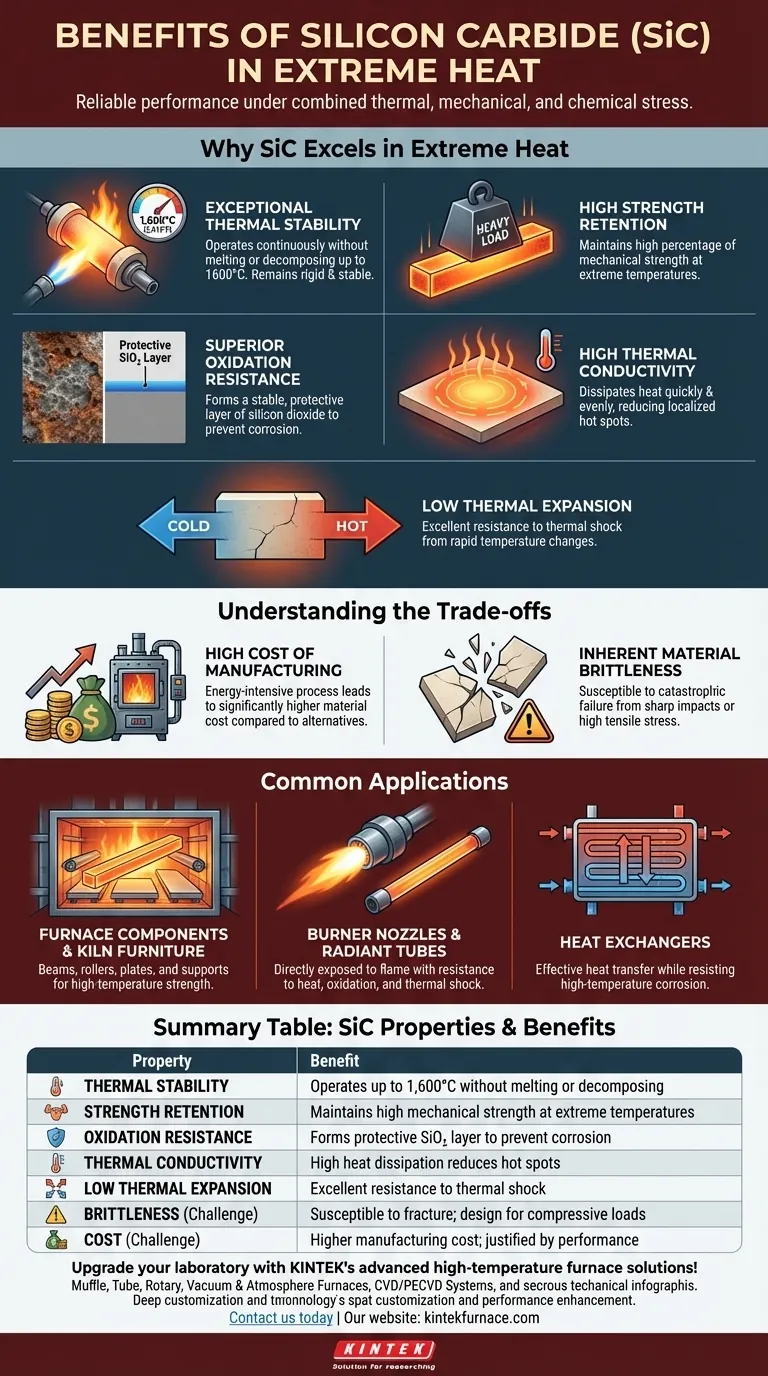
For extreme heat applications, the primary benefits of silicon carbide (SiC) are its exceptional thermal stability up to 1,600°C, its ability to retain mechanical strength at those temperatures, and its superior resistance to both chemical oxidation and physical wear. These properties allow it to function reliably in environments where most metals and other ceramics would quickly degrade or fail entirely.
Silicon carbide is more than just a heat-resistant material; it is a solution for maintaining structural and chemical integrity under combined thermal, mechanical, and chemical stress. While its cost is a key consideration, its true value is unlocked in applications where component failure is not an option.
