At their core, the primary benefits of resistance heating elements are exceptionally high energy efficiency, precise temperature control, and robust durability. Because they work by the simple principle of converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy, they are a foundational technology used in everything from common household toasters to high-temperature industrial furnaces.
Resistance heating's greatest advantage is its simplicity. This fundamental characteristic is the source of its most valuable benefits: cost-effectiveness, reliability, and ease of implementation in a vast range of applications.
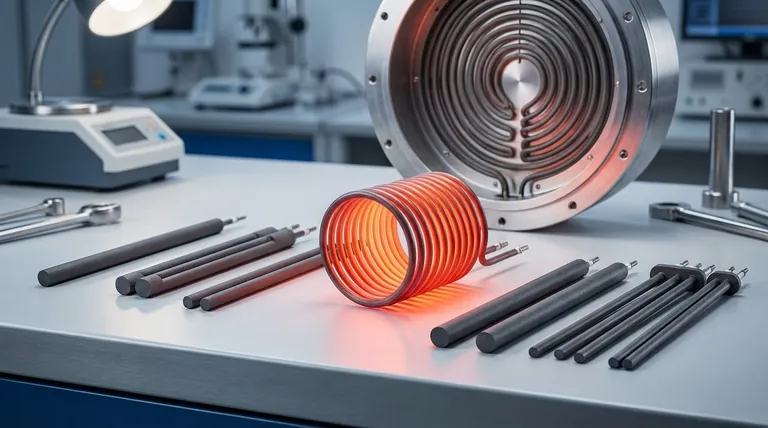

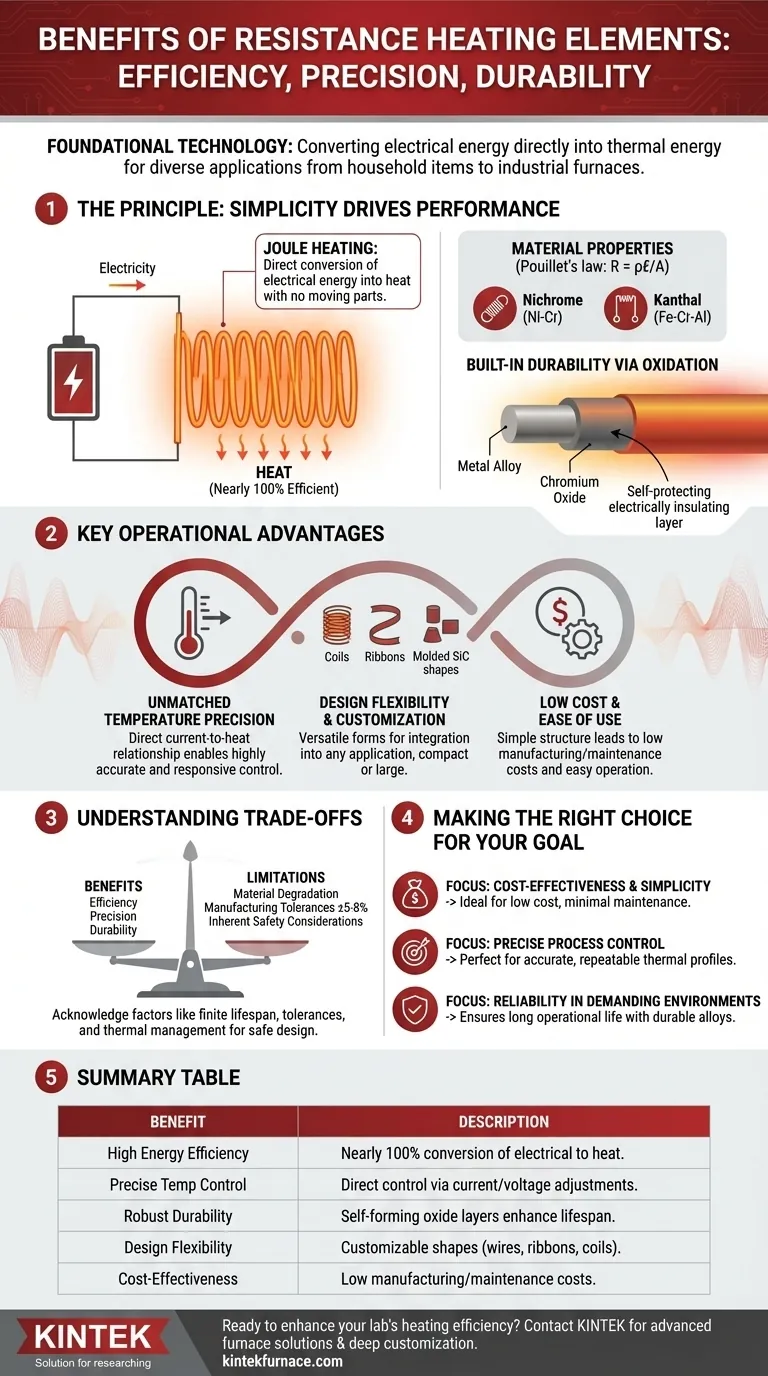
The Principle: How Simplicity Drives Performance
The effectiveness of resistance heating stems from its straightforward physical principle. Understanding this is key to appreciating its operational benefits.
