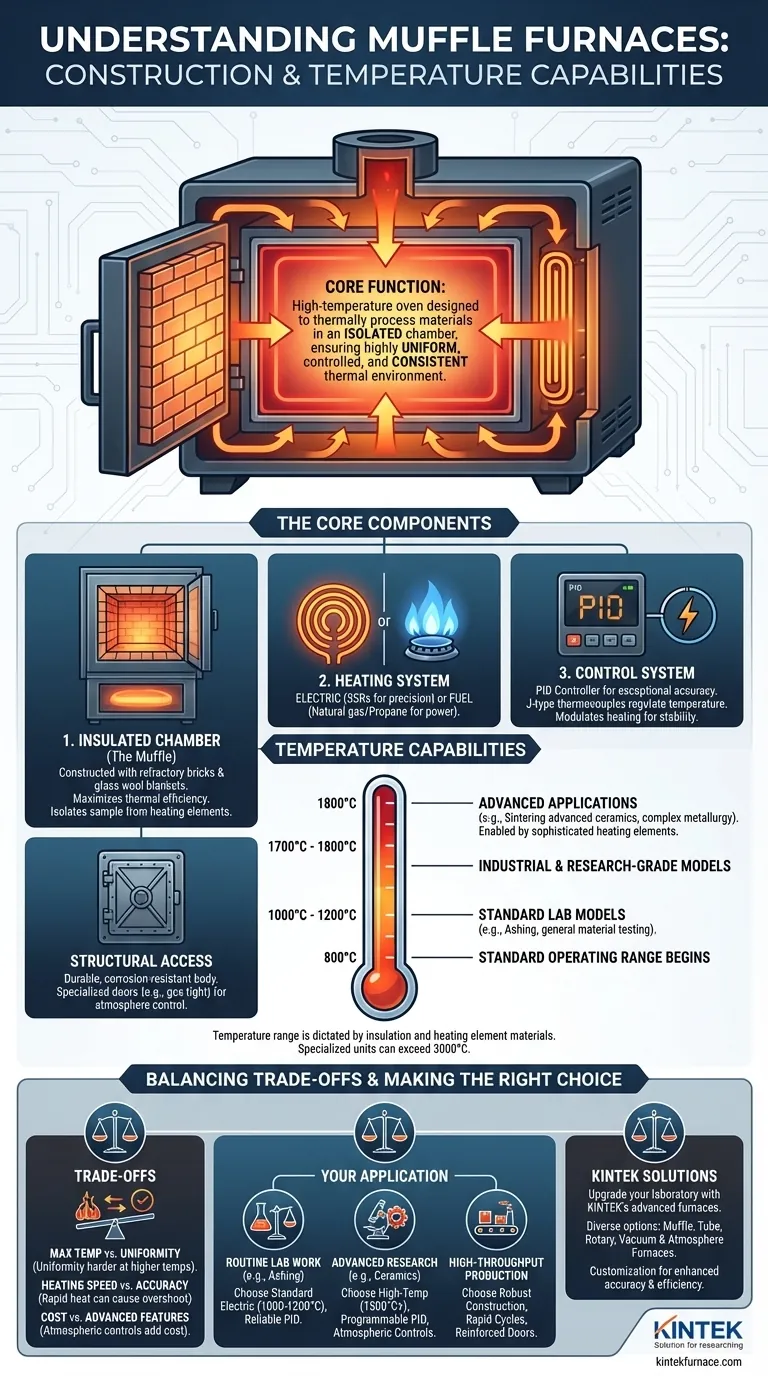
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven designed to thermally process materials inside a dedicated chamber, or "muffle," that isolates the sample from the direct effects of the heating elements. These furnaces are defined by their robust insulated construction, typically using refractory bricks, and their ability to reach temperatures ranging from 800°C to over 1800°C (3272°F) for advanced applications.
The true value of a muffle furnace is not simply its high heat, but its ability to create a highly uniform, controlled, and isolated thermal environment. This ensures that test results are accurate and material treatments are consistent.

The Core Components of a Muffle Furnace
Understanding a muffle furnace begins with its three primary systems: the chamber that holds the material, the system that generates heat, and the controls that manage the process.
