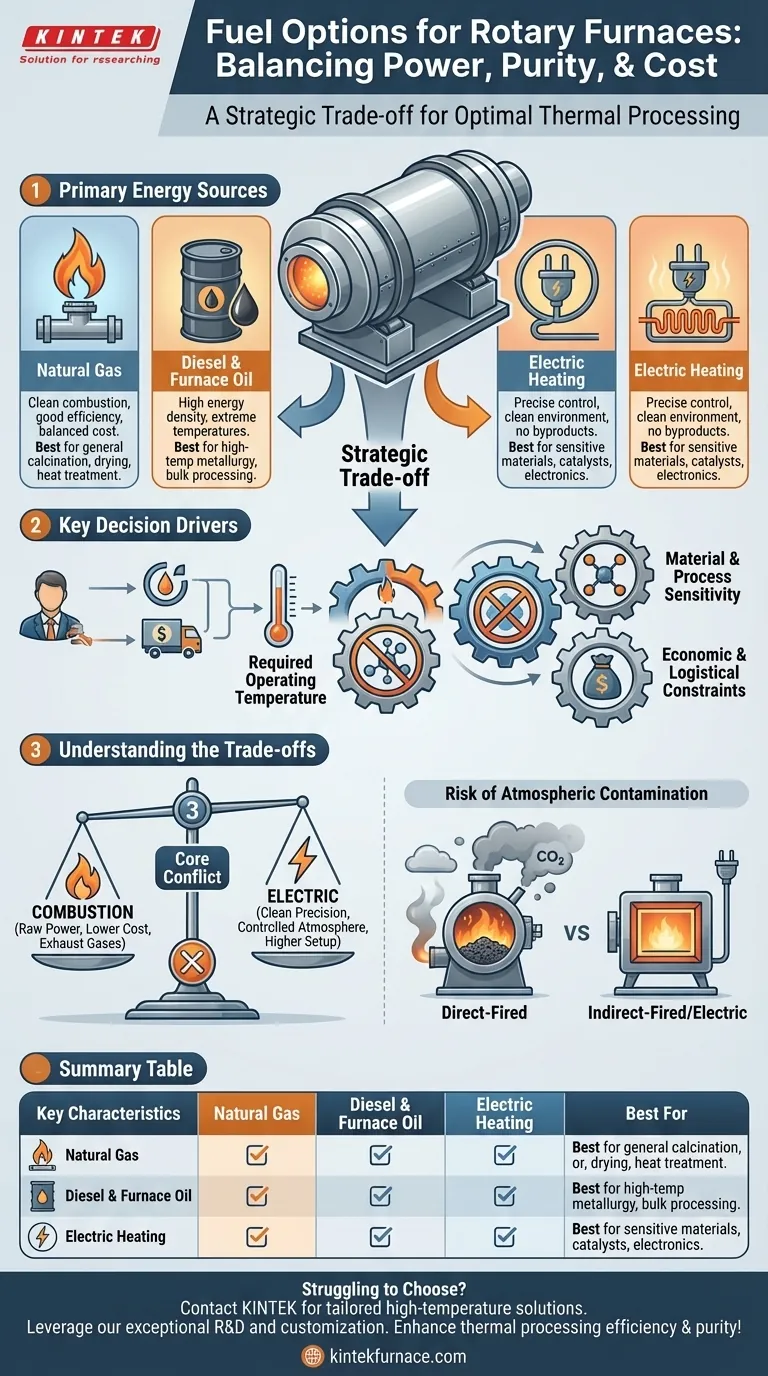
The primary energy sources for rotary furnaces are typically combustion fuels—specifically natural gas, diesel, and furnace oil—or electric heating elements. The selection is not arbitrary; it is a critical engineering decision dictated by the specific thermal process, the material being treated, and operational constraints like cost and environmental regulations.
Your choice of energy source is a strategic trade-off. You are balancing the need for raw thermal power against the demand for process purity and precise temperature control, all while navigating economic and logistical realities.