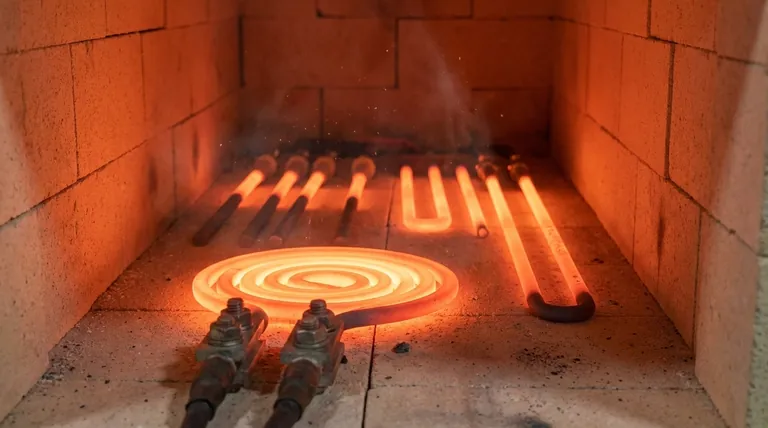

Why SiC Excels in Extreme Heat
Silicon carbide's performance in high-temperature environments stems from a unique combination of thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
The most cited benefit of SiC is its ability to operate continuously in temperatures up to 1,600°C (2,912°F) without melting or decomposing. Unlike many materials that soften significantly as they heat up, SiC remains rigid and stable.
High Strength Retention
Mere temperature resistance is insufficient for most industrial applications. SiC stands out because it maintains a very high percentage of its mechanical strength even at extreme temperatures, making it ideal for load-bearing components like kiln furniture and support beams inside furnaces.
Superior Oxidation Resistance
At high temperatures, oxygen aggressively attacks materials, causing corrosion and degradation. SiC naturally mitigates this by forming a thin, stable, and protective layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂) on its surface. This "passivation layer" effectively seals the underlying material from further chemical attack.
High Thermal Conductivity
For a ceramic, SiC has remarkably high thermal conductivity. This allows it to dissipate heat quickly and evenly, reducing the risk of localized hot spots that can cause material stress and failure.
Low Thermal Expansion
Combined with its high thermal conductivity, SiC's low coefficient of thermal expansion gives it excellent resistance to thermal shock. It can withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking, a common failure point for many other brittle materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its benefits are clear, adopting silicon carbide requires a full understanding of its associated challenges. Objectivity is critical when selecting a material for a demanding application.
The High Cost of Manufacturing
Producing high-purity, dense silicon carbide is an energy-intensive and complex process. This results in a significantly higher material cost compared to conventional refractories or high-temperature metal alloys. Its use must be justified by performance needs that other materials cannot meet.
Inherent Material Brittleness
Like most technical ceramics, silicon carbide is brittle. It has very low fracture toughness, meaning it is susceptible to catastrophic failure from sharp impacts or high tensile stress. Designs must carefully account for this by prioritizing compressive loads and avoiding stress concentrations.
Common Applications in High-Heat Industries
The properties of SiC make it an indispensable material in several key industrial sectors where extreme heat is a constant.
Furnace Components and Kiln Furniture
SiC is widely used for beams, rollers, plates, and supports inside industrial furnaces and ceramic kilns. Its high-temperature strength allows for thinner, lighter designs that hold heavy loads without sagging, which also improves energy efficiency.
Burner Nozzles and Radiant Tubes
In combustion systems, SiC is used for components like burner nozzles and radiant tubes that are directly exposed to flame. Its resistance to heat, oxidation, and thermal shock ensures a long and reliable service life in these punishing environments.
Heat Exchangers
SiC's ability to transfer heat effectively while resisting high-temperature corrosion makes it an excellent material for heat exchangers used in waste heat recovery systems and other chemical processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The decision to use silicon carbide should be based on a clear analysis of your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is maximum operational temperature and structural integrity: SiC is an excellent choice for load-bearing components inside furnaces where other materials would deform or fail.
- If your primary focus is resistance to thermal shock and abrasion: SiC is ideal for components like burner nozzles or thermocouple protection tubes that experience rapid temperature changes and erosive gas flows.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for a static, high-heat environment: You may want to evaluate other refractories, as SiC's premium cost is best justified when its superior mechanical and chemical properties are also required.
Ultimately, selecting silicon carbide is a strategic decision to invest in reliability and performance where extreme conditions make lesser materials a liability.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Operates up to 1,600°C without melting or decomposing |
| Strength Retention | Maintains high mechanical strength at extreme temperatures |
| Oxidation Resistance | Forms protective SiO₂ layer to prevent corrosion |
| Thermal Conductivity | High heat dissipation reduces hot spots |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Excellent resistance to thermal shock from rapid temperature changes |
| Brittleness | Susceptible to fracture under impact or tensile stress; design for compressive loads |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost compared to alternatives; justified by superior performance |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable SiC-based components like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, enhancing performance and durability in extreme heat applications. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















