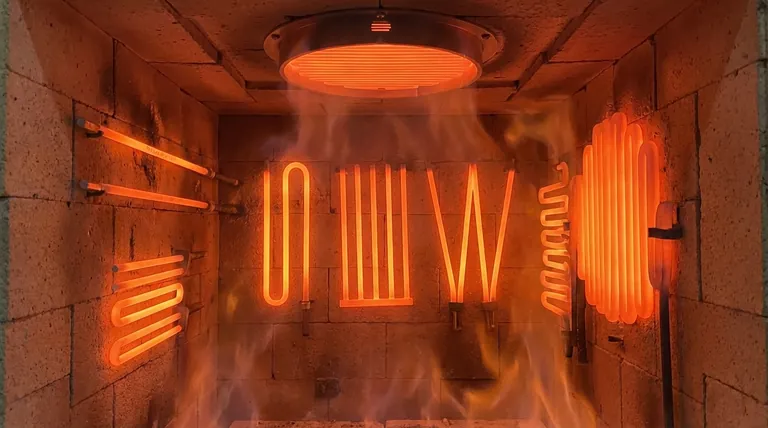
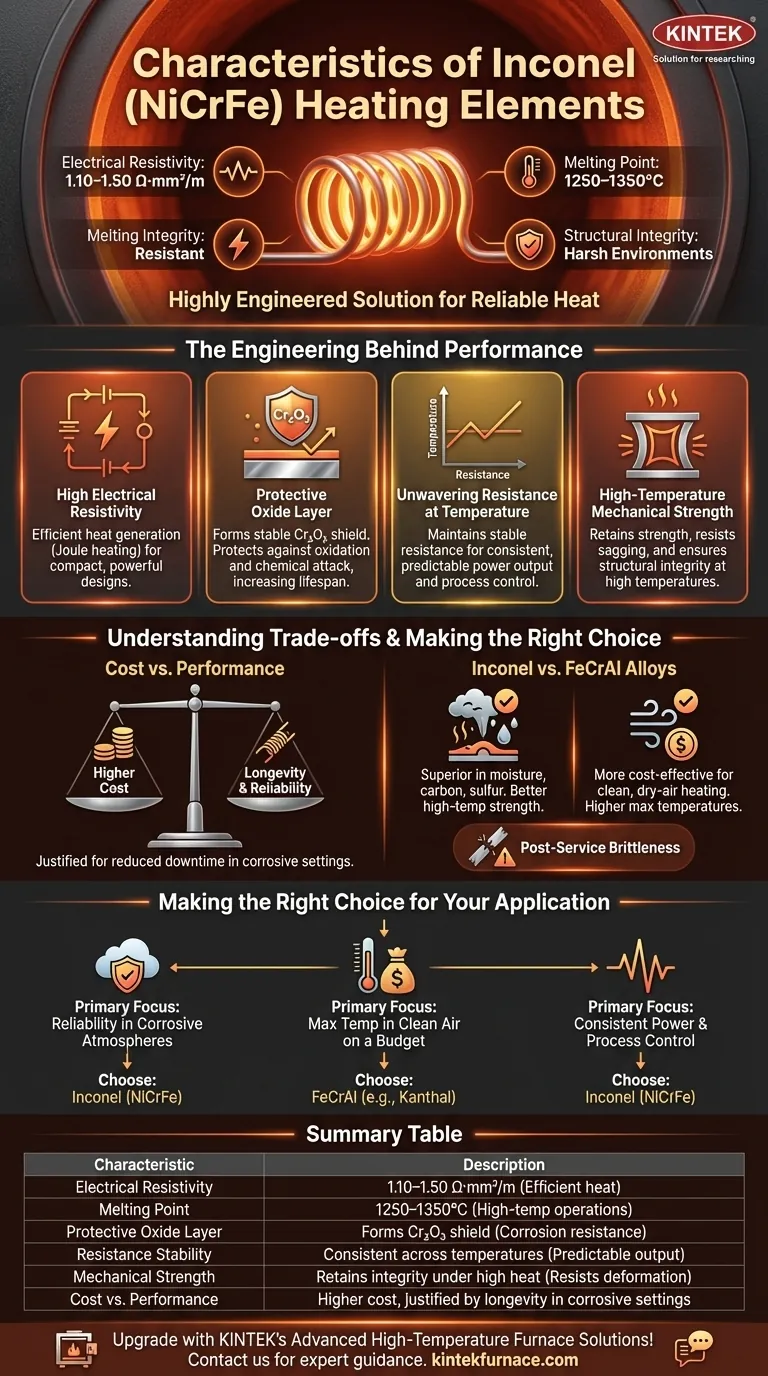
At its core, Inconel (a nickel-chromium-iron alloy) is defined as a heating element material by its exceptional resistance to oxidation and its stable electrical properties at high temperatures. It possesses an electrical resistivity of 1.10–1.50 Ω·mm²/m, a high melting point between 1250–1350°C, and maintains its structural integrity in harsh industrial environments.
