gas transport and reaction kinetics.
- Substrate Temperature: The primary driver for initiating the chemical reaction on the surface.
Balancing these interdependent variables to achieve a stable and repeatable reaction is the source of CVD's complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Simplicity vs. Performance
The added complexity of CVD is not without purpose. It unlocks capabilities that PVD cannot easily achieve, leading to a clear set of trade-offs.
PVD's Advantage: Purity and Precision
Because PVD physically transfers a source material with high purity, the resulting film is also exceptionally pure. It avoids the byproducts and potential impurities that can arise from chemical reactions. This makes PVD ideal for applications demanding precise control over material composition.
CVD's Advantage: Unmatched Conformality
This is the primary reason to choose CVD despite its complexity. Since the precursor gas flows around an object before reacting, CVD can deposit a perfectly uniform film on highly complex, three-dimensional shapes with hidden surfaces. PVD, being a line-of-sight process, struggles to coat these intricate geometries evenly.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
PVD's primary limitation is its line-of-sight nature, which leads to thinner coatings or "shadows" on complex parts.
CVD's main challenge is managing the chemical reactions, which can introduce impurities or structural defects into the film if not perfectly controlled. The precursor gases can also be toxic or hazardous, adding safety and handling complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific requirements of the component you are coating.
- If your primary focus is high-purity films on relatively simple geometries: PVD's straightforward physical process is the more efficient and often more cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform coating on complex, non-line-of-sight surfaces: The controlled chemical reactions of CVD are necessary, and its process complexity is a justifiable trade-off.
- If your primary focus is minimizing process hazards and material handling: PVD is generally simpler and safer due to the absence of volatile and often hazardous chemical precursors.
Understanding this fundamental trade-off between physical simplicity and chemical versatility is the key to selecting the optimal deposition technology for your specific goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical transfer in vacuum | Chemical reaction with gases |
| Key Control Variables | Vaporization rate, substrate temperature, deposition time | Gas concentration/flow rates, chamber pressure, substrate temperature |
| Complexity Level | Lower (simpler, mechanical-like) | Higher (complex, chemical-dependent) |
| Main Advantages | High purity, precise control, safer handling | Superior conformality on complex geometries |
| Common Limitations | Line-of-sight deposition, shadows on intricate parts | Potential impurities, hazardous precursors, more variables to manage |
Struggling to choose between PVD and CVD for your lab's coating applications? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental requirements, whether you prioritize purity, uniformity, or safety. Let us help you optimize your deposition processes—contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why Use PECVD for Monolithic Integrated Chip Isolation Layers? Protect Your Thermal Budget with High-Quality SiO2
- What are the technical advantages of using a CVD system? Optimize Carbon Nanotube Growth for Thermal Conductivity
- What is the necessity of high-bias gas ion cleaning? Achieve Atomic-Level Coating Adhesion
- What is the function of a PECVD system in the passivation of UMG silicon solar cells? Enhance Efficiency with Hydrogen
- What methods are used to analyze and characterize graphene samples? Unlock Key Techniques for Accurate Material Analysis



