The Insulated Chamber (The "Muffle")
The heart of the furnace is the muffle itself. This chamber is constructed from materials engineered to withstand extreme thermal stress, such as refractory bricks.
This chamber is heavily insulated, often with high-density glass wool blankets, to maximize thermal efficiency. This design ensures temperature is uniform throughout the chamber and minimizes heat loss to the outside environment.
Crucially, the muffle isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements and any byproducts of combustion in fuel-fired models, preventing contamination.
The Heating System
Muffle furnaces are heated in one of two ways: electricity or fuel.
Electric furnaces use high-resistance heating elements, often managed by Solid-State Relays (SSRs), for clean and highly precise temperature control.
Fuel-fired furnaces use natural gas, propane, or oil to generate heat. While potentially less precise than electric models, they can offer immense heating power for large industrial applications.
The Control System
The furnace's performance relies entirely on its control system. Modern furnaces use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller to regulate temperature with exceptional accuracy.
These controllers receive input from temperature sensors, such as J-type thermocouples, placed within the chamber. The PID algorithm then intelligently modulates the heating elements to hold the target temperature without significant over- or undershooting.
Structural and Access Features
The furnace body is built for durability, often using corrosion-resistant materials to handle harsh processes.
Many models include specialized doors, such as gas-tight doors, which allow for rapid sample loading while maintaining a specific atmosphere or positive pressure inside the chamber.
Understanding Temperature Capabilities
A furnace's temperature range dictates its applications. This range is determined by the quality of its insulation and, most importantly, the materials used for its heating elements.
The Standard Operating Range
Most muffle furnaces operate in a range of 800°C to 1800°C. The specific capability depends on the model's design and intended use.
Laboratory vs. Industrial Models
Standard laboratory muffle furnaces, used for applications like ashing or general material testing, typically operate up to 1000°C or 1200°C.
Industrial and research-grade models, built with more advanced materials, can reliably reach 1700°C to 1800°C. Specialized, high-cost units can even exceed 3000°C for extreme applications.
The Role of Heating Element Materials
The ability of modern furnaces to reach 1800°C is a direct result of advances in heating element technology. These sophisticated materials can operate at extreme temperatures without degrading, enabling demanding processes like sintering advanced ceramics and complex metallurgical treatments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a muffle furnace requires balancing performance characteristics. The highest specification is not always the best choice for every task.
Maximum Temperature vs. Thermal Uniformity
Achieving a very high peak temperature is one challenge; ensuring that temperature is consistent across the entire chamber is another. Excellent thermal uniformity is a critical feature for repeatable results but becomes more difficult and expensive to engineer at higher temperatures.
Heating Speed vs. Process Accuracy
Some models are designed for rapid heating and cooling. While efficient, this can sometimes lead to temperature overshoot, which may be unsuitable for sensitive materials. A slower, more controlled temperature ramp-up is often necessary for precision work.
Cost vs. Advanced Features
There is a significant cost difference between a basic 1100°C furnace and a programmable 1700°C model with atmospheric controls. Features like PID controllers, programmable cycles, and gas-tight construction add to the complexity and price but are essential for advanced applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal should guide your selection. Focus on the features that directly serve the needs of your process.
- If your primary focus is routine lab work (e.g., ashing, gravimetric analysis): A standard electric furnace reaching 1000°C-1200°C with a reliable PID controller is your most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced metallurgy or ceramics research: You will need a high-temperature model (1500°C+) with a highly accurate, programmable controller and potentially atmospheric controls.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: Look for robust construction, rapid heating cycles, and features like reinforced doors that prioritize durability and speed.
Ultimately, selecting the right muffle furnace means matching its specific capabilities to the precise thermal demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Construction | Insulated chamber with refractory bricks, heating elements (electric/fuel), PID controllers, corrosion-resistant body |
| Temperature Range | 800°C to 1800°C (standard), up to 3000°C for specialized units |
| Applications | Ashing, sintering, metallurgy, ceramics research, high-throughput production |
| Key Considerations | Thermal uniformity, heating speed, cost vs. features for precise process matching |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for enhanced accuracy and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your thermal processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















