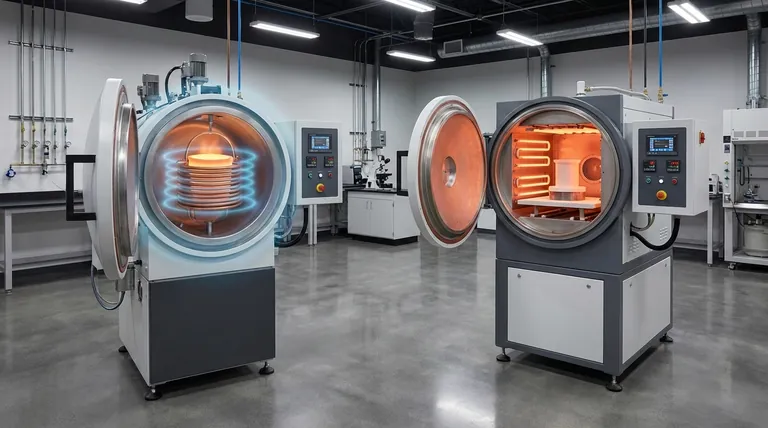
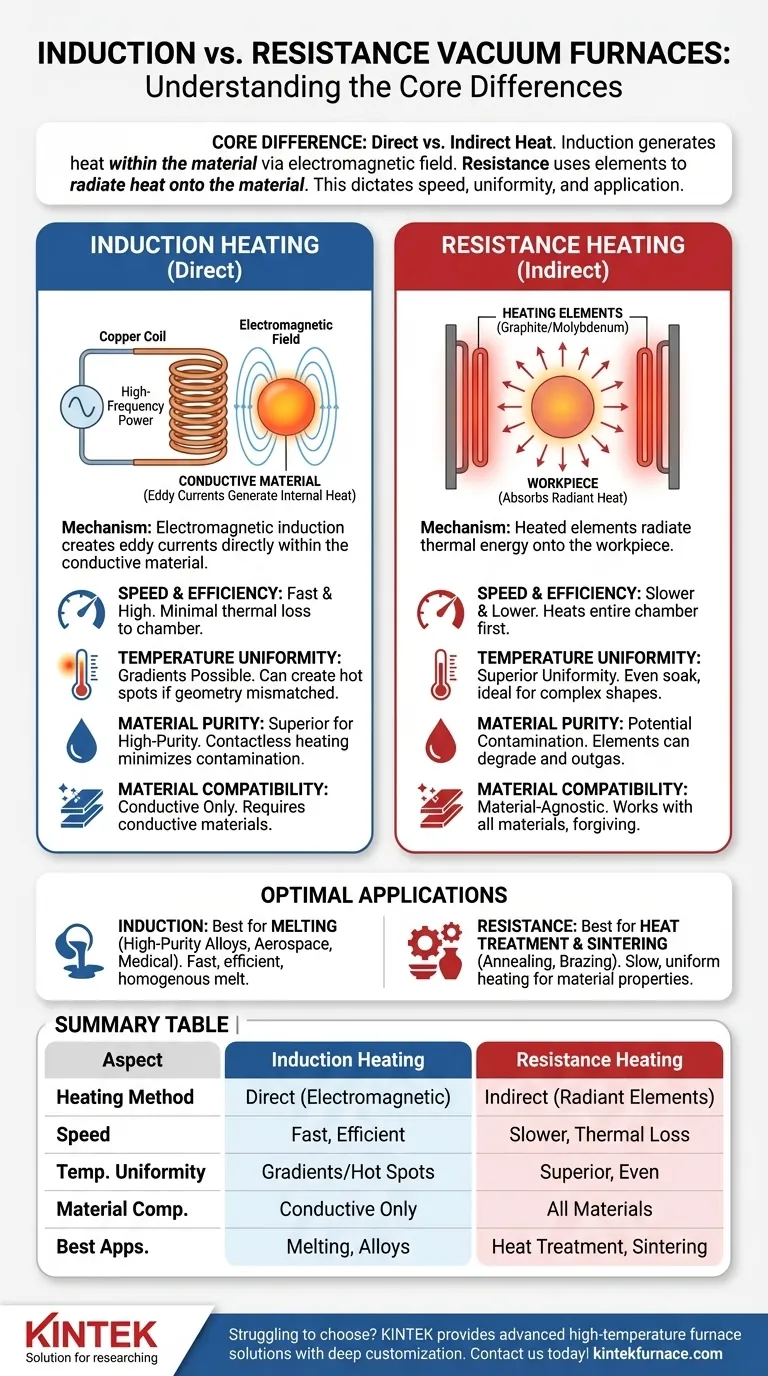
At their core, induction-heated and resistance-heated vacuum furnaces are distinguished by their fundamental method of heat transfer. Induction heating generates heat directly within the material using an electromagnetic field, while resistance heating uses heated elements to radiate heat onto the material. This core difference dictates their efficiency, speed, and ideal applications.