Breaking Down the Energy Options
Understanding the fundamental characteristics of each energy source is the first step toward making an informed decision. They are not interchangeable and serve different operational needs.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is often the default choice due to its wide availability and relatively clean combustion compared to liquid fuels. It provides a good balance of heating efficiency and operational cost, making it suitable for a broad range of applications.
Diesel and Furnace Oil
These liquid fuels are valued for their high energy density, allowing them to generate extreme temperatures required for certain metallurgical or refining processes. Furnace oil, in particular, is often reserved for applications demanding the highest levels of raw thermal energy.
Electric Heating
An increasingly common alternative to combustion is electric heating. In these furnaces, resistance wires or silicon carbon rods generate heat when powered. This method offers unparalleled precision and a completely clean heating environment, free from the byproducts of combustion.
Key Factors Driving the Decision
The "best" energy source is entirely contextual. The right choice for processing bulk minerals is often the wrong one for producing sensitive chemical catalysts.
Required Operating Temperature
The process dictates the temperature. For general-purpose drying or calcination, natural gas may be sufficient. For high-temperature sintering or smelting, the high energy density of furnace oil might be necessary. Electric furnaces can cover a wide range of temperatures with exceptional accuracy.
Material and Process Sensitivity
This is often the most critical factor. Processes requiring a controlled atmosphere—such as using inert gases like nitrogen to prevent oxidation or reactive gases like hydrogen—demand a clean heat source. The byproducts of fuel combustion (e.g., CO₂, H₂O) can contaminate the furnace atmosphere and interfere with sensitive chemical reactions.
Economic and Logistical Constraints
The final decision is always grounded in practicality. Factors include the local cost and availability of natural gas versus diesel, environmental regulations that may restrict certain fuels, and the existing infrastructure of the facility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every energy source comes with inherent compromises. Recognizing these trade-offs is crucial for avoiding costly operational mismatches.
Combustion vs. Electric: The Core Conflict
The central trade-off is often between the raw power of combustion and the clean precision of electricity. Combustion fuels can deliver immense thermal energy, often at a lower direct energy cost. However, this comes at the price of less precise control and the introduction of exhaust gases into the system.
The Risk of Atmospheric Contamination
Direct-fired combustion furnaces will always introduce byproducts into the processing chamber. For materials like catalysts, battery components, or specialized silica gels, this contamination is unacceptable. In these cases, electric heating or an indirect-fired furnace (where the combustion gases do not contact the material) is required.
Infrastructure and Maintenance
Each energy source requires different infrastructure. Natural gas requires a reliable pipeline connection. Diesel and furnace oil require large, contained storage tanks. Electric furnaces demand robust, high-amperage electrical service. Maintenance needs also vary, from burner cleaning on combustion systems to element replacement on electric ones.
Choosing the Right Energy Source for Your Application
To simplify the decision, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, high-temperature bulk processing: Furnace oil or diesel often provides the most cost-effective raw BTUs when process purity is a secondary concern.
- If your primary focus is process purity and precise temperature control: Electric heating is the superior choice, essential for sensitive materials like catalysts, pharmaceuticals, and advanced electronics.
- If your primary focus is a balance of operational cost and clean operation: Natural gas represents a versatile middle ground suitable for many calcination, drying, and general heat-treatment tasks.
Ultimately, selecting the right energy source is about aligning the furnace's capabilities with the specific thermal and chemical demands of your material.
Summary Table:
| Fuel Option | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | Clean combustion, good efficiency, balanced cost | General calcination, drying, heat treatment |
| Diesel / Furnace Oil | High energy density, extreme temperatures | High-temperature metallurgy, bulk processing |
| Electric Heating | Precise control, clean environment, no combustion byproducts | Sensitive materials, catalysts, pharmaceuticals, electronics |
Struggling to choose the right energy source for your rotary furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Enhance your thermal processing with optimal fuel efficiency and purity—contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















