At their core, tube furnaces provide an unmatched combination of precision, control, and versatility for thermal processing. They are engineered to deliver exceptional temperature uniformity within a tightly controlled atmosphere, making them indispensable tools in research and industry. Key benefits include rapid heating and cooling, high energy efficiency, and the flexibility to work with a wide range of materials and processes.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its power to create a highly stable, isolated, and repeatable processing environment. This control is the foundation for reliable scientific discovery and high-quality material production.

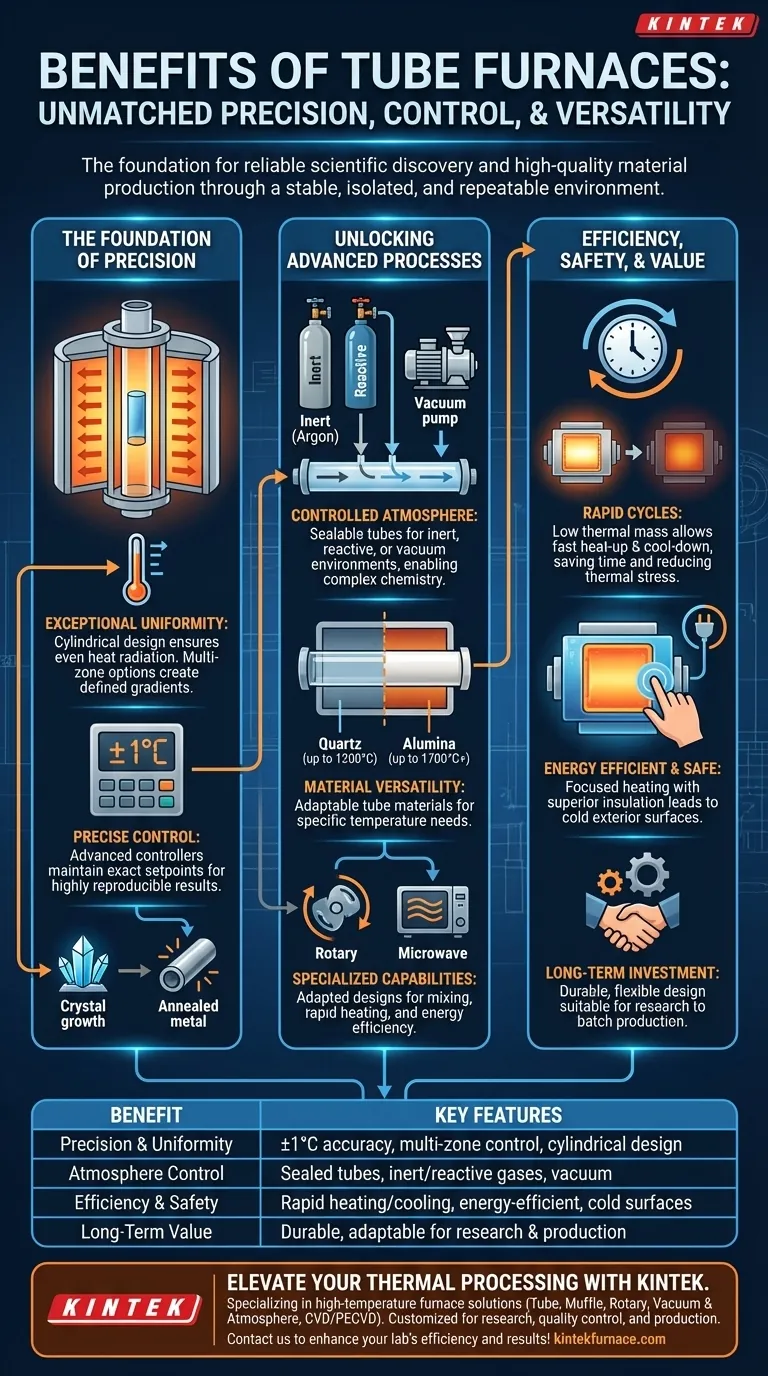
The Foundation of Precision: Temperature and Uniformity
The primary function of any furnace is to heat a sample, but tube furnaces excel by controlling how that heat is applied. This precision is what sets them apart.