Choosing between these technologies is a decision between speed and uniformity. Induction offers rapid, direct heating ideal for melting applications, whereas resistance provides slower, more uniform heat transfer perfectly suited for heat treatments and sintering.

The Core Mechanism: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
The most critical distinction is not the furnace itself, but how energy is delivered to the workpiece. This determines the entire process dynamic.
How Resistance Heating Works
A resistance-heated furnace operates much like a conventional oven. Electrical current passes through heating elements, typically made of graphite or molybdenum wire.
These elements become extremely hot and radiate thermal energy throughout the furnace chamber. The workpiece absorbs this radiant heat indirectly, gradually rising to the target temperature.
How Induction Heating Works
An induction furnace uses a powerful, high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a strong, fluctuating electromagnetic field around the workpiece.
This field induces powerful electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the conductive material of the workpiece itself. The material's own internal resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat from the inside out.
Key Differences in Application and Performance
The choice between induction and resistance is driven entirely by the process requirements. Each method excels in different scenarios.
Speed and Efficiency
Induction is significantly faster and more energy-efficient. Because it heats the material directly, very little energy is wasted heating the furnace chamber walls or atmosphere. This makes it ideal for rapid melting cycles.
Resistance heating is slower and less efficient by comparison. The entire chamber and its components must be heated before the workpiece can reach its target temperature, resulting in greater thermal loss.
Temperature Uniformity
Resistance heating provides superior temperature uniformity. The radiant elements create an even "soak," ensuring that the entire workpiece, including complex shapes, reaches a stable and consistent temperature. This is critical for processes like annealing.
Induction heating can create temperature gradients. Heat is concentrated where the electromagnetic field is strongest, which can lead to hot spots if the coil and part geometry are not perfectly matched.
Material Purity and Contamination
In a vacuum environment, induction heating offers a distinct advantage for high-purity applications. Since the heating mechanism is contactless, there are no heating elements that can degrade and release contaminants (outgas) into the melt.
This makes vacuum induction furnaces essential for producing high-purity alloys for the aerospace and medical industries, where material integrity is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior. The optimal choice depends on balancing performance characteristics against your specific goal.
Best for Melting
For melting metals, induction heating is the clear choice. Its speed, efficiency, and ability to stir the molten metal electromagnetically result in a faster, cleaner, and more homogenous melt.
Best for Heat Treatment and Sintering
For processes like annealing, brazing, and sintering ceramics, resistance heating is preferred. Its ability to deliver slow, uniform heating and hold a stable temperature across the entire part is paramount for achieving the desired material properties without distortion.
Material and Geometry Constraints
Induction heating only works with electrically conductive materials. Furthermore, the induction coil must be carefully designed to match the part's geometry for effective heating.
Resistance heating is material-agnostic and far more forgiving of complex part geometries, as radiant heat will eventually reach all surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To select the correct technology, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is melting metals for high-purity casting: Induction is superior due to its speed, efficiency, and the low risk of contamination from heating elements.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment, annealing, or sintering: Resistance heating provides the critical temperature uniformity and stability required for these sensitive processes.
- If you are working with non-conductive materials or highly complex geometries: Resistance heating offers greater operational flexibility and is often the only viable method.
Ultimately, the right furnace is determined not by which is "better," but by which heating method aligns precisely with your material's properties and process goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Heating | Resistance Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct heating via electromagnetic field | Indirect heating via radiant elements |
| Speed | Fast and efficient | Slower with more thermal loss |
| Temperature Uniformity | Can have gradients and hot spots | Superior, even heating for complex shapes |
| Material Compatibility | Only conductive materials | Works with all materials |
| Best Applications | Melting metals, high-purity alloys | Heat treatment, annealing, sintering |
Struggling to choose between induction and resistance heating for your vacuum furnace needs? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need rapid melting with induction or uniform heat treatment with resistance, we can tailor a solution to optimize your process efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and get expert advice!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment process? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Material Performance
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















