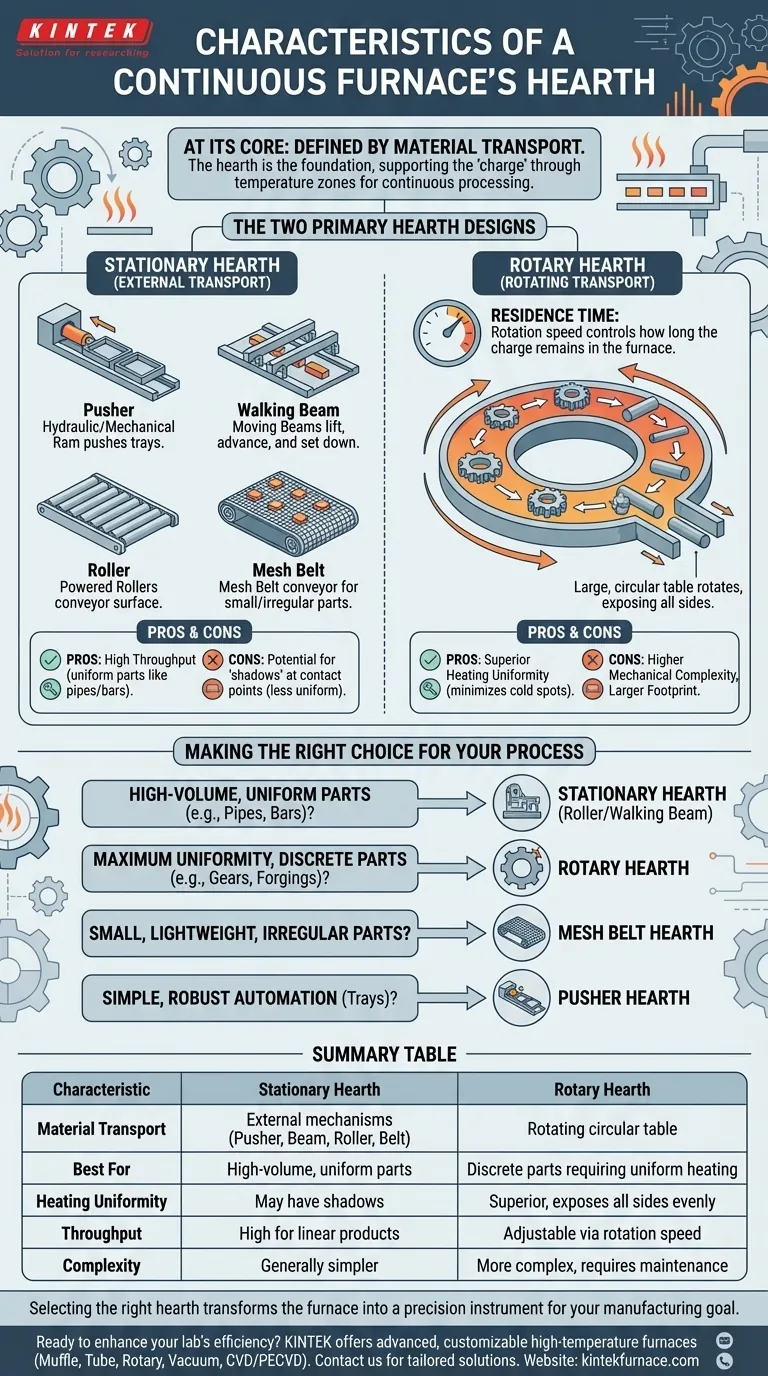
At its core, the hearth of a continuous furnace is defined by its method of material transport. The fundamental characteristic is that the hearth can be either stationary, where the furnace floor itself does not move, or rotary, where the floor rotates to carry materials through the heating process. This choice is the primary determinant of how a furnace operates and what it is best suited for.
The defining characteristic of a continuous furnace hearth is its method of transport—stationary or rotary. The choice between them is not arbitrary; it's a critical engineering decision driven by the product's geometry, required throughput, and the need for uniform heat exposure.

