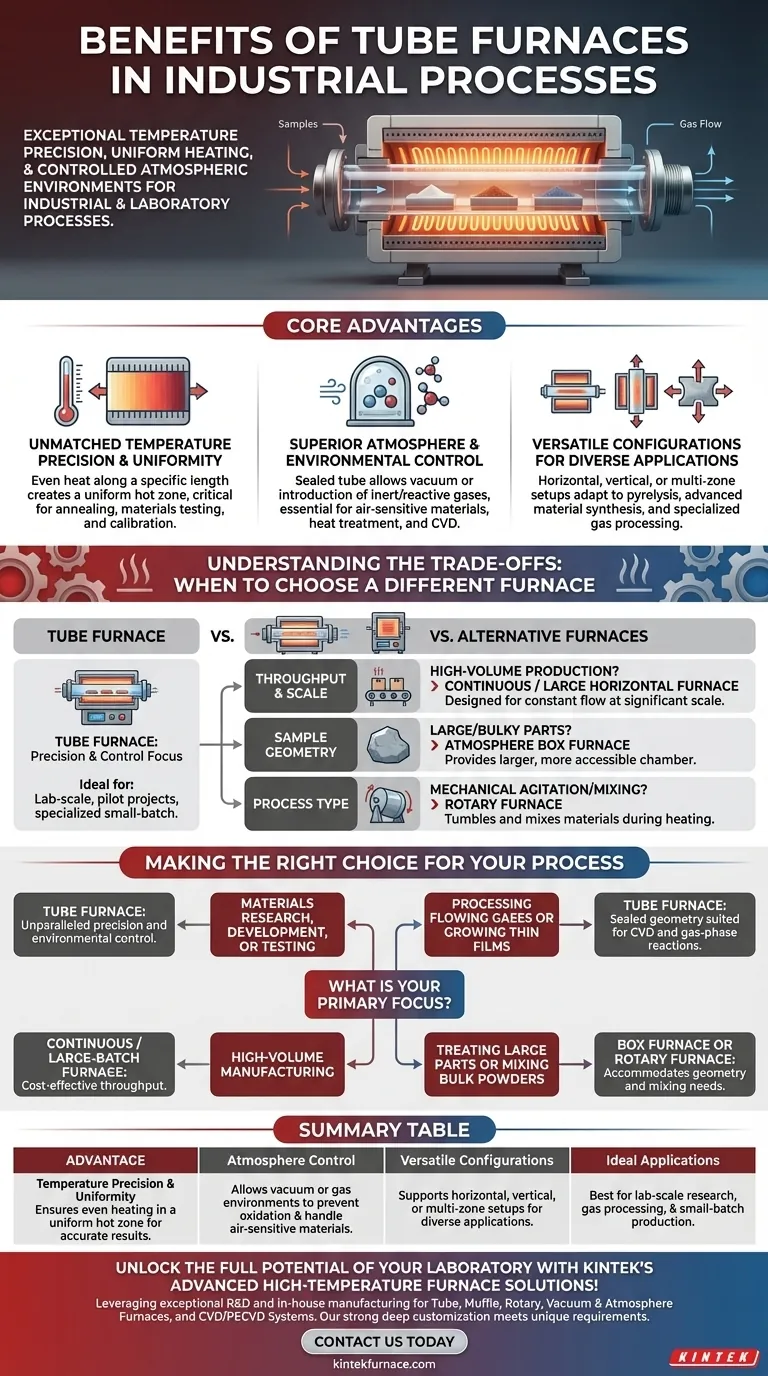
At their core, tube furnaces provide exceptional temperature precision, highly uniform heating, and a controlled atmospheric environment for industrial and laboratory processes. Their tubular design makes them uniquely suited for treating small samples, powders, or processing flowing gases with a high degree of accuracy and repeatability.
Choosing the right furnace is less about finding the "best" one and more about matching the tool to the specific task. A tube furnace excels where precise control over a contained environment is more critical than high-volume throughput.

The Core Advantages of Tube Furnace Design
A tube furnace's primary benefits stem directly from its simple, enclosed geometry. The heating elements surround a ceramic or metallic tube, creating an isolated environment that can be tightly regulated.
Unmatched Temperature Precision and Uniformity
The cylindrical heating chamber ensures that the sample receives heat evenly from all sides along a specific length. This creates a highly uniform hot zone.
This level of precision is critical for processes like annealing, materials testing, and calibration, where even minor temperature deviations can compromise results.
Superior Atmosphere and Environmental Control
The sealed nature of the tube allows you to completely control the internal environment. You can pull a vacuum to prevent oxidation or introduce specific inert or reactive gases.
This capability is essential for working with air-sensitive materials, performing heat treatment on advanced alloys, or conducting processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Versatile Configurations for Diverse Applications
Tube furnaces can be configured in multiple ways to suit the process. They can be horizontal, vertical (for preventing sample contamination or managing gravity's effects), or have multiple, independently controlled heating zones.
This flexibility makes them adaptable for a wide range of tasks, from the pyrolysis of biomass to synthesizing advanced materials and processing specialized gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When to Choose a Different Furnace
No single furnace is perfect for every job. The tube furnace's specialization in precision comes with limitations in scale and sample type. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Throughput and Scale: Tube vs. Continuous Furnaces
Tube furnaces are ideal for lab-scale research, pilot projects, or specialized, small-batch production. Their size inherently limits throughput.
For high-volume mass production, a continuous or large horizontal furnace is far more efficient, designed to process a constant flow of material at significant scale.
Sample Geometry: Tube vs. Box Furnaces
The primary limitation of a tube furnace is the sample size and shape; it must fit within the process tube's diameter.
If you need to heat treat large, bulky, or irregularly shaped parts, an atmosphere box furnace provides a much larger, more accessible chamber.
Process Type: Tube vs. Rotary Furnaces
A standard tube furnace is designed to heat a static sample or a controlled fluid flow. It does not provide any mechanical agitation.
For processes like calcination or oxidation that require materials to be tumbled and mixed during heating for uniform exposure, a rotary furnace is the correct tool.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right thermal processing equipment requires aligning the furnace's strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is materials research, development, or testing: The unparalleled precision and environmental control of a tube furnace make it the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is processing flowing gases or growing thin films: The sealed, tubular geometry is uniquely suited for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and gas-phase reactions.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: A continuous or large-batch furnace is designed for the cost-effective throughput you require.
- If your primary focus is treating large parts or mixing bulk powders: A box furnace or rotary furnace will better accommodate your sample's geometry and process needs.
By understanding these core principles, you can select the furnace that serves not just as a heat source, but as a precision instrument for your work.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Precision & Uniformity | Ensures even heating in a uniform hot zone for accurate results in processes like annealing and materials testing. |
| Atmosphere Control | Allows vacuum or gas environments to prevent oxidation and handle air-sensitive materials, ideal for CVD and heat treatment. |
| Versatile Configurations | Supports horizontal, vertical, or multi-zone setups for diverse applications such as pyrolysis and material synthesis. |
| Ideal Applications | Best for lab-scale research, gas processing, and small-batch production where precision outweighs high throughput. |
Unlock the full potential of your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with precision tools like Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in processes like materials testing and gas-phase reactions. Don't settle for one-size-fits-all—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can elevate your work and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