Inconel is not simply a material that gets hot; it is a highly engineered solution for generating reliable, consistent heat in environments where other materials would quickly degrade and fail. Its value lies in its ability to form a self-protecting shield against high-temperature corrosion.

The Engineering Behind Inconel's Performance
To understand why Inconel is specified for demanding applications, we must look beyond its specifications and analyze how its properties create a stable heating system.
High Electrical Resistivity
The relatively high electrical resistivity of Inconel is fundamental to its function. This property ensures that significant heat (Joule heating) is generated efficiently as electrical current passes through it, allowing for compact and powerful heating element designs.
The Protective Oxide Layer
This is Inconel's most critical characteristic. When heated, the chromium within the alloy reacts with oxygen to form a thin, stable, and adherent layer of chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) on the element's surface.
This microscopic shield is non-reactive and protects the underlying alloy from further oxidation or chemical attack, dramatically increasing its operational lifespan and reliability at extreme temperatures.
Unwavering Resistance at Temperature
Many materials exhibit significant changes in electrical resistance as they heat up, leading to unpredictable power output. Inconel, however, maintains a relatively stable resistance across its operating temperature range.
This stability is crucial for process control, as it ensures that the heat output remains consistent and predictable, a vital requirement for high-temperature furnaces and precision industrial processes.
High-Temperature Mechanical Strength
With a melting point exceeding 1250°C, Inconel alloys are designed to operate continuously at very high temperatures. More importantly, they retain their mechanical strength and resist sagging or deforming under their own weight when hot, ensuring the element's structural integrity over long service periods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every scenario. Choosing Inconel requires understanding its position relative to other common heating alloys.
Cost vs. Performance
Inconel is a nickel-based superalloy, making it significantly more expensive than iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys like Kanthal. This cost is a primary consideration in material selection.
The higher price is justified in applications where the longevity and corrosion resistance of Inconel prevent costly downtime and frequent element replacement.
Comparison to FeCrAl Alloys
FeCrAl alloys can often operate at even higher temperatures than Inconel and are more cost-effective for clean, dry-air heating.
However, Inconel typically demonstrates superior strength at high temperatures (less brittleness) and offers far better resistance in atmospheres containing moisture, carbon, or sulfur, where FeCrAl alloys would rapidly deteriorate.
Post-Service Brittleness
After extended periods at very high temperatures, some Inconel grades can become less ductile once cooled to room temperature. This can make maintenance or repositioning of used elements challenging, as they are more susceptible to breaking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your material choice should be driven by the specific demands of the operating environment and your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is reliability in corrosive or oxidizing atmospheres: Inconel is the superior choice due to its self-forming protective oxide layer.
- If your primary focus is maximum temperature in clean, dry air on a budget: A FeCrAl alloy (like Kanthal) is likely the more economical and suitable option.
- If your primary focus is consistent power output and process control: Inconel's stable resistance across its temperature range provides the predictability you need.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element is about matching the material's unique strengths to the specific challenges of your application.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | 1.10–1.50 Ω·mm²/m, enabling efficient heat generation |
| Melting Point | 1250–1350°C, suitable for high-temperature operations |
| Protective Oxide Layer | Forms Cr₂O₃ shield for corrosion and oxidation resistance |
| Resistance Stability | Maintains consistent electrical resistance across temperatures |
| Mechanical Strength | Retains integrity and resists deformation under high heat |
| Cost vs. Performance | Higher cost than FeCrAl, justified by longevity in corrosive settings |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable heating systems. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. For expert guidance on selecting the right heating elements and furnaces, contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and durability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