Converting Electricity Directly to Heat
A resistance heating element functions by passing an electric current through a material with high electrical resistivity. This process, known as Joule heating, is nearly 100% efficient at converting electrical energy into heat.
There are no intermediate energy conversion steps, moving parts, or significant energy losses, ensuring that the power you supply is the heat you get.
The Role of Material Properties
Materials like Nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy) and Kanthal (an iron-chromium-aluminum alloy) are chosen for a specific reason. Their high resistivity is defined by Pouillet's law (R = ρℓ/A), which dictates that resistance increases with material resistivity (ρ) and length (ℓ).
These materials are engineered to generate significant heat without degrading or melting, providing stable performance over long periods.
Built-in Durability via Oxidation
Many advanced heating element alloys, particularly Nichrome, create their own protection. When heated, the material forms a thin, adherent outer layer of chromium oxide.
This protective layer is electrically insulating and prevents the underlying metal from further oxidation, dramatically increasing the element's lifespan and durability even at high operational temperatures.
Key Operational Advantages
The simple design of resistance heaters translates directly into tangible benefits for designers and operators.
Unmatched Temperature Precision
Heat output is a direct function of the electrical current applied. This direct relationship allows for remarkably precise and responsive temperature control.
By simply adjusting the voltage or current, a system can maintain a target temperature with very high accuracy, which is critical for sensitive laboratory experiments and industrial processes.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Resistance elements are incredibly versatile. They can be manufactured as wires, ribbons, or coils, or molded into custom shapes from materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC).
This flexibility allows them to be integrated into nearly any form factor, from the compact heating element in a hair dryer to large, complex arrays inside industrial kilns.
Low Cost and Ease of Use
The simple structure of resistance heating systems results in low manufacturing and maintenance costs. The technology is mature, reliable, and well-understood.
Operators typically do not require complex training to use equipment based on resistance heating, making it an accessible and budget-friendly choice for many labs and businesses.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, resistance heating is not without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging them.
Material Degradation Over Time
Despite protective oxide layers, all resistance elements have a finite lifespan. High temperatures, aggressive thermal cycling (heating and cooling), and atmospheric contaminants can eventually cause the element to degrade and fail.
Manufacturing Tolerances
As specified by industry standards (like ASTM and DIN), the resistance per length of a heating wire has a manufacturing tolerance, often around ±5-8%. For applications requiring extreme precision, controllers must be able to compensate for these slight variations between individual elements.
Inherent Safety Considerations
While many elements, especially ceramic variants, have excellent electrical insulation, they are still high-temperature devices. Proper design must always account for thermal management, electrical protection, and safeguards to prevent fire hazards or contact burns.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if resistance heating is the correct technology, align its core benefits with your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and simplicity: Resistance heating is an ideal choice due to its low equipment cost, minimal maintenance, and straightforward operational principles.
- If your primary focus is precise process control: The direct, stable relationship between electricity and heat output makes it perfect for applications needing accurate and repeatable thermal profiles.
- If your primary focus is reliability in a demanding environment: The use of durable alloys that form self-protecting layers ensures a long operational life with minimal intervention.
By understanding these fundamental benefits and trade-offs, you can confidently leverage resistance heating as a robust and efficient solution for your thermal application.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High Energy Efficiency | Nearly 100% conversion of electrical energy to heat with minimal losses. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Direct control via current/voltage adjustments for accurate thermal management. |
| Robust Durability | Self-forming oxide layers (e.g., chromium oxide) enhance lifespan and resistance to degradation. |
| Design Flexibility | Customizable shapes (wires, ribbons, coils) for diverse applications. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Low manufacturing and maintenance costs with mature, reliable technology. |
Ready to enhance your lab's heating efficiency? Contact KINTEK today to explore our advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Get in touch now for reliable, tailored heating solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