Understanding the Hearth's Role
The Foundation for Continuous Processing
The hearth is the surface inside a furnace that supports the material being heated, known as the "charge." In a continuous furnace, the hearth system is engineered to move this charge through various temperature zones without interruption.
This contrasts with a batch furnace, where materials are loaded, heated, and unloaded in distinct, separate cycles. The continuous nature of the hearth is what enables high-volume, automated production.
The Two Primary Hearth Designs
The most significant distinction in continuous furnace hearths is whether the supporting surface itself moves or remains fixed.
The Stationary Hearth
A stationary hearth does not move. Instead, an external mechanism is used to push, carry, or roll the charge through the furnace.
Common examples of stationary hearth systems include:
- Pusher Furnaces: A hydraulic or mechanical ram pushes trays or the parts themselves along the hearth.
- Walking Beam Furnaces: A set of moving beams lifts the charge, advances it, and sets it back down on a fixed section of hearth.
- Roller Hearth Furnaces: Powered rollers form the hearth surface, directly conveying the charge through the furnace.
- Mesh Belt Furnaces: A high-temperature metal alloy belt acts as a conveyor, carrying smaller or irregularly shaped parts.
These designs are often favored for processing long, structurally consistent products like beams, pipes, plates, and bars.
The Rotary Hearth
A rotary hearth is a large, circular, donut-shaped table that rotates slowly within the furnace chamber.
Materials are charged onto the hearth at one point and are discharged near the same point after completing a full or partial revolution. This design is ideal for heating discrete, individual parts like billets, gears, or components for forging.
The rotation speed is a critical and adjustable parameter. It directly controls the residence time—how long the charge remains in the furnace. Adjusting the speed allows operators to precisely manage the heating cycle based on the size, mass, and metallurgical requirements of the charge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior. The choice involves a direct trade-off between throughput mechanics and heating quality.
Stationary Hearth: Pros and Cons
Stationary hearths, particularly walking beam and roller designs, can achieve extremely high throughput for the right kind of product. They offer a direct, linear path that is efficient for processing large volumes of uniform material.
However, they can create "shadows" where the points of contact with the hearth or transport mechanism heat more slowly. This can lead to less uniform temperatures compared to a rotary design.
Rotary Hearth: Pros and Cons
The primary advantage of a rotary hearth is superior heating uniformity. As the hearth rotates, it ensures all sides of the charge are exposed to the furnace's heat sources, minimizing cold spots.
The main trade-offs are mechanical complexity and footprint. The drive systems, seals, and overall structure of a large rotary furnace can be more complex and require more maintenance than a simple pusher furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be dictated entirely by your process goals and the nature of the product you are heating.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of uniform parts (like pipes or bars): A stationary hearth design, such as a roller or walking beam, is likely the most efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum temperature uniformity on discrete parts (like gears or forgings): A rotary hearth is the superior choice due to its ability to expose all surfaces evenly.
- If your primary focus is processing smaller, lightweight, or irregularly shaped parts: A stationary mesh belt hearth provides a flexible and continuous solution.
- If your primary focus is simple, robust automation for parts that can be pushed in trays: A stationary pusher hearth offers a mechanically straightforward and reliable option.
Ultimately, selecting the right hearth transforms the furnace from a simple heater into a precision instrument for your specific manufacturing goal.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Stationary Hearth | Rotary Hearth |
|---|---|---|
| Material Transport | External mechanisms (pusher, walking beam, roller, mesh belt) | Rotating circular table |
| Best For | High-volume, uniform parts (e.g., pipes, bars) | Discrete parts requiring uniform heating (e.g., gears, forgings) |
| Heating Uniformity | May have shadows at contact points | Superior, exposes all sides evenly |
| Throughput | High for linear, consistent products | Adjustable via rotation speed |
| Mechanical Complexity | Generally simpler | More complex, requires maintenance |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with a tailored furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for superior heat processing. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your production and achieve your specific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput



