Achieving Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of a tube furnace is inherently designed for uniform heating. Heating elements surround the process tube, ensuring that heat radiates evenly toward the sample from all sides.
This eliminates the hot and cold spots common in other furnace designs, which is critical for processes where every part of the sample must experience the exact same temperature. For even greater precision over longer lengths, multi-zone furnaces use multiple controllers to maintain uniformity or create intentional, well-defined temperature gradients.
The Power of Precise Control
Modern tube furnaces integrate advanced temperature controllers that can maintain a setpoint with remarkable accuracy, often to within ±1°C.
This level of precision is essential for reproducible results. Whether you are growing a crystal, annealing a metal, or synthesizing a nanomaterial, knowing the exact temperature ensures that the process can be repeated reliably day after day.
Gaining Efficiency with Rapid Cycles
Many tube furnace designs emphasize fast heat-up and cool-down rates. This is achieved through low thermal mass insulation and efficient heating elements.
Faster cycling saves valuable time in the lab or on the production floor. Furthermore, rapid cooling can be a critical process variable, helping to reduce thermal stress in materials and improve the quality and properties of the final product.
Unlocking Advanced Processes: Atmosphere and Material Control
A tube furnace is more than just a heater; it's a self-contained process chamber. Its sealed design enables complete control over the sample's environment.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
The process tube can be easily sealed, allowing you to introduce specific gases or create a vacuum. This is vital for a huge range of applications.
Using an inert gas like argon prevents oxidation of sensitive materials. Introducing reactive gases can be a key part of a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process. The ability to manage the atmosphere opens the door to complex chemical reactions that are impossible in open air.
Versatility Through Tube Materials
The choice of process tube material allows you to adapt the furnace to your specific needs. Quartz tubes are common for processes up to ~1200°C and offer the benefit of transparency, while alumina tubes are used for higher temperatures (up to 1700°C or more) due to their durability and chemical stability.
Specialized Furnace Capabilities
The basic tube furnace design has been adapted for specialized tasks. Rotary tube furnaces continuously tumble materials during heating, ensuring enhanced mixing and heat exposure. Microwave tube furnaces offer selective and extremely rapid heating by acting directly on the sample, which can drastically improve energy efficiency for certain materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Advantages
While powerful, it's important to understand both the practical benefits and the design considerations of a tube furnace.
Designing for Efficiency and Safety
Tube furnaces are generally very energy-efficient. Their superior insulation and ability to heat a focused area mean less energy is wasted heating the surrounding environment.
From a practical standpoint, this same efficiency results in a cold exterior surface. This is a critical safety feature in any lab or production setting, minimizing the risk of burns and creating a safer workspace.
Balancing Volume and Uniformity
While horizontal tube furnaces offer a larger working volume for bigger or multiple samples, it's important to recognize that the most thermally uniform zone is typically in the center of the heated length. The effective "sweet spot" of perfect uniformity is often smaller than the total heated length.
Long-Term Value and Flexibility
Tube furnaces are built for longevity and represent a sound economic investment. Their robust design ensures a long operational life, and their versatility means they can be adapted for new projects and processes in the future. Their operational flexibility makes them suitable for everything from one-off research experiments to batch production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right features depends entirely on your intended application.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or material synthesis: Prioritize precise temperature control, multi-zone options, and robust atmosphere management to explore new processes with maximum control.
- If your primary focus is quality control or standardized testing: Emphasize exceptional temperature uniformity and rapid, repeatable cycling to ensure consistent and reliable results.
- If your primary focus is process development or small-scale production: Look for a balance of working volume (like a horizontal furnace), energy efficiency, and ease of operation.
By understanding how these benefits align with your specific needs, you can confidently select a furnace that will serve as a reliable cornerstone for your work.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Precision & Uniformity | ±1°C accuracy, multi-zone control, cylindrical design for even heating |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed tubes for inert/reactive gases, vacuum capability |
| Efficiency & Safety | Rapid heating/cooling, energy-efficient, cold exterior surfaces |
| Versatility | Works with various materials, quartz/alumina tubes, rotary/microwave options |
| Long-Term Value | Durable, adaptable for research, testing, and production |
Ready to elevate your thermal processing with precision and reliability? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs—whether for research, quality control, or small-scale production. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















